 |
PDBsum entry 1thy

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase(methyltransferase)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1thy
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.45
- thymidylate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
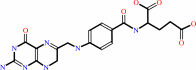
dUMP + (6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate = 7,8-dihydrofolate + dTMP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
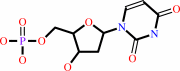 dUMP
dUMP
|
+
|
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 7,8-dihydrofolate
7,8-dihydrofolate
|
+
|
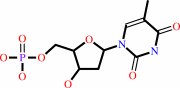 dTMP
dTMP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Mol Biol
232:1101-1116
(1993)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Refined structures of substrate-bound and phosphate-bound thymidylate synthase from Lactobacillus casei.
|
|
J.Finer-Moore,
E.B.Fauman,
P.G.Foster,
K.M.Perry,
D.V.Santi,
R.M.Stroud.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Crystal structures of two crystal forms of the complex of Lactobacillus casei
(TS) with its substrate dUMP have been solved and refined at 2.55 A resolution.
The two crystal forms differ by approximately 5% in the c-axis length. The
TS-dUMP complexes are symmetric dimers with dUMP bound equivalently in both
active sites. dUMP is non-covalently bound in the same conformation as in
ternary complexes of TS with dUMP and cofactor or cofactor analogs. The same
hydrogen bonds are made between TS and substrate in the binary and ternary
complexes. We have also determined the 2.36 A crystal structure of
phosphate-bound L. casei TS. This structure has been refined to an R-factor of
19.3% with highly constrained geometry. Refinement has revealed the locations of
all residues in the protein, including the disordered residues 90 to 119, which
are part of an insert found only in the L. casei and Staphylococcus aureus
transposon Tn4003 TS sequences. The 2.9 A multiple isomorphous replacement (MIR)
structure of L. casei TS in a complex with its substrate dUMP has been refined
to a crystallographic R-factor of 15.5%. Reducing agents were withheld from
crystallization solutions during MIR structure determination to allow
heavy-metal labeling of the cysteine residues. Therefore, the active-site
cysteine residue in this structure is oxidized and the dUMP is found at
half-occupancy in the active site. No significant conformational difference was
found between the phosphate-bound and dUMP-bound structures. The TS-dUMP
structures were better ordered than the phosphate-bound TS or the oxidized
TS-dUMP, particularly Arg23, which is clearly hydrogen-bonded to the phosphate
group of dUMP. A large and a small P6(1)22 crystal form are observed for both
phosphate-bound and dUMP-bound L. casei TS. The small cell forms of the
phosphate-bound and dUMP-bound enzyme are isomorphous, whereas the cell
constants of the larger cell form change slightly when dUMP is bound (c = 240 A
versus c = 243 A). For both liganded and unliganded enzyme, conversion from the
small to the large crystal form sometimes occurs spontaneously, and the crystal
packing changes at a single interface. Conversion may be the result of a small
change in pH in the mother liquor surrounding the crystal. A single
intermolecular contact between symmetry-related Asp287 residues is disrupted on
going from the small to the large crystal form.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Cardinale,
O.M.Salo-Ahen,
G.Guaitoli,
S.Ferrari,
A.Venturelli,
S.Franchini,
R.Battini,
G.Ponterini,
R.C.Wade,
and
M.P.Costi
(2010).
Design and characterization of a mutation outside the active site of human thymidylate synthase that affects ligand binding.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
23,
81-89.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Newby,
T.T.Lee,
R.J.Morse,
Y.Liu,
L.Liu,
P.Venkatraman,
D.V.Santi,
J.S.Finer-Moore,
and
R.M.Stroud
(2006).
The role of protein dynamics in thymidylate synthase catalysis: variants of conserved 2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate (dUMP)-binding Tyr-261.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
7415-7428.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Atreya,
E.F.Johnson,
J.Williamson,
S.Y.Chang,
P.H.Liang,
and
K.S.Anderson
(2003).
Probing electrostatic channeling in protozoal bifunctional thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolate reductase using site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
28901-28911.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ferrari,
P.M.Costi,
and
R.C.Wade
(2003).
Inhibitor specificity via protein dynamics: insights from the design of antibacterial agents targeted against thymidylate synthase.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
10,
1183-1193.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.F.Johnson,
W.Hinz,
C.E.Atreya,
F.Maley,
and
K.S.Anderson
(2002).
Mechanistic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii thymidylate synthase (TS-DHFR)-dihydrofolate reductase. Evidence for a TS intermediate and TS half-sites reactivity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
43126-43136.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Gołos,
J.M.Dzik,
Z.Kazimierczuk,
J.Cieśla,
Z.Zieliński,
J.Jankowska,
A.Kraszewski,
J.Stawiński,
W.Rode,
and
D.Shugar
(2001).
Interaction of thymidylate synthase with the 5'-thiophosphates, 5'-dithiophosphates, 5'-H-phosphonates and 5'-S-thiosulfates of 2'-deoxyuridine, thymidine and 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
382,
1439-1445.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Almog,
C.A.Waddling,
F.Maley,
G.F.Maley,
and
P.Van Roey
(2001).
Crystal structure of a deletion mutant of human thymidylate synthase Delta (7-29) and its ternary complex with Tomudex and dUMP.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
988-996.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Stevens,
S.Sanker,
C.Kent,
and
E.R.Zuiderweg
(2001).
Delineation of the allosteric mechanism of a cytidylyltransferase exhibiting negative cooperativity.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
8,
947-952.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Phan,
E.Mahdavian,
M.C.Nivens,
W.Minor,
S.Berger,
H.T.Spencer,
R.B.Dunlap,
and
L.Lebioda
(2000).
Catalytic cysteine of thymidylate synthase is activated upon substrate binding.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
6969-6978.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Morse,
S.Kawase,
D.V.Santi,
J.Finer-Moore,
and
R.M.Stroud
(2000).
Energetic contributions of four arginines to phosphate-binding in thymidylate synthase are more than additive and depend on optimization of "effective charge balance".
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
1011-1020.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.K.Shoichet,
A.R.Leach,
and
I.D.Kuntz
(1999).
Ligand solvation in molecular docking.
|
| |
Proteins,
34,
4.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.R.Sotelo-Mundo,
J.Ciesla,
J.M.Dzik,
W.Rode,
F.Maley,
G.F.Maley,
L.W.Hardy,
and
W.R.Montfort
(1999).
Crystal structures of rat thymidylate synthase inhibited by Tomudex, a potent anticancer drug.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
1087-1094.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Stout,
D.Tondi,
M.Rinaldi,
D.Barlocco,
P.Pecorari,
D.V.Santi,
I.D.Kuntz,
R.M.Stroud,
B.K.Shoichet,
and
M.P.Costi
(1999).
Structure-based design of inhibitors specific for bacterial thymidylate synthase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
1607-1617.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Prasanna,
B.Gopal,
M.R.Murthy,
D.V.Santi,
and
P.Balaram
(1999).
Effect of amino acid substitutions at the subunit interface on the stability and aggregation properties of a dimeric protein: role of Arg 178 and Arg 218 at the Dimer interface of thymidylate synthase.
|
| |
Proteins,
34,
356-368.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.Costi
(1998).
Thymidylate synthase inhibition: a structure-based rationale for drug design.
|
| |
Med Res Rev,
18,
21-42.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Aurora,
and
G.D.Rose
(1998).
Seeking an ancient enzyme in Methanococcus jannaschii using ORF, a program based on predicted secondary structure comparisons.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
2818-2823.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Stout,
C.R.Sage,
and
R.M.Stroud
(1998).
The additivity of substrate fragments in enzyme-ligand binding.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
839-848.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Tong,
X.Liu-Chen,
E.A.Ercikan-Abali,
G.M.Capiaux,
S.C.Zhao,
D.Banerjee,
and
J.R.Bertino
(1998).
Isolation and characterization of thymitaq (AG337) and 5-fluoro-2-deoxyuridylate-resistant mutants of human thymidylate synthase from ethyl methanesulfonate-exposed human sarcoma HT1080 cells.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
11611-11618.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Tong,
X.Liu-Chen,
E.A.Ercikan-Abali,
S.C.Zhao,
D.Banerjee,
F.Maley,
and
J.R.Bertino
(1998).
Probing the folate-binding site of human thymidylate synthase by site-directed mutagenesis. Generation of mutants that confer resistance to raltitrexed, Thymitaq, and BW1843U89.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
31209-31214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.C.Hyatt,
F.Maley,
and
W.R.Montfort
(1997).
Use of strain in a stereospecific catalytic mechanism: crystal structures of Escherichia coli thymidylate synthase bound to FdUMP and methylenetetrahydrofolate.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
4585-4594.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.T.Spencer,
J.E.Villafranca,
and
J.R.Appleman
(1997).
Kinetic scheme for thymidylate synthase from Escherichia coli: determination from measurements of ligand binding, primary and secondary isotope effects, and pre-steady-state catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
4212-4222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Huang,
and
D.V.Santi
(1997).
Active site general catalysts are not necessary for some proton transfer reactions of thymidylate synthase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
1869-1873.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.R.Montfort,
and
A.Weichsel
(1997).
Thymidylate synthase: structure, inhibition, and strained conformations during catalysis.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
76,
29-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.L.Stoddard
(1996).
Intermediate trapping and laue X-ray diffraction: potential for enzyme mechanism, dynamics, and inhibitor screening.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
70,
215-256.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.G.Vassylyev,
and
K.Morikawa
(1996).
Precluding uracil from DNA.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
1381-1385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.S.Finer-Moore,
L.Liu,
C.E.Schafmeister,
D.L.Birdsall,
T.Mau,
D.V.Santi,
and
R.M.Stroud
(1996).
Partitioning roles of side chains in affinity, orientation, and catalysis with structures for mutant complexes: asparagine-229 in thymidylate synthase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
5125-5136.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.M.Costi,
L.Liu,
J.S.Finer-Moore,
R.M.Stroud,
and
D.V.Santi
(1996).
Asparagine 229 mutants of thymidylate synthase catalyze the methylation of 3-methyl-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
3944-3949.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.S.Gokhale,
S.Agarwalla,
D.V.Santi,
and
P.Balaram
(1996).
Covalent reinforcement of a fragile region in the dimeric enzyme thymidylate synthase stabilizes the protein against chaotrope-induced unfolding.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
7150-7158.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Stout,
and
R.M.Stroud
(1996).
The complex of the anti-cancer therapeutic, BW1843U89, with thymidylate synthase at 2.0 A resolution: implications for a new mode of inhibition.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
67-77.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Weichsel,
W.R.Montfort,
J.Cieśla,
and
F.Maley
(1995).
Promotion of purine nucleotide binding to thymidylate synthase by a potent folate analogue inhibitor, 1843U89.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
3493-3497.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.García-Fuentes,
P.Reche,
O.López-Mayorga,
D.V.Santi,
D.González-Pacanowska,
and
C.Barón
(1995).
Thermodynamic analysis of the binding of 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate to thymidylate synthase over a range of temperatures.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
232,
641-645.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.R.Knighton,
C.C.Kan,
E.Howland,
C.A.Janson,
Z.Hostomska,
K.M.Welsh,
and
D.A.Matthews
(1994).
Structure of and kinetic channelling in bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
1,
186-194.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Hardy,
D.F.Pacitti,
and
E.Nalivaika
(1994).
Use of a purified heterodimer to test negative cooperativity as the basis of substrate inactivation of Escherichia coli thymidylate synthase (Asn177-->Asp).
|
| |
Structure,
2,
833-838.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Stroud
(1994).
An electrostatic highway.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
1,
131-134.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

