 |
PDBsum entry 1q0h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1q0h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.267
- 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate + NADP+ = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 44.44% similarity
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 64.58% similarity
|
=
|
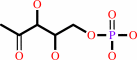 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+) or cobalt cation or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
345:115-127
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of E.coli 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase in a ternary complex with the antimalarial compound fosmidomycin and NADPH reveals a tight-binding closed enzyme conformation.
|
|
A.Mac Sweeney,
R.Lange,
R.P.Fernandes,
H.Schulz,
G.E.Dale,
A.Douangamath,
P.J.Proteau,
C.Oefner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The key enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis,
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR) has been shown to be the
target enzyme of fosmidomycin, an antimalarial, antibacterial and herbicidal
compound. Here we report the crystal structure of selenomethionine-labelled
Escherichia coli DXR in a ternary complex with NADPH and fosmidomycin at 2.2 A
resolution. The structure reveals a considerable conformational rearrangement
upon fosmidomycin binding and provides insights into the slow, tight binding
inhibition mode of the inhibitor. Although the inhibitor displays an unusual
non-metal mediated mode of inhibition, which is an artefact most likely due to
the low metal affinity of DXR at the pH used for crystallization, the structural
data add valuable information for the rational design of novel DXR inhibitors.
Using this structure together with the published structural data and the 1.9 A
crystal structure of DXR in a ternary complex with NADPH and the substrate
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate, a model for the physiologically relevant
tight-binding mode of inhibition is proposed. The structure of the substrate
complex must be interpreted with caution due to the presence of a second
diastereomer in the active site.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. (A) An FoKFc omit electron density map of fosmidomycin in the active site of DXR, contoured at 3s. Met276
is shown in orange on the left and Met214 is shown in two conformations: that of SeMet214 in magenta (right) and that of
wild-type Met214 in orange (left). (B) Hydrogen bonding interactions of the inhibitor fosmidomycin in the active site of
DXR. (C) A schematic diagram of fosmidomycin binding to SeMet-labelled DXR.
|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. (A) An FoKFc omit electron density map of the substrate DXP in the active site of DXR, contoured at 3s. The
position of the hydroxyl group in the L-configuration at C4 is depicted in green. (B) Hydrogen bonding interactions of
the substrate DXP in the active site of DXR. The position of the hydroxyl group in the L-configuration at C4 is depicted in
green. (C) A schematic diagram of the substrate DXP binding to DXR. For clarity, the bond between the carboxylate of
E231 and the hydroxyl group of C4 of DXP has been omitted.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2005,
345,
115-127)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.E.Englert,
C.Richter,
J.Wiesner,
M.Hintz,
H.Jomaa,
and
H.Schwalbe
(2011).
NMR Studies of DOXP Reductoisomerase and its Inhibitor Complex.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
12,
468-476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Behrendt,
A.Kunfermann,
V.Illarionova,
A.Matheeussen,
T.Gräwert,
M.Groll,
F.Rohdich,
A.Bacher,
W.Eisenreich,
M.Fischer,
L.Maes,
and
T.Kurz
(2010).
Synthesis and antiplasmodial activity of highly active reverse analogues of the antimalarial drug candidate fosmidomycin.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
5,
1673-1676.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.W.Johannes,
M.A.DeSieno,
B.M.Griffin,
P.M.Thomas,
N.L.Kelleher,
W.W.Metcalf,
and
H.Zhao
(2010).
Deciphering the late biosynthetic steps of antimalarial compound FR-900098.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
17,
57-64.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Jawaid,
H.Seidle,
W.Zhou,
H.Abdirahman,
M.Abadeer,
J.H.Hix,
M.L.van Hoek,
and
R.D.Couch
(2009).
Kinetic characterization and phosphoregulation of the Francisella tularensis 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (MEP synthase).
|
| |
PLoS One,
4,
e8288.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Williams,
and
J.Andrew McCammon
(2009).
Conformational Dynamics of the Flexible Catalytic Loop in Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-Phosphate Reductoisomerase.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
73,
26-38.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Ganta,
S.Perumal,
S.R.Pagadala,
O.Samuelsen,
J.Spencer,
R.F.Pratt,
and
J.D.Buynak
(2009).
Approaches to the simultaneous inactivation of metallo- and serine-beta-lactamases.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
19,
1618-1622.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lauw,
V.Illarionova,
A.Bacher,
F.Rohdich,
and
W.Eisenreich
(2008).
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: studies on the mechanism of 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate synthase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
4060-4073.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Henriksson,
T.Unge,
J.Carlsson,
J.Aqvist,
S.L.Mowbray,
and
T.A.Jones
(2007).
Structures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase provide new insights into catalysis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
19905-19916.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Singh,
M.A.Avery,
and
C.R.McCurdy
(2007).
Toward Mycobacterium tuberculosis DXR inhibitor design: homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulations.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
21,
511-522.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Yajima,
K.Hara,
D.Iino,
Y.Sasaki,
T.Kuzuyama,
K.Ohsawa,
and
H.Seto
(2007).
Structure of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in a quaternary complex with a magnesium ion, NADPH and the antimalarial drug fosmidomycin.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
466-470.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.N.Hunter
(2007).
The non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
21573-21577.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Barker
(2006).
Antibacterial drug discovery and structure-based design.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
11,
391-404.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Henriksson,
C.Björkelid,
S.L.Mowbray,
and
T.Unge
(2006).
The 1.9 A resolution structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, a potential drug target.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
807-813.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Mercklé,
A.de Andrés-Gómez,
B.Dick,
R.J.Cox,
and
C.R.Godfrey
(2005).
A fragment-based approach to understanding inhibition of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
6,
1866-1874.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

