 |
PDBsum entry 1kux

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.87
- aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2-arylethylamine + acetyl-CoA = an N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
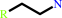 2-arylethylamine
2-arylethylamine
|
+
|
acetyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 74.63% similarity
|
=
|
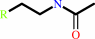 N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine
N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
317:215-224
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
X-ray crystallographic studies of serotonin N-acetyltransferase catalysis and inhibition.
|
|
E.Wolf,
J.De Angelis,
E.M.Khalil,
P.A.Cole,
S.K.Burley.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of serotonin N-acetyltransferase (also known as arylalkylamine
N-acetyltransferase; AANAT) bound to a potent bisubstrate analog inhibitor has
been determined at 2.0 A resolution using a two-edge (Se, Br) multiwavelength
anomalous diffraction (MAD) experiment. This acetyl-CoA dependent enzyme is a
member of the GCN5-related family of N-acetyltransferases (GNATs), which share
four conserved sequence motifs (A-D). In serotonin N-acetyltransferase, motif A
adopts an alpha/beta conformation characteristic of the phylogenetically
invariant cofactor binding site seen in all previously characterized GNATs.
Motif B displays a significantly lower level of conservation among family
members, giving rise to a novel alpha/beta structure for the serotonin binding
slot. Utilization of a brominated CoA-S-acetyl-tryptamine-bisubstrate analog
inhibitor and the MAD method permitted conclusive identification of two
radically different conformations for the tryptamine moiety in the catalytic
site (cis and trans). A second high-resolution X-ray structure of the enzyme
bound to a bisubstrate analog inhibitor, with a longer tether between the
acetyl-CoA and tryptamine moieties, demonstrates only the trans conformation.
Given a previous proposal that AANAT can catalyze an alkyltransferase reaction
in a conformationally altered active site relative to its acetyltransferase
activity, it is possible that the two conformations of the bisubstrate analog
observed crystallographically correspond to these alternative reaction pathways.
Our findings may ultimately lead to the design of analogs with improved AANAT
inhibitory properties for in vivo applications.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Enzyme-catalyzed reactions and inhibitors for
serotonin N-acetyltransferase. (a) Serotonin
N-acetyltransferase-catalyzed reaction between serotonin and
acetyl-CoA. (b) Alkyl transfer reaction between CoASH and
N-bromoacetyltryptamine. (c) Bisubstrate analog inhibitors 1, 2,
and 3.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Overlay of compounds 1 and 3 in the active site
of AANAT. Left: a stereodrawing of compounds 1 (green) and 3
(red) drawn as atomic stick figures with selected atoms labeled.
Right: the atomic numbering scheme for the tryptamine moieties
of compounds 1, 2, and 3.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2002,
317,
215-224)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Pavlicek,
S.L.Coon,
S.Ganguly,
J.L.Weller,
S.A.Hassan,
D.L.Sackett,
and
D.C.Klein
(2008).
Evidence that proline focuses movement of the floppy loop of arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.87).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
14552-14558.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Vetting,
D.C.Bareich,
M.Yu,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2008).
Crystal structure of RimI from Salmonella typhimurium LT2, the GNAT responsible for N(alpha)-acetylation of ribosomal protein S18.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
17,
1781-1790.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kotani,
and
H.Takagi
(2008).
Identification of amino acid residues essential for the yeast N-acetyltransferase Mpr1 activity by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
FEMS Yeast Res,
8,
607-614.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.C.Klein
(2007).
Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase: "the Timezyme".
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
4233-4237.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Szewczuk,
S.A.Saldanha,
S.Ganguly,
E.M.Bowers,
M.Javoroncov,
B.Karanam,
J.C.Culhane,
M.A.Holbert,
D.C.Klein,
R.Abagyan,
and
P.A.Cole
(2007).
De novo discovery of serotonin N-acetyltransferase inhibitors.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
50,
5330-5338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Toleman,
A.J.Paterson,
and
J.E.Kudlow
(2006).
The histone acetyltransferase NCOAT contains a zinc finger-like motif involved in substrate recognition.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
3918-3925.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.N.Hung,
E.Rangarajan,
C.Munger,
G.Nadeau,
T.Sulea,
and
A.Matte
(2006).
Crystal structure of TDP-fucosamine acetyltransferase (WecD) from Escherichia coli, an enzyme required for enterobacterial common antigen synthesis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
5606-5617.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Gao,
X.Yan,
O.M.Baettig,
A.M.Berghuis,
and
K.Auclair
(2005).
Regio- and chemoselective 6'-N-derivatization of aminoglycosides: bisubstrate inhibitors as probes to study aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferases.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
44,
6859-6862.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Boutin,
V.Audinot,
G.Ferry,
and
P.Delagrange
(2005).
Molecular tools to study melatonin pathways and actions.
|
| |
Trends Pharmacol Sci,
26,
412-419.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Ferry,
C.Ubeaud,
J.Mozo,
C.Péan,
P.Hennig,
M.Rodriguez,
C.Scoul,
A.Bonnaud,
O.Nosjean,
J.P.Galizzi,
P.Delagrange,
P.Renard,
J.P.Volland,
S.Yous,
D.Lesieur,
and
J.A.Boutin
(2004).
New substrate analogues of human serotonin N-acetyltransferase produce in situ specific and potent inhibitors.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
418-428.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.D.Boehr,
S.I.Jenkins,
and
G.D.Wright
(2003).
The molecular basis of the expansive substrate specificity of the antibiotic resistance enzyme aminoglycoside acetyltransferase-6'-aminoglycoside phosphotransferase-2". The role of ASP-99 as an active site base important for acetyl transfer.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
12873-12880.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.N.Poux,
M.Cebrat,
C.M.Kim,
P.A.Cole,
and
R.Marmorstein
(2002).
Structure of the GCN5 histone acetyltransferase bound to a bisubstrate inhibitor.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
14065-14070.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Scheibner,
J.De Angelis,
S.K.Burley,
and
P.A.Cole
(2002).
Investigation of the roles of catalytic residues in serotonin N-acetyltransferase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
18118-18126.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

