 |
PDBsum entry 1l0c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.87
- aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2-arylethylamine + acetyl-CoA = an N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
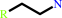 2-arylethylamine
2-arylethylamine
|
+
|
acetyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 78.12% similarity
|
=
|
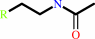 N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine
N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
277:18118-18126
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Investigation of the roles of catalytic residues in serotonin N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
K.A.Scheibner,
J.De Angelis,
S.K.Burley,
P.A.Cole.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Serotonin N-acetyltransferase (arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT)) is a
critical enzyme in the light-mediated regulation of melatonin production and
circadian rhythm. It is a member of the GNAT (GCN-5-related N-acetyltransferase)
superfamily of enzymes, which catalyze a diverse array of biologically important
acetyl transfer reactions from antibiotic resistance to chromatin remodeling. In
this study, we probed the functional properties of two histidines (His-120 and
His-122) and a tyrosine (Tyr-168) postulated to be important in the mechanism of
AANAT based on prior x-ray structural and biochemical studies. Using a
combination of steady-state kinetic measurements of microviscosity effects and
pH dependence on the H122Q, H120Q, and H120Q/H122Q AANAT mutants, we show that
His-122 (with an apparent pK(a) of 7.3) contributes approximately 6-fold to the
acetyltransferase chemical step as either a remote catalytic base or hydrogen
bond donor. Furthermore, His-120 and His-122 appear to contribute redundantly to
this function. By analysis of the Y168F AANAT mutant, it was demonstrated that
Tyr-168 contributes approximately 150-fold to the acetyltransferase chemical
step and is responsible for the basic limb of the pH-rate profile with an
apparent (subnormal) pK(a) of 8.5. Paradoxically, Y168F AANAT showed 10-fold
enhanced apparent affinity for acetyl-CoA despite the loss of a hydrogen bond
between the Tyr phenol and the CoA sulfur atom. The X-ray crystal structure of
Y168F AANAT bound to a bisubstrate analog inhibitor showed no significant
structural perturbation of the enzyme compared with the wild-type complex, but
revealed the loss of dual inhibitor conformations present in the wild-type
complex. Taken together with kinetic measurements, these crystallographic
studies allow us to propose the relevant structural conformations related to the
distinct alkyltransferase and acetyltransferase reactions catalyzed by AANAT.
These findings have significant implications for understanding GNAT catalysis
and the design of potent and selective inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Mechanism of the acetyltransferase reaction
catalyzed by AANAT (A) and alkyl transfer between CoASH and
N-bromoacetyltryptamine (compound 1), resulting in the
bisubstrate analog inhibitor (compound 2) (B).
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. X-ray structure of AANAT bound to the bisubstrate
analog (compound 2). Tyr-168, His-120, and His-122 are
highlighted and were the focus of the mutational studies
detailed in this report.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2002,
277,
18118-18126)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Pavlicek,
S.Sauzet,
L.Besseau,
S.L.Coon,
J.L.Weller,
G.Boeuf,
P.Gaildrat,
M.V.Omelchenko,
E.V.Koonin,
J.Falcón,
and
D.C.Klein
(2010).
Evolution of AANAT: expansion of the gene family in the cephalochordate amphioxus.
|
| |
BMC Evol Biol,
10,
154.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Brent,
A.Iwata,
J.Carten,
K.Zhao,
and
R.Marmorstein
(2009).
Structure and biochemical characterization of protein acetyltransferase from Sulfolobus solfataricus.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
19412-19419.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Frankel,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2008).
Mechanistic analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv1347c, a lysine Nepsilon-acyltransferase involved in mycobactin biosynthesis.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
477,
259-266.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Pavlicek,
S.L.Coon,
S.Ganguly,
J.L.Weller,
S.A.Hassan,
D.L.Sackett,
and
D.C.Klein
(2008).
Evidence that proline focuses movement of the floppy loop of arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.87).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
14552-14558.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Wang,
Y.Tang,
P.A.Cole,
and
R.Marmorstein
(2008).
Structure and chemistry of the p300/CBP and Rtt109 histone acetyltransferases: implications for histone acetyltransferase evolution and function.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
18,
741-747.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Vetting,
C.H.Park,
S.S.Hegde,
G.A.Jacoby,
D.C.Hooper,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2008).
Mechanistic and structural analysis of aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-Ib and its bifunctional, fluoroquinolone-active AAC(6')-Ib-cr variant.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
9825-9835.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kotani,
and
H.Takagi
(2008).
Identification of amino acid residues essential for the yeast N-acetyltransferase Mpr1 activity by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
FEMS Yeast Res,
8,
607-614.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Liu,
L.Wang,
K.Zhao,
P.R.Thompson,
Y.Hwang,
R.Marmorstein,
and
P.A.Cole
(2008).
The structural basis of protein acetylation by the p300/CBP transcriptional coactivator.
|
| |
Nature,
451,
846-850.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Szewczuk,
S.A.Saldanha,
S.Ganguly,
E.M.Bowers,
M.Javoroncov,
B.Karanam,
J.C.Culhane,
M.A.Holbert,
D.C.Klein,
R.Abagyan,
and
P.A.Cole
(2007).
De novo discovery of serotonin N-acetyltransferase inhibitors.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
50,
5330-5338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.N.Hung,
E.Rangarajan,
C.Munger,
G.Nadeau,
T.Sulea,
and
A.Matte
(2006).
Crystal structure of TDP-fucosamine acetyltransferase (WecD) from Escherichia coli, an enzyme required for enterobacterial common antigen synthesis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
5606-5617.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Van Wagoner,
and
J.Clardy
(2006).
FeeM, an N-acyl amino acid synthase from an uncultured soil microbe: structure, mechanism, and acyl carrier protein binding.
|
| |
Structure,
14,
1425-1435.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.S.Hsiao,
G.Jogl,
and
L.Tong
(2006).
Crystal structures of murine carnitine acetyltransferase in ternary complexes with its substrates.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
28480-28487.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Meurisse,
R.Brasseur,
and
A.Thomas
(2004).
Aromatic side-chain interactions in proteins: near- and far-sequence Tyr-X pairs.
|
| |
Proteins,
54,
478-490.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

