 |
PDBsum entry 1j09

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of thermus thermophilus glutamyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with atp and glu
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase. Chain: a. Synonym: glurs, glutamate--tRNA ligase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Thermus thermophilus. Organism_taxid: 274. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.199
|
R-free:
|
0.227
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Sekine,O.Nureki,D.Y.Dubois,S.Bernier,R.Chenevert,J.Lapointe, D.G.Vassylyev,S.Yokoyama,Riken Structural Genomics/proteomics Initiative (Rsgi)
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Sekine
et al.
(2003).
ATP binding by glutamyl-tRNA synthetase is switched to the productive mode by tRNA binding.
EMBO J,
22,
676-688.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
12-Nov-02
|
Release date:
|
25-Feb-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P27000
(SYE_THET8) -
Glutamate--tRNA ligase from Thermus thermophilus (strain ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / HB8)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
468 a.a.
468 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.17
- glutamate--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Glu) + L-glutamate + ATP = L-glutamyl-tRNA(Glu) + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
tRNA(Glu)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
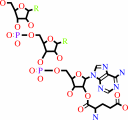 L-glutamyl-tRNA(Glu)
L-glutamyl-tRNA(Glu)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
EMBO J
22:676-688
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
ATP binding by glutamyl-tRNA synthetase is switched to the productive mode by tRNA binding.
|
|
S.Sekine,
O.Nureki,
D.Y.Dubois,
S.Bernier,
R.Chênevert,
J.Lapointe,
D.G.Vassylyev,
S.Yokoyama.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the formation of an aminoacyl-AMP from an
amino acid and ATP, prior to the aminoacyl transfer to tRNA. A subset of
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, including glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (GluRS), have a
regulation mechanism to avoid aminoacyl-AMP formation in the absence of tRNA. In
this study, we determined the crystal structure of the 'non-productive' complex
of Thermus thermophilus GluRS, ATP and L-glutamate, together with those of the
GluRS.ATP, GluRS.tRNA.ATP and GluRS.tRNA.GoA (a glutamyl-AMP analog) complexes.
In the absence of tRNA(Glu), ATP is accommodated in a 'non-productive' subsite
within the ATP-binding site, so that the ATP alpha-phosphate and the glutamate
alpha-carboxyl groups in GluRS. ATP.Glu are too far from each other (6.2 A) to
react. In contrast, the ATP-binding mode in GluRS.tRNA. ATP is dramatically
different from those in GluRS.ATP.Glu and GluRS.ATP, but corresponds to the AMP
moiety binding mode in GluRS.tRNA.GoA (the 'productive' subsite). Therefore,
tRNA binding to GluRS switches the ATP-binding mode. The interactions of the
three tRNA(Glu) regions with GluRS cause conformational changes around the
ATP-binding site, and allow ATP to bind to the 'productive' subsite.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1 Thermus thermophilus GluRS crystal structures. (A)
Ribbon representation of the ERS/ATP/Glu structure. Five
domains, the Rossmann fold (1), connective peptide (or
acceptor-binding) (2), stem-contact fold (3) and two
anticodon-binding (4 and 5) domains, are colored khaki, light
blue, pink, steel blue and deep blue, respectively. The HVGT and
KISKR motifs of GluRS are highlighted in purple. The ATP and
glutamate molecules in the GluRS catalytic pocket are shown in
green. (B) Overall structure of ERS/tRNA/ATP. The ATP and
tRNA^Glu molecules in the complex are shown in orange and
turquoise, respectively. These figures were produced using the
MOLSCRIPT (Kraulis, 1991) and RASTER3D (Merritt and Murphy,
1994) programs.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4 Substrate/ligand(s) binding in the GluRS complexes. (A
-D) The GluRS catalytic site structures in the present complexes
are shown in the same orientation. The HVGT and KISKR motifs are
highlighted in purple. (A) The ERS/ATP/Glu structure. The
ATP-Mg2+ and glutamate molecules are shown in green. (B) The
ERS/ATP structure. The ATP-Mg2+ is colored light blue. (C) The
ERS/tRNA/ATP structure. The ATP molecule is colored salmon, and
the 3'-terminal adenosine (A76) of tRNA^Glu is cyan. (D) The
ERS/tRNA/GoA structure. The GoA (glutamol-AMP) molecule is
colored yellow. (E) A stereo view showing the ATP recognition in
ERS/tRNA/ATP. (F) A stereo view showing the GoA recognition in
ERS/tRNA/GoA.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
EMBO J
(2003,
22,
676-688)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Palencia,
T.Crépin,
M.T.Vu,
T.L.Lincecum,
S.A.Martinis,
and
S.Cusack
(2012).
Structural dynamics of the aminoacylation and proofreading functional cycle of bacterial leucyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
19,
677-684.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Katz,
R.Banerjee,
M.de Armas,
M.Ibba,
and
O.Orellana
(2010).
Redox status affects the catalytic activity of glutamyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
398,
51-55.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kawai,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2010).
Professor Tatsuo Miyazawa: from molecular structure to biological function.
|
| |
J Biochem,
148,
631-638.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ito,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2010).
Two enzymes bound to one transfer RNA assume alternative conformations for consecutive reactions.
|
| |
Nature,
467,
612-616.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.B.Chen,
W.B.Arendall,
J.J.Headd,
D.A.Keedy,
R.M.Immormino,
G.J.Kapral,
L.W.Murray,
J.S.Richardson,
and
D.C.Richardson
(2010).
MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
12-21.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Gulick
(2009).
Conformational dynamics in the Acyl-CoA synthetases, adenylation domains of non-ribosomal peptide synthetases, and firefly luciferase.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
4,
811-827.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Sethi,
J.Eargle,
A.A.Black,
and
Z.Luthey-Schulten
(2009).
Dynamical networks in tRNA:protein complexes.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
6620-6625.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Konno,
T.Sumida,
E.Uchikawa,
Y.Mori,
T.Yanagisawa,
S.Sekine,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2009).
Modeling of tRNA-assisted mechanism of Arg activation based on a structure of Arg-tRNA synthetase, tRNA, and an ATP analog (ANP).
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
4763-4779.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Paravisi,
G.Fumagalli,
M.Riva,
P.Morandi,
R.Morosi,
P.V.Konarev,
M.V.Petoukhov,
S.Bernier,
R.Chênevert,
D.I.Svergun,
B.Curti,
and
M.A.Vanoni
(2009).
Kinetic and mechanistic characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis glutamyl-tRNA synthetase and determination of its oligomeric structure in solution.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
1398-1417.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Francklyn
(2008).
DNA polymerases and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: shared mechanisms for ensuring the fidelity of gene expression.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
11695-11703.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Ellis,
and
S.Jones
(2008).
Evaluating conformational changes in protein structures binding RNA.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
1518-1526.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.C.Chen,
and
C.Lim
(2008).
Predicting RNA-binding sites from the protein structure based on electrostatics, evolution and geometry.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
e29.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.A.Vasil'eva,
and
N.A.Moor
(2007).
Interaction of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases with tRNA: general principles and distinguishing characteristics of the high-molecular-weight substrate recognition.
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
72,
247-263.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Budiman,
M.H.Knaggs,
J.S.Fetrow,
and
R.W.Alexander
(2007).
Using molecular dynamics to map interaction networks in an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Proteins,
68,
670-689.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kapustina,
V.Weinreb,
L.Li,
B.Kuhlman,
and
C.W.Carter
(2007).
A conformational transition state accompanies tryptophan activation by B. stearothermophilus tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
1272-1284.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Retailleau,
V.Weinreb,
M.Hu,
and
C.W.Carter
(2007).
Crystal structure of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with adenosine-5' tetraphosphate: evidence for distributed use of catalytic binding energy in amino acid activation by class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
369,
108-128.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Tyagi,
and
D.H.Mathews
(2007).
Predicting helical coaxial stacking in RNA multibranch loops.
|
| |
RNA,
13,
939-951.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Devedjiev,
C.N.Steussy,
and
D.G.Vassylyev
(2007).
Crystal structure of an asymmetric complex of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 3 with lipoyl domain 2 and its biological implications.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
370,
407-416.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Wang,
M.Praetorius-Ibba,
S.F.Ataide,
H.Roy,
and
M.Ibba
(2006).
Discrimination of cognate and noncognate substrates at the active site of class I lysyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
3646-3652.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Roach,
S.Sharma,
M.Kapustina,
and
C.W.Carter
(2005).
Structure alignment via Delaunay tetrahedralization.
|
| |
Proteins,
60,
66-81.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.T.Uter,
I.Gruic-Sovulj,
and
J.J.Perona
(2005).
Amino acid-dependent transfer RNA affinity in a class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
23966-23977.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
L.Wang,
P.G.Schultz,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2005).
Crystal structures of apo wild-type M. jannaschii tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (TyrRS) and an engineered TyrRS specific for O-methyl-L-tyrosine.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
1340-1349.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Y.Dubois,
M.Blaise,
H.D.Becker,
V.Campanacci,
G.Keith,
R.Giegé,
C.Cambillau,
J.Lapointe,
and
D.Kern
(2004).
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-like protein encoded by the Escherichia coli yadB gene glutamylates specifically tRNAAsp.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
7530-7535.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Salazar,
A.Ambrogelly,
P.F.Crain,
J.A.McCloskey,
and
D.Söll
(2004).
A truncated aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase modifies RNA.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
7536-7541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jia,
X.L.Chen,
L.T.Guo,
Y.D.Yu,
J.P.Ding,
and
Y.X.Jin
(2004).
Residues Lys-149 and Glu-153 switch the aminoacylation of tRNA(Trp) in Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
41960-41965.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Lee,
and
T.L.Hendrickson
(2004).
Divergent anticodon recognition in contrasting glutamyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
344,
1167-1174.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Levengood,
S.F.Ataide,
H.Roy,
and
M.Ibba
(2004).
Divergence in noncognate amino acid recognition between class I and class II lysyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
17707-17714.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Randau,
S.Schauer,
A.Ambrogelly,
J.C.Salazar,
J.Moser,
S.Sekine,
S.Yokoyama,
D.Söll,
and
D.Jahn
(2004).
tRNA recognition by glutamyl-tRNA reductase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
34931-34937.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ibba,
and
C.Francklyn
(2004).
Turning tRNA upside down: When aminoacylation is not a prerequisite to protein synthesis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
7493-7494.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Buddha,
K.M.Keery,
and
B.R.Crane
(2004).
An unusual tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase interacts with nitric oxide synthase in Deinococcus radiodurans.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
15881-15886.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Banerjee,
D.Y.Dubois,
J.Gauthier,
S.X.Lin,
S.Roy,
and
J.Lapointe
(2004).
The zinc-binding site of a class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is a SWIM domain that modulates amino acid binding via the tRNA acceptor arm.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
724-733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Hauenstein,
C.M.Zhang,
Y.M.Hou,
and
J.J.Perona
(2004).
Shape-selective RNA recognition by cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
11,
1134-1141.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kaya,
M.Del Campo,
J.Ofengand,
and
A.Malhotra
(2004).
Crystal structure of TruD, a novel pseudouridine synthase with a new protein fold.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
18107-18110.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Cavarelli
(2003).
Pushing induced fit to its limits: tRNA-dependent active site assembly in class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
484-486.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Bovee,
M.A.Pierce,
and
C.S.Francklyn
(2003).
Induced fit and kinetic mechanism of adenylation catalyzed by Escherichia coli threonyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
15102-15113.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Geslain,
G.Bey,
J.Cavarelli,
and
G.Eriani
(2003).
Limited set of amino acid residues in a class Ia aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is crucial for tRNA binding.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
15092-15101.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

