 |
PDBsum entry 1hg0

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.1
- asparaginase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-asparagine + H2O = L-aspartate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
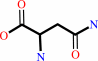 L-asparagine
L-asparagine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-aspartate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 88.89% similarity
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
40:5655-5664
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the activity and substrate specificity of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase.
|
|
K.Aghaiypour,
A.Wlodawer,
J.Lubkowski.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Bacterial L-asparaginases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of L-asparagine
to aspartic acid, have been used for over 30 years as therapeutic agents in the
treatment of acute childhood lymphoblastic leukemia. Other substrates of
asparaginases include L-glutamine, D-asparagine, and succinic acid monoamide. In
this report, we present high-resolution crystal structures of the complexes of
Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase (ErA) with the products of such reactions
that also can serve as substrates, namely L-glutamic acid (L-Glu), D-aspartic
acid (D-Asp), and succinic acid (Suc). Comparison of the four independent active
sites within each complex indicates unique and specific binding of the ligand
molecules; the mode of binding is also similar between complexes. The lack of
the alpha-NH3(+) group in Suc, compared to L-Asp, does not affect the binding
mode. The side chain of L-Glu, larger than that of L-Asp, causes several
structural distortions in the ErA active side. The active site flexible loop
(residues 15-33) does not exhibit stable conformation, resulting in suboptimal
orientation of the nucleophile, Thr15. Additionally, the delta-COO(-) plane of
L-Glu is approximately perpendicular to the plane of gamma-COO(-) in L-Asp bound
to the asparaginase active site. Binding of D-Asp to the ErA active site is very
distinctive compared to the other ligands, suggesting that the low activity of
ErA against D-Asp could be mainly attributed to the low k(cat) value. A
comparison of the amino acid sequence and the crystal structure of ErA with
those of other bacterial L-asparaginases shows that the presence of two
active-site residues, Glu63(ErA) and Ser254(ErA), may correlate with significant
glutaminase activity, while their substitution by Gln and Asn, respectively, may
lead to minimal L-glutaminase activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Yoshimune,
Y.Shirakihara,
M.Wakayama,
and
I.Yumoto
(2010).
Crystal structure of salt-tolerant glutaminase from Micrococcus luteus K-3 in the presence and absence of its product L-glutamate and its activator Tris.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
738-748.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Warangkar,
and
C.N.Khobragade
(2010).
Purification, Characterization, and Effect of Thiol Compounds on Activity of the Erwinia carotovora L-Asparaginase.
|
| |
Enzyme Res,
2010,
165878.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.A.Kotzia,
and
N.E.Labrou
(2009).
Engineering thermal stability of L-asparaginase by in vitro directed evolution.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
1750-1761.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Dhavala,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2009).
Structure of Helicobacter pyloriL-asparaginase at 1.4 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
1253-1261.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sheppard,
J.Yuan,
M.J.Hohn,
B.Jester,
K.M.Devine,
and
D.Söll
(2008).
From one amino acid to another: tRNA-dependent amino acid biosynthesis.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
1813-1825.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.V.Kravchenko,
Y.A.Kislitsin,
A.N.Popov,
S.V.Nikonov,
and
I.P.Kuranova
(2008).
Three-dimensional structures of L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora complexed with aspartate and glutamate.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
248-256.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Dhavala,
J.Krasotkina,
C.Dubreuil,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2008).
Expression, purification and crystallization of Helicobacter pylori L-asparaginase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
740-742.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Yun,
A.Nourse,
S.W.White,
C.O.Rock,
and
R.J.Heath
(2007).
Crystal structure and allosteric regulation of the cytoplasmic Escherichia coli L-asparaginase I.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
369,
794-811.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Verma,
K.Kumar,
G.Kaur,
and
S.Anand
(2007).
L-asparaginase: a promising chemotherapeutic agent.
|
| |
Crit Rev Biotechnol,
27,
45-62.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Tardito,
J.Uggeri,
C.Bozzetti,
M.G.Bianchi,
B.M.Rotoli,
R.Franchi-Gazzola,
G.C.Gazzola,
R.Gatti,
and
O.Bussolati
(2007).
The inhibition of glutamine synthetase sensitizes human sarcoma cells to L-asparaginase.
|
| |
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,
60,
751-758.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Gutierrez,
Y.X.Pan,
L.Koroniak,
J.Hiratake,
M.S.Kilberg,
and
N.G.Richards
(2006).
An inhibitor of human asparagine synthetase suppresses proliferation of an L-asparaginase-resistant leukemia cell line.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
13,
1339-1347.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Wikman,
J.Krasotkina,
A.Kuchumova,
N.N.Sokolov,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2005).
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
407-409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Feng,
K.Sheppard,
D.Tumbula-Hansen,
and
D.Söll
(2005).
Gln-tRNAGln formation from Glu-tRNAGln requires cooperation of an asparaginase and a Glu-tRNAGln kinase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
8150-8155.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yao,
Y.Yasutake,
H.Morita,
and
I.Tanaka
(2005).
Structure of the type I L-asparaginase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii at 2.16 angstroms resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
294-301.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Lubkowski,
M.Dauter,
K.Aghaiypour,
A.Wlodawer,
and
Z.Dauter
(2003).
Atomic resolution structure of Erwinia chrysanthemi L-asparaginase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
84-92.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

