 |
PDBsum entry 2wt4

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.1
- asparaginase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-asparagine + H2O = L-aspartate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
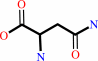 L-asparagine
L-asparagine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-aspartate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
65:1253-1261
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of Helicobacter pyloriL-asparaginase at 1.4 A resolution.
|
|
P.Dhavala,
A.C.Papageorgiou.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Bacterial L-asparaginases have been used in the treatment of childhood acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia for over 30 years. Their therapeutic effect is based on
their ability to catalyze the conversion of L-asparagine, an essential amino
acid in certain tumours, to L-aspartic acid and ammonia. Two L-asparaginases,
one from Escherichia coli and the other from Erwinia chrysanthemi, have been
widely employed in clinical practice as anti-leukaemia drugs. However,
L-asparaginases are also able to cause severe side effects owing to their
intrinsic glutaminase activity. Helicobacter pylori L-asparaginase (HpA) has
been reported to have negligible glutaminase activity. To gain insight into the
properties of HpA, its crystal structure in the presence of L-aspartate was
determined to 1.4 A resolution, which is one of the highest resolutions obtained
for an L-asparaginase structure. The final structure has an R(cryst) of 12.6%
(R(free) = 16.9%) with good stereochemistry. A detailed analysis of the active
site showed major differences in the active-site flexible loop and in the
286-297 loop from the second subunit, which is involved in active-site
formation. Accordingly, Glu289, Asn255 and Gln63 are suggested to play roles in
modulating the accessibility of the active site. Overall, the structural
comparison revealed that HpA has greater structural similarity to E. coli
L-asparaginase than to any other L-asparaginase, including Er. carotovora
L-asparaginase, despite the fact that the latter is also characterized by low
glutaminase activity.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1 (a) Cartoon diagram of HpA. The colouring scheme is
from blue (N-terminus) to red (C-terminus). The active-site
location is indicated by the bound L-Asp (shown in stick
representation). Secondary-structure elements were assigned with
DSSP (Kabsch & Sander, 1983[Kabsch, W. & Sander, C. (1983).
Biopolymers, 22, 2577-2637.]). (b) Cartoon representation of the
HpA tetramer. Each monomer is shown in a different colour. The
orientation of the blue-coloured monomer is the same as in (a).
The blue-salmon and green-magenta pairs correspond to intimate
dimers. L-Asp is depicted as a space-filling model. The same
structure after a 90° rotation is shown on the right. This
figure was created with PyMOL v.0.99 (DeLano Scientific, Palo
Alto, California, USA).
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 Close-up stereodiagram of the active-site flexible
loop. Residues are shown in stick representation. HpA, EwA and
EcAII are coloured blue, green and magenta, respectively. L-Asp
is labelled.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2009,
65,
1253-1261)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

