 |
PDBsum entry 1fuy

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.4.2.1.20
- tryptophan synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Tryptophan Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate + L-serine = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + L-tryptophan + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
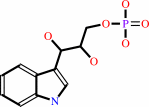 (1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate
(1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate
|
+
|
L-serine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 85.00% similarity
|
=
|
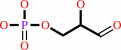 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
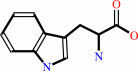 L-tryptophan
L-tryptophan
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
275:41058-41063
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the impaired channeling and allosteric inter-subunit communication in the beta A169L/beta C170W mutant of tryptophan synthase.
|
|
M.Weyand,
I.Schlichting.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We determined the 2.25 A resolution crystal structure of the betaA169L/betaC170W
mutant form of the tryptophan synthase alpha(2)beta(2) complex from Salmonella
typhimurium complexed with the alpha-active site substrate analogue
5-fluoro-indole-propanol-phosphate to identify the structural basis for the
changed kinetic properties of the mutant (Anderson, K. S., Kim, A. Y., Quillen,
J. M., Sayers, E., Yang, X. J., and Miles, E. W. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270,
29936-29944). Comparison with the wild-type enzyme showed that the betaTrp(170)
side chain occludes the tunnel connecting the alpha- and beta-active sites,
explaining the accumulation of the intermediate indole during a single enzyme
turnover. To prevent a steric clash between betaLeu(169) and betaGly(135),
located in the beta-sheet of the COMM (communication) domain
(betaGly(102)-betaGly(189)), the latter reorganizes. The changed COMM domain
conformation results in a loss of the hydrogen bonding networks between the
alpha- and beta-active sites, explaining the poor activation of the
alpha-reaction upon formation of the aminoacrylate complex at the beta-active
site. The 100-fold reduced affinity for serine seems to result from a movement
of betaAsp(305) away from the beta-active site so that it cannot interact with
the hydroxyl group of a pyridoxal phosphate-bound serine. The proposed
structural dissection of the effects of each single mutation in the
betaA169L/betaC170W mutant would explain the very different kinetics of this
mutant and betaC170F.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. A, residual B-factor plot for the wild-type
TRPSIPP (green) and the  A169L/ A169L/  C170WF-IPP
(black) structures (top). The plot of the residual B-factor
ratio (mutant B[fac]/wild-type B[fac]) is shown. Although both
complexes have different mean B-factors, the B-factor comparison
allows the identification of changes within the COMM domain
(bottom). B, C[ C170WF-IPP
(black) structures (top). The plot of the residual B-factor
ratio (mutant B[fac]/wild-type B[fac]) is shown. Although both
complexes have different mean B-factors, the B-factor comparison
allows the identification of changes within the COMM domain
(bottom). B, C[  ]r.m.s.
deviation (RMSD) of TRPSIPP and ]r.m.s.
deviation (RMSD) of TRPSIPP and  A169L/ A169L/  C179WF-IPP
for the C179WF-IPP
for the  (top) and (top) and
 (bottom)
subunits. Points I[ (bottom)
subunits. Points I[  ]and I[ ]and I[
 ]represent
flexible surface residues. The insert shows a detailed view of
the r.m.s. deviation and the secondary structure assignment
within the COMM domain. ]represent
flexible surface residues. The insert shows a detailed view of
the r.m.s. deviation and the secondary structure assignment
within the COMM domain.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. A, stereo drawing of Sigma A-weighted 2 mF[o]
 DF[c] maps
(20) contoured at 1 DF[c] maps
(20) contoured at 1  around the around the
 A169L/ A169L/  C170W
mutation site showing the good definition of the two new side
chains and the reorientation of both gating residues tyrosine C170W
mutation site showing the good definition of the two new side
chains and the reorientation of both gating residues tyrosine
 Tyr279 and
phenylalanine Tyr279 and
phenylalanine  Phe^280. The
figure was prepared using BOBSCRIPT (24) and RASTER3D (25, 26).
B, stereo view of the superposition of the COMM domains of
wild-type TRPSIPP and Phe^280. The
figure was prepared using BOBSCRIPT (24) and RASTER3D (25, 26).
B, stereo view of the superposition of the COMM domains of
wild-type TRPSIPP and  A169L/ A169L/  C170WF-IPP.
Mutated and gating residues of the C170WF-IPP.
Mutated and gating residues of the  -subunit are
shown in a ball-and-stick representation. C -subunit are
shown in a ball-and-stick representation. C  trace and
residues of wild-type TRPSIPP are red ( trace and
residues of wild-type TRPSIPP are red (  -subunit),
dark blue, ( -subunit),
dark blue, (  -subunit),
and yellow (COMM domain, the double mutant is green, carbon
atoms of the -subunit),
and yellow (COMM domain, the double mutant is green, carbon
atoms of the  -ligands
and the cofactor PLP are gray, oxygen atoms red, nitrogen atoms
blue, and phosphate is magenta. Panels A and B are related by an
~90° rotation around the axis perpendicular to the paper
plane. The figure was prepared using MOLSCRIPT (27) and RASTER3D
(25, 26). -ligands
and the cofactor PLP are gray, oxygen atoms red, nitrogen atoms
blue, and phosphate is magenta. Panels A and B are related by an
~90° rotation around the axis perpendicular to the paper
plane. The figure was prepared using MOLSCRIPT (27) and RASTER3D
(25, 26).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2000,
275,
41058-41063)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
We determined the 2.25 Å resolution crystal structure
of the betaA169L/betaC170W mutant form of the tryptophan
synthase alapha2beta2 complex from Salmonella typhimurium
complexed with the alpha-active site substrate analogue
5-fluoro-indole-propanol-phosphate to identify the
structural basis for the changed kinetic properties of
the mutant (Anderson, K. S., Kim, A. Y., Quillen, J. M.,
Sayers, E., Yang, X. J., and Miles, E. W. (1995) J. Biol.
Chem. 270, 29936–29944). Comparison with the wild-type
enzyme showed that the betaTrp170 side chain occludes the
tunnel connecting the alpha- and beta-active sites, explaining
the accumulation of the intermediate indole during a
single enzyme turnover. To prevent a steric clash between
betaLeu169 and betaGly135, located in the beta-sheet of the
COMM (communication) domain (betaGly102-betaGly189), the
latter reorganizes. The changed COMM domain conformation
results in a loss of the hydrogen bonding networks
between the alpha- and beta-active sites, explaining the
poor activation of the alpha-reaction upon formation of the
aminoacrylate complex at the beta-active site. The 100-fold
reduced affinity for serine seems to result from a movement
of betaAsp305 away from the beta-active site so that it
cannot interact with the hydroxyl group of a pyridoxal
phosphate-bound serine. The proposed structural dissection
of the effects of each single mutation in the
betaA169L/betaC170W mutant would explain the very different
kinetics of this mutant and betaC170F.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.F.Dunn,
D.Niks,
H.Ngo,
T.R.Barends,
and
I.Schlichting
(2008).
Tryptophan synthase: the workings of a channeling nanomachine.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
33,
254-264.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.R.Barends,
M.F.Dunn,
and
I.Schlichting
(2008).
Tryptophan synthase, an allosteric molecular factory.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
12,
593-600.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Hioki,
K.Ogasahara,
S.J.Lee,
J.Ma,
M.Ishida,
Y.Yamagata,
Y.Matsuura,
M.Ota,
M.Ikeguchi,
S.Kuramitsu,
and
K.Yutani
(2004).
The crystal structure of the tryptophan synthase beta subunit from the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus. Investigation of stabilization factors.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
2624-2635.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

