 |
PDBsum entry 1dgd

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.64
- 2,2-dialkylglycine decarboxylase (pyruvate).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2,2-dialkylglycine + pyruvate + H+ = dialkyl ketone + L-alanine + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
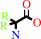 2,2-dialkylglycine
2,2-dialkylglycine
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 dialkyl ketone
dialkyl ketone
|
+
|
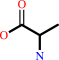 L-alanine
L-alanine
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
33:13561-13570
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
An alkali metal ion size-dependent switch in the active site structure of dialkylglycine decarboxylase.
|
|
E.Hohenester,
J.W.Keller,
J.N.Jansonius.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme dialkylglycine decarboxylase (DGD)
is activated by K+ and Rb+ ions, whereas Li+ and Na+ ions are inhibitory. A
binding site for alkali metal ions close to the active site (site 1) was
discovered in the crystal structure of DGD, and an exchange of K+ for Na+ at
this site was shown to affect the conformation of two active site residues
[Toney, M. D., Hohenester, E., Cowan, S. W., & Jansonius, J. N. (1993)
Science 261, 756-759]. We have investigated the effects of alkali metal ions on
DGD activity and have determined the crystal structures at 2.8 A resolution of
DGD with Li+ and Rb+ bound at site 1. Due to the weak scattering of the Li+ ion,
its position had to be modeled using information from small molecule structures.
A comparison of the DGD structures with Li+, Na+, K+, and Rb+ bound at site 1
reveals a striking correlation between active site structure and enzymatic
activity. The small, inhibitory ions Li+ and Na+ are accommodated by replacing
two protein-derived ligands of the larger, activating ions K+ and Rb+ by a
single water molecule. This actuates a two-state structural switch between
active and inactive enzyme that involves a concerted reorientation of the active
site residues Ser80 and Tyr301 and a small change in the quaternary structure of
the DGD tetramer. An important role of the essential K+ ion in both cofactor
binding and the organization of a catalytically competent active site structure
is proposed. In the structure of DGD with Rb+ bound at site 1, a second Rb+ ion
has partially replaced the structural Na+ ion at metal binding site 2 on the
surface of the DGD molecule, without significantly altering the protein
structure. In contrast to Na+, the Rb+ ion is bound with unfavorable geometry,
and it is proposed that the rigid site 2 structure results in a pronounced
selectivity for Na+ ions.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Berchanski,
B.Shapira,
and
M.Eisenstein
(2004).
Hydrophobic complementarity in protein-protein docking.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
130-142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Paiardini,
F.Bossa,
and
S.Pascarella
(2004).
Evolutionarily conserved regions and hydrophobic contacts at the superfamily level: The case of the fold-type I, pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
2992-3005.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Berchanski,
and
M.Eisenstein
(2003).
Construction of molecular assemblies via docking: modeling of tetramers with D2 symmetry.
|
| |
Proteins,
53,
817-829.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Lah,
J.Lah,
I.Zegers,
L.Wyns,
and
J.Messens
(2003).
Specific potassium binding stabilizes pI258 arsenate reductase from Staphylococcus aureus.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
24673-24679.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.K.Wang,
V.Tereshko,
P.Boccuni,
D.MacGrogan,
S.D.Nimer,
and
D.J.Patel
(2003).
Malignant brain tumor repeats: a three-leaved propeller architecture with ligand/peptide binding pockets.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
775-789.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Cheong,
J.C.Escalante-Semerena,
and
I.Rayment
(2002).
Structural studies of the L-threonine-O-3-phosphate decarboxylase (CobD) enzyme from Salmonella enterica: the apo, substrate, and product-aldimine complexes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9079-9089.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jin,
A.A.Guffanti,
D.H.Bechhofer,
and
T.A.Krulwich
(2002).
Tet(L) and tet(K) tetracycline-divalent metal/H+ antiporters: characterization of multiple catalytic modes and a mutagenesis approach to differences in their efflux substrate and coupling ion preferences.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
184,
4722-4732.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ahmad,
M.S.Akhtar,
and
V.Bhakuni
(2001).
Monovalent cation-induced conformational change in glucose oxidase leading to stabilization of the enzyme.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
1945-1955.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Toney
(2001).
Computational studies on nonenzymatic and enzymatic pyridoxal phosphate catalyzed decarboxylations of 2-aminoisobutyrate.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
1378-1384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhou,
X.Jin,
R.Medhekar,
X.Chen,
T.Dieckmann,
and
M.D.Toney
(2001).
Rapid kinetic and isotopic studies on dialkylglycine decarboxylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
1367-1377.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.C.Ngoka,
and
M.L.Gross
(2000).
Location of alkali metal binding sites in endothelin A selective receptor antagonists, cyclo(D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu) and cyclo(D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Ile-Leu), from multistep collisionally activated decompositions.
|
| |
J Mass Spectrom,
35,
265-276.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.W.Niu,
and
R.W.Meech
(2000).
Potassium inhibition of sodium-activated potassium (K(Na)) channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes.
|
| |
J Physiol,
526,
81-90.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Poupon,
F.Jebai,
G.Labesse,
F.Gros,
J.Thibault,
J.P.Mornon,
and
M.Krieger
(1999).
Structure modelling and site-directed mutagenesis of the rat aromatic L-amino acid pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent decarboxylase: a functional study.
|
| |
Proteins,
37,
191-203.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhou,
and
M.D.Toney
(1999).
pH studies on the mechanism of the pyridoxal phosphate-dependent dialkylglycine decarboxylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
311-320.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.N.Jansonius
(1998).
Structure, evolution and action of vitamin B6-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
8,
759-769.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.D.Schnackerz,
and
A.Mozzarelli
(1998).
Plasticity of the tryptophan synthase active site probed by 31P NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
33247-33253.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhou,
S.Kay,
and
M.D.Toney
(1998).
Coexisting kinetically distinguishable forms of dialkylglycine decarboxylase engendered by alkali metal ions.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
5761-5769.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Hirayama,
D.D.Loo,
and
E.M.Wright
(1997).
Cation effects on protein conformation and transport in the Na+/glucose cotransporter.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
2110-2115.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kaim,
F.Wehrle,
U.Gerike,
and
P.Dimroth
(1997).
Molecular basis for the coupling ion selectivity of F1F0 ATP synthases: probing the liganding groups for Na+ and Li+ in the c subunit of the ATP synthase from Propionigenium modestum.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
9185-9194.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Ramírez-Silva,
J.Oria,
A.Gómez-Puyou,
and
M.Tuena de Gómez-Puyou
(1997).
The contribution of water to the selectivity of pyruvate kinase for Na+ and K+.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
250,
583-589.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.MacKinnon,
and
D.A.Doyle
(1997).
Prokaryotes offer hope for potassium channel structural studies.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
4,
877-879.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Xiang,
J.C.Taylor,
and
G.D.Markham
(1996).
Monovalent cation activation and kinetic mechanism of inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
1435-1440.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.R.Guinto,
and
E.Di Cera
(1996).
Large heat capacity change in a protein-monovalent cation interaction.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
8800-8804.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Favre,
E.Moczydlowski,
and
L.Schild
(1996).
On the structural basis for ionic selectivity among Na+, K+, and Ca2+ in the voltage-gated sodium channel.
|
| |
Biophys J,
71,
3110-3125.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Rhee,
K.D.Parris,
S.A.Ahmed,
E.W.Miles,
and
D.R.Davies
(1996).
Exchange of K+ or Cs+ for Na+ induces local and long-range changes in the three-dimensional structure of the tryptophan synthase alpha2beta2 complex.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
4211-4221.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Di Cera
(1995).
Preferential interactions: it's as simple as 1, 2, 3.
|
| |
Biophys J,
68,
727-728.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.MacKinnon
(1995).
Pore loops: an emerging theme in ion channel structure.
|
| |
Neuron,
14,
889-892.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Ruvinov,
S.A.Ahmed,
P.McPhie,
and
E.W.Miles
(1995).
Monovalent cations partially repair a conformational defect in a mutant tryptophan synthase alpha 2 beta 2 complex (beta-E109A).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
17333-17338.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

