 |
PDBsum entry 1dff

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.88
- peptide deformylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide] + H2O = N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide] + formate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide]
|
+
|
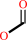 formate
formate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
36:13904-13909
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of the Escherichia coli peptide deformylase.
|
|
M.K.Chan,
W.Gong,
P.T.Rajagopalan,
B.Hao,
C.M.Tsai,
D.Pei.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Protein synthesis in bacteria involves the formylation and deformylation of the
N-terminal methionine. As eukaryotic organisms differ in their protein
biosynthetic mechanisms, peptide deformylase, the bacterial enzyme responsible
for deformylation, represents a potential target for antibiotic studies. Here we
report the crystallization and 2.9 A X-ray structure solution of the zinc
containing Escherichia coli peptide deformylase. While the primary sequence,
tertiary structure, and use of coordinated cysteine suggest that E. coli
deformylase belongs to a new subfamily of metalloproteases, the environment
around the metal appears to have strong geometric similarity to the active sites
of the thermolysin family. This suggests a possible similarity in their
hydrolytic mechanisms. Another important issue is the origin of the enzyme's
specificity for N-formylated over N-acetylated substrates. Based on the
structure, the specificity appears to result from hydrogen-bonding interactions
which orient the substrate for cleavage, and steric factors which physically
limit the size of the N-terminal carbonyl group.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Hernick,
S.G.Gattis,
J.E.Penner-Hahn,
and
C.A.Fierke
(2010).
Activation of Escherichia coli UDP-3-O-[(R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl]-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase by Fe2+ yields a more efficient enzyme with altered ligand affinity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
2246-2255.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Lin,
T.Hu,
J.Hu,
W.Yu,
C.Han,
J.Zhang,
G.Qin,
K.Yu,
F.Götz,
X.Shen,
H.Jiang,
and
D.Qu
(2010).
Characterization of peptide deformylase homologues from Staphylococcus epidermidis.
|
| |
Microbiology,
156,
3194-3202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Berg,
and
D.K.Srivastava
(2009).
Delineation of alternative conformational states in Escherichia coli peptide deformylase via thermodynamic studies for the binding of actinonin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
1584-1594.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.D.Amero,
D.W.Byerly,
C.A.McElroy,
A.Simmons,
and
M.P.Foster
(2009).
Ligand-induced changes in the structure and dynamics of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
7595-7607.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Escobar-Alvarez,
Y.Goldgur,
G.Yang,
O.Ouerfelli,
Y.Li,
and
D.A.Scheinberg
(2009).
Structure and activity of human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a novel cancer target.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
387,
1211-1228.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Berg,
S.Manokaran,
D.Eiler,
J.Kooren,
S.Mallik,
and
D.K.Srivastava
(2008).
Energetic rationale for an unexpected and abrupt reversal of guanidinium chloride-induced unfolding of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
17,
11-15.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.T.Nguyen,
J.C.Wu,
J.A.Boylan,
F.C.Gherardini,
and
D.Pei
(2007).
Zinc is the metal cofactor of Borrelia burgdorferi peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
468,
217-225.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Teo,
P.Thayalan,
D.Beer,
A.S.Yap,
M.Nanjundappa,
X.Ngew,
J.Duraiswamy,
S.Liung,
V.Dartois,
M.Schreiber,
S.Hasan,
M.Cynamon,
N.S.Ryder,
X.Yang,
B.Weidmann,
K.Bracken,
T.Dick,
and
K.Mukherjee
(2006).
Peptide deformylase inhibitors as potent antimycobacterial agents.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
50,
3665-3673.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Chen,
and
Z.Yuan
(2005).
Therapeutic potential of peptide deformylase inhibitors.
|
| |
Expert Opin Investig Drugs,
14,
1107-1116.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fieulaine,
C.Juillan-Binard,
A.Serero,
F.Dardel,
C.Giglione,
T.Meinnel,
and
J.L.Ferrer
(2005).
The crystal structure of mitochondrial (Type 1A) peptide deformylase provides clear guidelines for the design of inhibitors specific for the bacterial forms.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
42315-42324.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Zhou,
X.Song,
and
W.Gong
(2005).
Novel conformational states of peptide deformylase from pathogenic bacterium Leptospira interrogans: implications for population shift.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
42391-42396.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Lee,
Y.She,
M.J.Soskis,
C.P.Borella,
J.R.Gardner,
P.A.Hayes,
B.M.Dy,
M.L.Heaney,
M.R.Philips,
W.G.Bornmann,
F.M.Sirotnak,
and
D.A.Scheinberg
(2004).
Human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a new anticancer target of actinonin-based antibiotics.
|
| |
J Clin Invest,
114,
1107-1116.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kamo,
N.Kudo,
W.C.Lee,
H.Motoshima,
and
M.Tanokura
(2004).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of peptide deformylase from Thermus thermophilus HB8.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
1299-1300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.Smith,
C.M.Petit,
K.Aubart,
M.Smyth,
E.McManus,
J.Jones,
A.Fosberry,
C.Lewis,
M.Lonetto,
and
S.B.Christensen
(2003).
Structural variation and inhibitor binding in polypeptide deformylase from four different bacterial species.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
349-360.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kumar,
K.T.Nguyen,
S.Srivathsan,
B.Ornstein,
S.Turley,
I.Hirsh,
D.Pei,
and
W.G.Hol
(2002).
Crystals of peptide deformylase from Plasmodium falciparum reveal critical characteristics of the active site for drug design.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
357-367.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Hackbarth,
D.Z.Chen,
J.G.Lewis,
K.Clark,
J.B.Mangold,
J.A.Cramer,
P.S.Margolis,
W.Wang,
J.Koehn,
C.Wu,
S.Lopez,
G.Withers,
H.Gu,
E.Dunn,
R.Kulathila,
S.H.Pan,
W.L.Porter,
J.Jacobs,
J.Trias,
D.V.Patel,
B.Weidmann,
R.J.White,
and
Z.Yuan
(2002).
N-alkyl urea hydroxamic acids as a new class of peptide deformylase inhibitors with antibacterial activity.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
46,
2752-2764.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Byerly,
C.A.McElroy,
and
M.P.Foster
(2002).
Mapping the surface of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase by NMR with organic solvents.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1850-1853.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.T.Baldwin,
M.S.Harris,
A.W.Yem,
C.L.Wolfe,
A.F.Vosters,
K.A.Curry,
R.W.Murray,
J.H.Bock,
V.P.Marshall,
J.I.Cialdella,
M.H.Merchant,
G.Choi,
and
M.R.Deibel
(2002).
Crystal structure of type II peptide deformylase from Staphylococcus aureus.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
31163-31171.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Arndt,
B.Hao,
V.Ramakrishnan,
T.Cheng,
S.I.Chan,
and
M.K.Chan
(2002).
Crystal structure of a novel carboxypeptidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
215-224.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Li,
S.Ren,
and
W.Gong
(2002).
Cloning, high-level expression, purification and crystallization of peptide deformylase from Leptospira interrogans.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
846-848.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Giglione,
and
T.Meinnel
(2001).
Peptide deformylase as an emerging target for antiparasitic agents.
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
5,
41-57.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.McDevitt,
and
M.Rosenberg
(2001).
Exploiting genomics to discover new antibiotics.
|
| |
Trends Microbiol,
9,
611-617.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Pei
(2001).
Peptide deformylase: a target for novel antibiotics?
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
5,
23-40.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Clements,
R.P.Beckett,
A.Brown,
G.Catlin,
M.Lobell,
S.Palan,
W.Thomas,
M.Whittaker,
S.Wood,
S.Salama,
P.J.Baker,
H.F.Rodgers,
V.Barynin,
D.W.Rice,
and
M.G.Hunter
(2001).
Antibiotic activity and characterization of BB-3497, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
45,
563-570.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Hilgers,
and
M.L.Ludwig
(2001).
Crystal structure of the quorum-sensing protein LuxS reveals a catalytic metal site.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
11169-11174.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Margolis,
C.Hackbarth,
S.Lopez,
M.Maniar,
W.Wang,
Z.Yuan,
R.White,
and
J.Trias
(2001).
Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae to deformylase inhibitors is due to mutations in defB.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
45,
2432-2435.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Yuan,
J.Trias,
and
R.J.White
(2001).
Deformylase as a novel antibacterial target.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
6,
954-961.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Giglione,
M.Pierre,
and
T.Meinnel
(2000).
Peptide deformylase as a target for new generation, broad spectrum antimicrobial agents.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
36,
1197-1205.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Z.Chen,
D.V.Patel,
C.J.Hackbarth,
W.Wang,
G.Dreyer,
D.C.Young,
P.S.Margolis,
C.Wu,
Z.J.Ni,
J.Trias,
R.J.White,
and
Z.Yuan
(2000).
Actinonin, a naturally occurring antibacterial agent, is a potent deformylase inhibitor.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
1256-1262.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Huntington,
T.Yi,
Y.Wei,
and
D.Pei
(2000).
Synthesis and antibacterial activity of peptide deformylase inhibitors.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
4543-4551.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.T.Rajagopalan,
S.Grimme,
and
D.Pei
(2000).
Characterization of cobalt(II)-substituted peptide deformylase: function of the metal ion and the catalytic residue Glu-133.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
779-790.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Hao,
W.Gong,
P.T.Rajagopalan,
Y.Zhou,
D.Pei,
and
M.K.Chan
(1999).
Structural basis for the design of antibiotics targeting peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
4712-4719.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Makarova,
and
N.V.Grishin
(1999).
Thermolysin and mitochondrial processing peptidase: how far structure-functional convergence goes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
2537-2540.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Maroney
(1999).
Structure/function relationships in nickel metallobiochemistry.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
3,
188-199.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Meinnel,
L.Patiny,
S.Ragusa,
and
S.Blanquet
(1999).
Design and synthesis of substrate analogue inhibitors of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
4287-4295.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.J.Hu,
Y.Wei,
Y.Zhou,
P.T.Rajagopalan,
and
D.Pei
(1999).
Determination of substrate specificity for peptide deformylase through the screening of a combinatorial peptide library.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
643-650.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Becker,
I.Schlichting,
W.Kabsch,
D.Groche,
S.Schultz,
and
A.F.Wagner
(1998).
Iron center, substrate recognition and mechanism of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
5,
1053-1058.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Becker,
I.Schlichting,
W.Kabsch,
S.Schultz,
and
A.F.Wagner
(1998).
Structure of peptide deformylase and identification of the substrate binding site.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
11413-11416.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.T.Rajagopalan,
and
D.Pei
(1998).
Oxygen-mediated inactivation of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
22305-22310.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Born,
R.Zheng,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(1998).
Hydrolysis of N-succinyl-L,L-diaminopimelic acid by the Haemophilus influenzae dapE-encoded desuccinylase: metal activation, solvent isotope effects, and kinetic mechanism.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
10478-10487.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.J.Hu,
P.T.Rajagopalan,
and
D.Pei
(1998).
H-phosphonate derivatives as novel peptide deformylase inhibitors.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
8,
2479-2482.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

