 |
PDBsum entry 1bs7

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.88
- peptide deformylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide] + H2O = N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide] + formate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide]
|
+
|
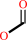 formate
formate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
273:11413-11416
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of peptide deformylase and identification of the substrate binding site.
|
|
A.Becker,
I.Schlichting,
W.Kabsch,
S.Schultz,
A.F.Wagner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Peptide deformylase is an essential metalloenzyme required for the removal of
the formyl group at the N terminus of nascent polypeptide chains in eubacteria.
The Escherichia coli enzyme uses Fe2+ and nearly retains its activity on
substitution of the metal ion by Ni2+. We have solved the structure of the Ni2+
enzyme at 1.9-A resolution by x-ray crystallography. Each of the three monomers
in the asymmetric unit contains one Ni2+ ion and, in close proximity, one
molecule of polyethylene glycol. Polyethylene glycol is shown to be a
competitive inhibitor with a KI value of 6 mM with respect to formylmethionine
under conditions similar to those used for crystallization. We have also solved
the structure of the inhibitor-free enzyme at 2.5-A resolution. The two
structures are identical within the estimated errors of the models. The hydrogen
bond network stabilizing the active site involves nearly all conserved amino
acid residues and well defined water molecules, one of which ligates to the
tetrahedrally coordinated Ni2+ ion.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Schematic representation of secondary structure
as analyzed by the program DSSP (14). First and last amino acid
residues in the helices and sheet strands are specified.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Fig. 5. Interaction scheme between the catalytic Ni2+
ion, water molecules W1, W2, W3, and amino acid residues in the
active site of peptide deformylase. With the exception of Leu-6,
all residues shown in the figure are well conserved. Bonds and
bond angles between the Ni2+ ion and its ligands are shown.
Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds with distances between
donor and acceptor atom given in Å. The second proton of
W1 and the distance to the side chain of Gln-50 are in brackets
to indicate the absence of a hydrogen bond.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(1998,
273,
11413-11416)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.Lin,
T.Hu,
J.Hu,
W.Yu,
C.Han,
J.Zhang,
G.Qin,
K.Yu,
F.Götz,
X.Shen,
H.Jiang,
and
D.Qu
(2010).
Characterization of peptide deformylase homologues from Staphylococcus epidermidis.
|
| |
Microbiology,
156,
3194-3202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.D.Amero,
D.W.Byerly,
C.A.McElroy,
A.Simmons,
and
M.P.Foster
(2009).
Ligand-induced changes in the structure and dynamics of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
7595-7607.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Escobar-Alvarez,
Y.Goldgur,
G.Yang,
O.Ouerfelli,
Y.Li,
and
D.A.Scheinberg
(2009).
Structure and activity of human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a novel cancer target.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
387,
1211-1228.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.T.Nguyen,
J.C.Wu,
J.A.Boylan,
F.C.Gherardini,
and
D.Pei
(2007).
Zinc is the metal cofactor of Borrelia burgdorferi peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
468,
217-225.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.McClerren,
S.Endsley,
J.L.Bowman,
N.H.Andersen,
Z.Guan,
J.Rudolph,
and
C.R.Raetz
(2005).
A slow, tight-binding inhibitor of the zinc-dependent deacetylase LpxC of lipid A biosynthesis with antibiotic activity comparable to ciprofloxacin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
44,
16574-16583.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.W.Aufhammer,
E.Warkentin,
U.Ermler,
C.H.Hagemeier,
R.K.Thauer,
and
S.Shima
(2005).
Crystal structure of methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase (Mer) in complex with coenzyme F420: Architecture of the F420/FMN binding site of enzymes within the nonprolyl cis-peptide containing bacterial luciferase family.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
1840-1849.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.Smith,
C.M.Petit,
K.Aubart,
M.Smyth,
E.McManus,
J.Jones,
A.Fosberry,
C.Lewis,
M.Lonetto,
and
S.B.Christensen
(2003).
Structural variation and inhibitor binding in polypeptide deformylase from four different bacterial species.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
349-360.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Mulrooney,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2003).
Nickel uptake and utilization by microorganisms.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
27,
239-261.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Hackbarth,
D.Z.Chen,
J.G.Lewis,
K.Clark,
J.B.Mangold,
J.A.Cramer,
P.S.Margolis,
W.Wang,
J.Koehn,
C.Wu,
S.Lopez,
G.Withers,
H.Gu,
E.Dunn,
R.Kulathila,
S.H.Pan,
W.L.Porter,
J.Jacobs,
J.Trias,
D.V.Patel,
B.Weidmann,
R.J.White,
and
Z.Yuan
(2002).
N-alkyl urea hydroxamic acids as a new class of peptide deformylase inhibitors with antibacterial activity.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
46,
2752-2764.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Byerly,
C.A.McElroy,
and
M.P.Foster
(2002).
Mapping the surface of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase by NMR with organic solvents.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1850-1853.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.A.Wabnitz,
and
J.A.Loo
(2002).
Drug screening of pharmaceutical discovery compounds by micro-size exclusion chromatography/mass spectrometry.
|
| |
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,
16,
85-91.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Li,
S.Ren,
and
W.Gong
(2002).
Cloning, high-level expression, purification and crystallization of peptide deformylase from Leptospira interrogans.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
846-848.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Giglione,
and
T.Meinnel
(2001).
Peptide deformylase as an emerging target for antiparasitic agents.
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
5,
41-57.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.McDevitt,
and
M.Rosenberg
(2001).
Exploiting genomics to discover new antibiotics.
|
| |
Trends Microbiol,
9,
611-617.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Pei
(2001).
Peptide deformylase: a target for novel antibiotics?
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
5,
23-40.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Clements,
R.P.Beckett,
A.Brown,
G.Catlin,
M.Lobell,
S.Palan,
W.Thomas,
M.Whittaker,
S.Wood,
S.Salama,
P.J.Baker,
H.F.Rodgers,
V.Barynin,
D.W.Rice,
and
M.G.Hunter
(2001).
Antibiotic activity and characterization of BB-3497, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
45,
563-570.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Margolis,
C.Hackbarth,
S.Lopez,
M.Maniar,
W.Wang,
Z.Yuan,
R.White,
and
J.Trias
(2001).
Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae to deformylase inhibitors is due to mutations in defB.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
45,
2432-2435.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Yuan,
J.Trias,
and
R.J.White
(2001).
Deformylase as a novel antibacterial target.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
6,
954-961.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Giglione,
M.Pierre,
and
T.Meinnel
(2000).
Peptide deformylase as a target for new generation, broad spectrum antimicrobial agents.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
36,
1197-1205.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Huntington,
T.Yi,
Y.Wei,
and
D.Pei
(2000).
Synthesis and antibacterial activity of peptide deformylase inhibitors.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
4543-4551.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.S.Margolis,
C.J.Hackbarth,
D.C.Young,
W.Wang,
D.Chen,
Z.Yuan,
R.White,
and
J.Trias
(2000).
Peptide deformylase in Staphylococcus aureus: resistance to inhibition is mediated by mutations in the formyltransferase gene.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
44,
1825-1831.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.T.Rajagopalan,
S.Grimme,
and
D.Pei
(2000).
Characterization of cobalt(II)-substituted peptide deformylase: function of the metal ion and the catalytic residue Glu-133.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
779-790.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Hao,
W.Gong,
P.T.Rajagopalan,
Y.Zhou,
D.Pei,
and
M.K.Chan
(1999).
Structural basis for the design of antibiotics targeting peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
4712-4719.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Maroney
(1999).
Structure/function relationships in nickel metallobiochemistry.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
3,
188-199.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Gouet,
B.Fabry,
V.Guillet,
C.Birck,
L.Mourey,
D.Kahn,
and
J.P.Samama
(1999).
Structural transitions in the FixJ receiver domain.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
1517-1526.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Meinnel,
L.Patiny,
S.Ragusa,
and
S.Blanquet
(1999).
Design and synthesis of substrate analogue inhibitors of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
4287-4295.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.J.Hu,
Y.Wei,
Y.Zhou,
P.T.Rajagopalan,
and
D.Pei
(1999).
Determination of substrate specificity for peptide deformylase through the screening of a combinatorial peptide library.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
643-650.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Becker,
I.Schlichting,
W.Kabsch,
D.Groche,
S.Schultz,
and
A.F.Wagner
(1998).
Iron center, substrate recognition and mechanism of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
5,
1053-1058.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.J.Hu,
P.T.Rajagopalan,
and
D.Pei
(1998).
H-phosphonate derivatives as novel peptide deformylase inhibitors.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
8,
2479-2482.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

