 |
PDBsum entry 1g2a

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The crystal structure of e.Coli peptide deformylase complexed with actinonin
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Polypeptide deformylase. Chain: a, b, c. Synonym: n-formylmethionylaminoacyl-tRNA deformylase, pdf, fms. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: def. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.75Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.191
|
R-free:
|
0.250
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.M.Clements,P.Beckett,A.Brown,C.Catlin,M.Lobell,S.Palan,W.Thomas, M.Whittaker,P.J.Baker,H.F.Rodgers,V.Barynin,D.W.Rice,M.G.Hunter
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.M.Clements
et al.
(2001).
Antibiotic activity and characterization of BB-3497, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
45,
563-570.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
18-Oct-00
|
Release date:
|
17-Oct-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A6K3
(DEF_ECOLI) -
Peptide deformylase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
169 a.a.
164 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.88
- peptide deformylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide] + H2O = N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide] + formate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide]
|
+
|
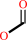 formate
formate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Antimicrob Agents Chemother
45:563-570
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Antibiotic activity and characterization of BB-3497, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor.
|
|
J.M.Clements,
R.P.Beckett,
A.Brown,
G.Catlin,
M.Lobell,
S.Palan,
W.Thomas,
M.Whittaker,
S.Wood,
S.Salama,
P.J.Baker,
H.F.Rodgers,
V.Barynin,
D.W.Rice,
M.G.Hunter.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Peptide deformylase (PDF) is an essential bacterial metalloenzyme which
deformylates the N-formylmethionine of newly synthesized polypeptides and as
such represents a novel target for antibacterial chemotherapy. To identify novel
PDF inhibitors, we screened a metalloenzyme inhibitor library and identified an
N-formyl-hydroxylamine derivative, BB-3497, and a related natural hydroxamic
acid antibiotic, actinonin, as potent and selective inhibitors of PDF. To
elucidate the interactions that contribute to the binding affinity of these
inhibitors, we determined the crystal structures of BB-3497 and actinonin bound
to Escherichia coli PDF at resolutions of 2.1 and 1.75 A, respectively. In both
complexes, the active-site metal atom was pentacoordinated by the side chains of
Cys 90, His 132, and His 136 and the two oxygen atoms of N-formyl-hydroxylamine
or hydroxamate. BB-3497 had activity against gram-positive bacteria, including
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant
Enterococcus faecalis, and activity against some gram-negative bacteria.
Time-kill analysis showed that the mode of action of BB-3497 was primarily
bacteriostatic. The mechanism of resistance was via mutations within the
formyltransferase gene, as previously described for actinonin. While actinonin
and its derivatives have not been used clinically because of their poor
pharmacokinetic properties, BB-3497 was shown to be orally bioavailable. A
single oral dose of BB-3497 given 1 h after intraperitoneal injection of S.
aureus Smith or methicillin-resistant S. aureus protected mice from infection
with median effective doses of 8 and 14 mg/kg of body weight, respectively.
These data validate PDF as a novel target for the design of a new generation of
antibacterial agents.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Berg,
Q.Yu,
S.Y.Qian,
M.K.Haldar,
and
D.K.Srivastava
(2010).
Solvent-assisted slow conversion of a dithiazole derivative produces a competitive inhibitor of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1804,
704-713.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Zhang,
J.Jia,
L.Meng,
W.Xu,
L.Tang,
and
J.Wang
(2010).
Synthesis and preliminary antibacterial evaluation of 2-butyl succinate-based hydroxamate derivatives containing isoxazole rings.
|
| |
Arch Pharm Res,
33,
831-842.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Berg,
and
D.K.Srivastava
(2009).
Delineation of alternative conformational states in Escherichia coli peptide deformylase via thermodynamic studies for the binding of actinonin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
1584-1594.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.D.Amero,
D.W.Byerly,
C.A.McElroy,
A.Simmons,
and
M.P.Foster
(2009).
Ligand-induced changes in the structure and dynamics of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
7595-7607.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Escobar-Alvarez,
Y.Goldgur,
G.Yang,
O.Ouerfelli,
Y.Li,
and
D.A.Scheinberg
(2009).
Structure and activity of human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a novel cancer target.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
387,
1211-1228.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Duroc,
C.Giglione,
and
T.Meinnel
(2009).
Mutations in three distinct loci cause resistance to peptide deformylase inhibitors in Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
53,
1673-1678.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.G.Dover,
A.Bhatt,
V.Bhowruth,
B.E.Willcox,
and
G.S.Besra
(2008).
New drugs and vaccines for drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections.
|
| |
Expert Rev Vaccines,
7,
481-497.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.M.McArdle,
and
R.J.Quinn
(2007).
Identification of protein fold topology shared between different folds inhibited by natural products.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
8,
788-798.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Antczak,
D.Shum,
S.Escobar,
B.Bassit,
E.Kim,
V.E.Seshan,
N.Wu,
G.Yang,
O.Ouerfelli,
Y.M.Li,
D.A.Scheinberg,
and
H.Djaballah
(2007).
High-throughput identification of inhibitors of human mitochondrial peptide deformylase.
|
| |
J Biomol Screen,
12,
521-535.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Galardon,
M.Giorgi,
and
I.Artaud
(2007).
Modeling the inhibition of peptide deformylase by hydroxamic acids: influence of the sulfur donor.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
1047-1052.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Bylander,
G.P.Bertenshaw,
G.L.Matters,
S.J.Hubbard,
and
J.S.Bond
(2007).
Human and mouse homo-oligomeric meprin A metalloendopeptidase: substrate and inhibitor specificities.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
388,
1163-1172.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Lee,
M.R.Doddareddy,
Y.S.Cho,
H.Choo,
H.Y.Koh,
J.H.Kang,
K.T.No,
and
A.N.Pae
(2007).
Comparative QSAR studies on peptide deformylase inhibitors.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
13,
543-558.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.T.Nguyen,
J.C.Wu,
J.A.Boylan,
F.C.Gherardini,
and
D.Pei
(2007).
Zinc is the metal cofactor of Borrelia burgdorferi peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
468,
217-225.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yoneyama,
and
R.Katsumata
(2006).
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria and its future for novel antibiotic development.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
70,
1060-1075.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Huang,
G.S.Van Aller,
A.N.Taylor,
J.J.Kerrigan,
W.S.Liu,
J.M.Trulli,
Z.Lai,
D.Holmes,
K.M.Aubart,
J.R.Brown,
and
M.Zalacain
(2006).
Phylogenomic and biochemical characterization of three Legionella pneumophila polypeptide deformylases.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
5249-5257.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Teo,
P.Thayalan,
D.Beer,
A.S.Yap,
M.Nanjundappa,
X.Ngew,
J.Duraiswamy,
S.Liung,
V.Dartois,
M.Schreiber,
S.Hasan,
M.Cynamon,
N.S.Ryder,
X.Yang,
B.Weidmann,
K.Bracken,
T.Dick,
and
K.Mukherjee
(2006).
Peptide deformylase inhibitors as potent antimycobacterial agents.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
50,
3665-3673.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Bogdanovich,
K.A.Smith,
C.Clark,
G.A.Pankuch,
G.Lin,
P.McGhee,
B.Dewasse,
and
P.C.Appelbaum
(2006).
Activity of LBM415 compared to those of 11 other agents against Haemophilus species.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
50,
2323-2329.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.R.Dean,
S.Narayan,
D.M.Daigle,
J.L.Dzink-Fox,
X.Puyang,
K.R.Bracken,
K.E.Dean,
B.Weidmann,
Z.Yuan,
R.Jain,
and
N.S.Ryder
(2005).
Role of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump in determining susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae to the novel peptide deformylase inhibitor LBM415.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
49,
3129-3135.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Chen,
and
Z.Yuan
(2005).
Therapeutic potential of peptide deformylase inhibitors.
|
| |
Expert Opin Investig Drugs,
14,
1107-1116.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Bidaut,
K.Suhre,
J.M.Claverie,
and
M.F.Ochs
(2005).
Bayesian decomposition analysis of bacterial phylogenomic profiles.
|
| |
Am J Pharmacogenomics,
5,
63-70.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Fonseca-Aten,
C.M.Salvatore,
A.Mejías,
A.M.Ríos,
S.Chávez-Bueno,
K.Katz,
A.M.Gómez,
G.H.McCracken,
and
R.D.Hardy
(2005).
Evaluation of LBM415 (NVP PDF-713), a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor, for treatment of experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
49,
4128-4136.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.R.Fritsche,
H.S.Sader,
R.Cleeland,
and
R.N.Jones
(2005).
Comparative antimicrobial characterization of LBM415 (NVP PDF-713), a new peptide deformylase inhibitor of clinical importance.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
49,
1468-1476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Chen,
C.Hackbarth,
Z.J.Ni,
C.Wu,
W.Wang,
R.Jain,
Y.He,
K.Bracken,
B.Weidmann,
D.V.Patel,
J.Trias,
R.J.White,
and
Z.Yuan
(2004).
Peptide deformylase inhibitors as antibacterial agents: identification of VRC3375, a proline-3-alkylsuccinyl hydroxamate derivative, by using an integrated combinatorial and medicinal chemistry approach.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
48,
250-261.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Azoulay-Dupuis,
J.Mohler,
and
J.P.Bédos
(2004).
Efficacy of BB-83698, a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor, in a mouse model of pneumococcal pneumonia.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
48,
80-85.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Yoon,
H.L.Kim,
S.K.Lee,
H.W.Kim,
H.W.Kim,
J.Y.Lee,
B.Mikami,
and
S.W.Suh
(2004).
Crystal structure of peptide deformylase from Staphylococcus aureus in complex with actinonin, a naturally occurring antibacterial agent.
|
| |
Proteins,
57,
639-642.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Robien,
K.T.Nguyen,
A.Kumar,
I.Hirsh,
S.Turley,
D.Pei,
and
W.G.Hol
(2004).
An improved crystal form of Plasmodium falciparum peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
1155-1163.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Lee,
Y.She,
M.J.Soskis,
C.P.Borella,
J.R.Gardner,
P.A.Hayes,
B.M.Dy,
M.L.Heaney,
M.R.Philips,
W.G.Bornmann,
F.M.Sirotnak,
and
D.A.Scheinberg
(2004).
Human mitochondrial peptide deformylase, a new anticancer target of actinonin-based antibiotics.
|
| |
J Clin Invest,
114,
1107-1116.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Gil,
F.J.Silva,
J.Peretó,
and
A.Moya
(2004).
Determination of the core of a minimal bacterial gene set.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
68,
518-537.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ramanathan-Girish,
J.McColm,
J.M.Clements,
P.Taupin,
S.Barrowcliffe,
J.Hevizi,
S.Safrin,
C.Moore,
G.Patou,
H.Moser,
A.Gadd,
U.Hoch,
V.Jiang,
D.Lofland,
and
K.W.Johnson
(2004).
Pharmacokinetics in animals and humans of a first-in-class peptide deformylase inhibitor.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
48,
4835-4842.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.R.Fritsche,
G.J.Moet,
and
R.N.Jones
(2004).
Commercial broth microdilution panel validation and reproducibility trials for NVP PDF-713 (LBM 415), a novel inhibitor of bacterial peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Clin Microbiol Infect,
10,
857-860.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Hughes
(2003).
Exploiting genomics, genetics and chemistry to combat antibiotic resistance.
|
| |
Nat Rev Genet,
4,
432-441.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Fu,
C.Dahlgren,
and
J.Bylund
(2003).
Subinhibitory concentrations of the deformylase inhibitor actinonin increase bacterial release of neutrophil-activating peptides: a new approach to antimicrobial chemotherapy.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
47,
2545-2550.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Miesel,
J.Greene,
and
T.A.Black
(2003).
Genetic strategies for antibacterial drug discovery.
|
| |
Nat Rev Genet,
4,
442-456.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kumar,
K.T.Nguyen,
S.Srivathsan,
B.Ornstein,
S.Turley,
I.Hirsh,
D.Pei,
and
W.G.Hol
(2002).
Crystals of peptide deformylase from Plasmodium falciparum reveal critical characteristics of the active site for drug design.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
357-367.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Hackbarth,
D.Z.Chen,
J.G.Lewis,
K.Clark,
J.B.Mangold,
J.A.Cramer,
P.S.Margolis,
W.Wang,
J.Koehn,
C.Wu,
S.Lopez,
G.Withers,
H.Gu,
E.Dunn,
R.Kulathila,
S.H.Pan,
W.L.Porter,
J.Jacobs,
J.Trias,
D.V.Patel,
B.Weidmann,
R.J.White,
and
Z.Yuan
(2002).
N-alkyl urea hydroxamic acids as a new class of peptide deformylase inhibitors with antibacterial activity.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
46,
2752-2764.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Byerly,
C.A.McElroy,
and
M.P.Foster
(2002).
Mapping the surface of Escherichia coli peptide deformylase by NMR with organic solvents.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1850-1853.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Blasi,
P.Braga,
M.Cazzola,
R.Cosentini,
and
P.Tarsia
(2002).
Therapies in development for community-acquired pneumonia.
|
| |
Expert Opin Investig Drugs,
11,
545-552.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.W.Kim,
B.W.Han,
H.J.Yoon,
J.K.Yang,
B.I.Lee,
H.H.Lee,
H.J.Ahn,
and
S.W.Suh
(2002).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of peptide deformylase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
1874-1875.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Wijkmans,
and
R.P.Beckett
(2002).
Combinatorial chemistry in anti-infectives research.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
7,
126-132.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Clements,
F.Coignard,
I.Johnson,
S.Chandler,
S.Palan,
A.Waller,
J.Wijkmans,
and
M.G.Hunter
(2002).
Antibacterial activities and characterization of novel inhibitors of LpxC.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
46,
1793-1799.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Harris,
J.H.Bock,
G.Choi,
J.S.Cialdella,
K.A.Curry,
M.R.Deibel,
E.J.Jacobsen,
V.P.Marshall,
R.W.Murray,
A.F.Vosters,
C.L.Wolfe,
A.W.Yem,
and
E.T.Baldwin
(2002).
Co-crystallization of Staphylococcus aureus peptide deformylase (PDF) with potent inhibitors.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
2153-2156.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Wise,
J.M.Andrews,
and
J.Ashby
(2002).
In vitro activities of peptide deformylase inhibitors against gram-positive pathogens.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
46,
1117-1118.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Li,
S.Ren,
and
W.Gong
(2002).
Cloning, high-level expression, purification and crystallization of peptide deformylase from Leptospira interrogans.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
846-848.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Giglione,
and
T.Meinnel
(2001).
Resistance to anti-peptide deformylase drugs.
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
5,
415-418.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Giglione,
and
T.Meinnel
(2001).
Peptide deformylase as an emerging target for antiparasitic agents.
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
5,
41-57.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.McDevitt,
and
M.Rosenberg
(2001).
Exploiting genomics to discover new antibiotics.
|
| |
Trends Microbiol,
9,
611-617.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Margolis,
C.Hackbarth,
S.Lopez,
M.Maniar,
W.Wang,
Z.Yuan,
R.White,
and
J.Trias
(2001).
Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae to deformylase inhibitors is due to mutations in defB.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
45,
2432-2435.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Yuan,
J.Trias,
and
R.J.White
(2001).
Deformylase as a novel antibacterial target.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
6,
954-961.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

