 |
PDBsum entry 1al8

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.3.15
- (S)-2-hydroxy-acid oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (2S)-2-hydroxycarboxylate + O2 = a 2-oxocarboxylate + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2S)-2-hydroxycarboxylate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
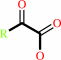 2-oxocarboxylate
2-oxocarboxylate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FMN)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
6:1009-1015
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Three-dimensional structures of glycolate oxidase with bound active-site inhibitors.
|
|
K.Stenberg,
Y.Lindqvist.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A key step in plant photorespiration, the oxidation of glycolate to glyoxylate,
is carried out by the peroxisomal flavoprotein glycolate oxidase (EC 1.1.3.15).
The three-dimensional structure of this alpha/beta barrel protein has been
refined to 2 A resolution (Lindqvist Y. 1989. J Mol Biol 209:151-166). FMN
dependent glycolate oxidase is a member of the family of alpha-hydroxy acid
oxidases. Here we describe the crystallization and structure determination of
two inhibitor complexes of the enzyme, TKP
(3-Decyl-2,5-dioxo-4-hydroxy-3-pyrroline) and TACA
(4-Carboxy-5-(1-pentyl)hexylsulfanyl-1,2,3-triazole). The structure of the TACA
complex has been refined to 2.6 A resolution and the TKP complex, solved with
molecular replacement, to 2.2 A resolution. The Rfree for the TACA and TKP
complexes are 24.2 and 25.1%, respectively. The overall structures are very
similar to the unliganded holoenzyme, but a closer examination of the active
site reveals differences in the positioning of the flavin isoalloxazine ring and
a displaced flexible loop in the TKP complex. The two inhibitors differ in
binding mode and hydrophobic interactions, and these differences are reflected
by the very different Ki values for the inhibitors, 16 nM for TACA and 4.8
microM for TKP. Implications of the structures of these enzyme-inhibitor
complexes for the model for substrate binding and catalysis proposed from the
holo-enzyme structure are discussed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Shirfule,
A.T.Sangamwar,
and
C.N.Khobragade
(2011).
Exploring glycolate oxidase (GOX) as an antiurolithic drug target: Molecular modeling and in vitro inhibitor study.
|
| |
Int J Biol Macromol,
49,
62-70.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Pennati,
and
G.Gadda
(2009).
Involvement of ionizable groups in catalysis of human liver glycolate oxidase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
31214-31222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Abat,
A.K.Mattoo,
and
R.Deswal
(2008).
S-nitrosylated proteins of a medicinal CAM plant Kalanchoe pinnata- ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity targeted for inhibition.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
2862-2872.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Murray,
R.P.Holmes,
and
W.T.Lowther
(2008).
Active site and loop 4 movements within human glycolate oxidase: implications for substrate specificity and drug design.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
2439-2449.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Sacquin-Mora,
E.Laforet,
and
R.Lavery
(2007).
Locating the active sites of enzymes using mechanical properties.
|
| |
Proteins,
67,
350-359.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Mattevi
(2006).
To be or not to be an oxidase: challenging the oxygen reactivity of flavoenzymes.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
31,
276-283.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.M.Moustafa,
S.Foster,
A.Y.Lyubimov,
and
A.Vrielink
(2006).
Crystal structure of LAAO from Calloselasma rhodostoma with an L-phenylalanine substrate: insights into structure and mechanism.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
364,
991.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Yang,
and
I.Bahar
(2005).
Coupling between catalytic site and collective dynamics: a requirement for mechanochemical activity of enzymes.
|
| |
Structure,
13,
893-904.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Laupitz,
S.Hecht,
S.Amslinger,
F.Zepeck,
J.Kaiser,
G.Richter,
N.Schramek,
S.Steinbacher,
R.Huber,
D.Arigoni,
A.Bacher,
W.Eisenreich,
and
F.Rohdich
(2004).
Biochemical characterization of Bacillus subtilis type II isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase, and phylogenetic distribution of isoprenoid biosynthesis pathways.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
2658-2669.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Bourne,
H.C.Kolb,
Z.Radić,
K.B.Sharpless,
P.Taylor,
and
P.Marchot
(2004).
Freeze-frame inhibitor captures acetylcholinesterase in a unique conformation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
1449-1454.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Binda,
R.T.Bossi,
S.Wakatsuki,
S.Arzt,
A.Coda,
B.Curti,
M.A.Vanoni,
and
A.Mattevi
(2000).
Cross-talk and ammonia channeling between active centers in the unexpected domain arrangement of glutamate synthase.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
1299-1308.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Mowat,
I.Beaudoin,
R.C.Durley,
J.D.Barton,
A.D.Pike,
Z.W.Chen,
G.A.Reid,
S.K.Chapman,
F.S.Mathews,
and
F.Lederer
(2000).
Kinetic and crystallographic studies on the active site Arg289Lys mutant of flavocytochrome b2 (yeast L-lactate dehydrogenase).
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
3266-3275.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Yorita,
T.Matsuoka,
H.Misaki,
and
V.Massey
(2000).
Interaction of two arginine residues in lactate oxidase with the enzyme flavin: conversion of FMN to 8-formyl-FMN.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
13039-13044.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.E.Lehoux,
and
B.Mitra
(1999).
(S)-Mandelate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida: mechanistic studies with alternate substrates and pH and kinetic isotope effects.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
5836-5848.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Douce,
and
M.Neuburger
(1999).
Biochemical dissection of photorespiration.
|
| |
Curr Opin Plant Biol,
2,
214-222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Mattevi,
M.A.Vanoni,
and
B.Curti
(1997).
Structure of D-amino acid oxidase: new insights from an old enzyme.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
7,
804-810.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Yorita,
K.Janko,
K.Aki,
S.Ghisla,
B.A.Palfey,
and
V.Massey
(1997).
On the reaction mechanism of L-lactate oxidase: quantitative structure-activity analysis of the reaction with para-substituted L-mandelates.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
94,
9590-9595.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

