 |
PDBsum entry 1ea0

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ea0
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.1.13
- glutamate synthase (NADPH).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 L-glutamate + NADP+ = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
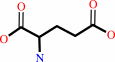 2
×
L-glutamate
2
×
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
L-glutamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD; FMN; Iron-sulfur
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
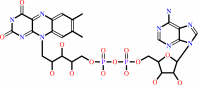 FAD
FAD
|
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FMN)
corresponds exactly
|
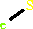 Iron-sulfur
Iron-sulfur
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
8:1299-1308
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Cross-talk and ammonia channeling between active centers in the unexpected domain arrangement of glutamate synthase.
|
|
C.Binda,
R.T.Bossi,
S.Wakatsuki,
S.Arzt,
A.Coda,
B.Curti,
M.A.Vanoni,
A.Mattevi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
INTRODUCTION: The complex iron-sulfur flavoprotein glutamate synthase catalyses
the reductive synthesis of L-glutamate from 2-oxoglutarate and L-glutamine, a
reaction in the plant and bacterial pathway for ammonia assimilation. The enzyme
functions through three distinct active centers carrying out L-glutamine
hydrolysis, conversion of 2-oxoglutarate into L-glutamate, and electron uptake
from an electron donor. RESULTS: The 3.0 A crystal structure of the dimeric 324
kDa core protein of a bacterial glutamate synthase was solved by the MAD method,
using the very weak anomalous signal of the two 3Fe-4S clusters present in the
asymmetric unit. The 1,472 amino acids of the monomer fold into a four-domain
architecture. The two catalytic domains have canonical Ntn-amidotransferase and
FMN binding (beta/alpha)8 barrel folds, respectively. The other two domains have
an unusual "cut (beta/alpha)8 barrel" topology and an unexpected novel
beta-helix structure. Channeling of the ammonia intermediate is brought about by
an internal tunnel of 31 A length, which runs from the site of L-glutamine
hydrolysis to the site of L-glutamate synthesis. CONCLUSIONS: The outstanding
property of glutamate synthase is the ability to coordinate the activity of its
various functional sites to avoid wasteful consumption of L-glutamine. The
structure reveals two polypeptide segments that connect the catalytic centers
and embed the ammonia tunnel, thus being ideally suited to function in
interdomain signaling. Depending on the enzyme redox and ligation states, these
signal-transducing elements may affect the active site geometry and control
ammonia diffusion through a gating mechanism.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Scheme of the Overall Reaction Catalyzed by the a
Subunit of A. brasilense GltS

|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2000,
8,
1299-1308)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.B.Dincturk,
R.Cunin,
and
H.Akce
(2011).
Expression and functional analysis of glutamate synthase small subunit-like proteins from archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii.
|
| |
Microbiol Res,
166,
294-303.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Glass,
F.Wolfe-Simon,
and
A.D.Anbar
(2009).
Coevolution of metal availability and nitrogen assimilation in cyanobacteria and algae.
|
| |
Geobiology,
7,
100-123.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Vanoni,
and
B.Curti
(2008).
Structure-function studies of glutamate synthases: a class of self-regulated iron-sulfur flavoenzymes essential for nitrogen assimilation.
|
| |
IUBMB Life,
60,
287-300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Cottevieille,
E.Larquet,
S.Jonic,
M.V.Petoukhov,
G.Caprini,
S.Paravisi,
D.I.Svergun,
M.A.Vanoni,
and
N.Boisset
(2008).
The subnanometer resolution structure of the glutamate synthase 1.2-MDa hexamer by cryoelectron microscopy and its oligomerization behavior in solution: functional implications.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
8237-8249.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Podar,
I.Anderson,
K.S.Makarova,
J.G.Elkins,
N.Ivanova,
M.A.Wall,
A.Lykidis,
K.Mavromatis,
H.Sun,
M.E.Hudson,
W.Chen,
C.Deciu,
D.Hutchison,
J.R.Eads,
A.Anderson,
F.Fernandes,
E.Szeto,
A.Lapidus,
N.C.Kyrpides,
M.H.Saier,
P.M.Richardson,
R.Rachel,
H.Huber,
J.A.Eisen,
E.V.Koonin,
M.Keller,
and
K.O.Stetter
(2008).
A genomic analysis of the archaeal system Ignicoccus hospitalis-Nanoarchaeum equitans.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
9,
R158.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Jonić,
C.O.Sorzano,
and
N.Boisset
(2008).
Comparison of single-particle analysis and electron tomography approaches: an overview.
|
| |
J Microsc,
232,
562-579.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.O.Sorzano,
S.Jonic,
M.Cottevieille,
E.Larquet,
N.Boisset,
and
S.Marco
(2007).
3D electron microscopy of biological nanomachines: principles and applications.
|
| |
Eur Biophys J,
36,
995.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kameya,
T.Ikeda,
M.Nakamura,
H.Arai,
M.Ishii,
and
Y.Igarashi
(2007).
A novel ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase from the hydrogen-oxidizing chemoautotrophic bacterium Hydrogenobacter thermophilus TK-6.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
2805-2812.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Cámara-Artigas,
M.Hirasawa,
D.B.Knaff,
M.Wang,
and
J.P.Allen
(2006).
Crystallization and structural analysis of GADPH from Spinacia oleracea in a new form.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
1087-1092.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.van Breukelen,
A.Barendregt,
A.J.Heck,
and
R.H.van den Heuvel
(2006).
Resolving stoichiometries and oligomeric states of glutamate synthase protein complexes with curve fitting and simulation of electrospray mass spectra.
|
| |
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,
20,
2490-2496.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Demir,
and
H.B.Dincturk
(2006).
Semi-anaerobic growth conditions are favoured by some Escherichia coli strains during heterologous expression of some archaeal proteins.
|
| |
Mol Biol Rep,
33,
59-63.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Suzuki,
and
D.B.Knaff
(2005).
Glutamate synthase: structural, mechanistic and regulatory properties, and role in the amino acid metabolism.
|
| |
Photosynth Res,
83,
191-217.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zhu,
J.W.Burgner,
E.Harms,
B.R.Belitsky,
and
J.L.Smith
(2005).
A new arrangement of (beta/alpha)8 barrels in the synthase subunit of PLP synthase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
27914-27923.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Vanoni,
L.Dossena,
R.H.van den Heuvel,
and
B.Curti
(2005).
Structure-function studies on the complex iron-sulfur flavoprotein glutamate synthase: the key enzyme of ammonia assimilation.
|
| |
Photosynth Res,
83,
219-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Coiro,
A.Di Nola,
M.A.Vanoni,
M.Aschi,
A.Coda,
B.Curti,
and
D.Roccatano
(2004).
Molecular dynamics simulation of the interaction between the complex iron-sulfur flavoprotein glutamate synthase and its substrates.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
2979-2991.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.H.Hefti,
J.Vervoort,
and
W.J.van Berkel
(2003).
Deflavination and reconstitution of flavoproteins.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
4227-4242.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.V.Petoukhov,
D.I.Svergun,
P.V.Konarev,
S.Ravasio,
R.H.van den Heuvel,
B.Curti,
and
M.A.Vanoni
(2003).
Quaternary structure of Azospirillum brasilense NADPH-dependent glutamate synthase in solution as revealed by synchrotron radiation x-ray scattering.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
29933-29939.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.H.van den Heuvel,
D.Ferrari,
R.T.Bossi,
S.Ravasio,
B.Curti,
M.A.Vanoni,
F.J.Florencio,
and
A.Mattevi
(2002).
Structural studies on the synchronization of catalytic centers in glutamate synthase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
24579-24583.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ravasio,
B.Curti,
and
M.A.Vanoni
(2001).
Determination of the midpoint potential of the FAD and FMN flavin cofactors and of the 3Fe-4S cluster of glutamate synthase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
5533-5541.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

