 |
PDBsum entry 5ikq

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5ikq
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The structure of meclofenamic acid bound to human cyclooxygenase-2
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Prostaglandin g/h synthase 2. Chain: a, b. Synonym: cyclooxygenase-2,cox-2,phs ii,prostaglandin h2 synthase 2, pghs-2,prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ptgs2, cox2. Expressed in: spodoptera frugiperda. Expression_system_taxid: 7108
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.41Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.173
|
R-free:
|
0.212
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
B.J.Orlando,M.G.Malkowski
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
B.J.Orlando
and
M.G.Malkowski
(2016).
Substrate-selective Inhibition of Cyclooxygeanse-2 by Fenamic Acid Derivatives Is Dependent on Peroxide Tone.
J Biol Chem,
291,
15069-15081.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
03-Mar-16
|
Release date:
|
25-May-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P35354
(PGH2_HUMAN) -
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
604 a.a.
551 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.99.1
- prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate + AH2 + 2 O2 = prostaglandin H2 + A + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate
|
+
|
AH2
|
+
|
 2
×
O2
2
×
O2
|
=
|
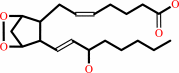 prostaglandin H2
prostaglandin H2
|
+
|
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 51.11% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
291:15069-15081
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate-selective Inhibition of Cyclooxygeanse-2 by Fenamic Acid Derivatives Is Dependent on Peroxide Tone.
|
|
B.J.Orlando,
M.G.Malkowski.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) catalyzes the oxygenation of arachidonic acid (AA) and
endocannabinoid substrates, placing the enzyme at a unique junction between the
eicosanoid and endocannabinoid signaling pathways. COX-2 is a sequence
homodimer, but the enzyme displays half-of-site reactivity, such that only one
monomer of the dimer is active at a given time. Certain rapid reversible,
competitive nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have been shown to
inhibit COX-2 in a substrate-selective manner, with the binding of inhibitor to
a single monomer sufficient to inhibit the oxygenation of endocannabinoids but
not arachidonic acid. The underlying mechanism responsible for
substrate-selective inhibition has remained elusive. We utilized structural and
biophysical methods to evaluate flufenamic acid, meclofenamic acid, mefenamic
acid, and tolfenamic acid for their ability to act as substrate-selective
inhibitors. Crystal structures of each drug in complex with human COX-2 revealed
that the inhibitor binds within the cyclooxygenase channel in an inverted
orientation, with the carboxylate group interacting with Tyr-385 and Ser-530 at
the top of the channel. Tryptophan fluorescence quenching, continuous-wave
electron spin resonance, and UV-visible spectroscopy demonstrate that flufenamic
acid, mefenamic acid, and tolfenamic acid are substrate-selective inhibitors
that bind rapidly to COX-2, quench tyrosyl radicals, and reduce higher oxidation
states of the heme moiety. Substrate-selective inhibition was attenuated by the
addition of the lipid peroxide 15-hydroperoxyeicosatertaenoic acid.
Collectively, these studies implicate peroxide tone as an important mechanistic
component of substrate-selective inhibition by flufenamic acid, mefenamic acid,
and tolfenamic acid.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

