 |
PDBsum entry 3k40

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of drosophila 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aromatic-l-amino-acid decarboxylase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: aadc, dopa decarboxylase, ddc. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Drosophila melanogaster. Fruit fly. Organism_taxid: 7227. Gene: cg10697, ddc. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Other_details: hypoderm isoform
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.75Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.198
|
R-free:
|
0.226
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Q.Han,H.Ding,H.Robinson,B.M.Christensen,J.Li
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Q.Han
et al.
(2010).
Crystal structure and substrate specificity of Drosophila 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylase.
Plos One,
5,
e8826.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-Oct-09
|
Release date:
|
02-Feb-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P05031
(DDC_DROME) -
Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase from Drosophila melanogaster
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
510 a.a.
448 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.28
- aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Dopa Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-dopa + H+ = dopamine + CO2
|
|
2.
|
5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan + H+ = serotonin + CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
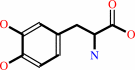 L-dopa
L-dopa
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
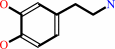 dopamine
dopamine
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.67% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
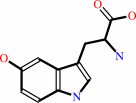 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan
5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 serotonin
serotonin
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
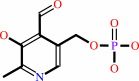 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Plos One
5:e8826
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure and substrate specificity of Drosophila 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylase.
|
|
Q.Han,
H.Ding,
H.Robinson,
B.M.Christensen,
J.Li.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylase (DDC), also known as
aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, catalyzes the decarboxylation of a number
of aromatic L-amino acids. Physiologically, DDC is responsible for the
production of dopamine and serotonin through the decarboxylation of
3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and 5-hydroxytryptophan, respectively. In insects,
both dopamine and serotonin serve as classical neurotransmitters,
neuromodulators, or neurohormones, and dopamine is also involved in insect
cuticle formation, eggshell hardening, and immune responses. PRINCIPAL FINDINGS:
In this study, we expressed a typical DDC enzyme from Drosophila melanogaster,
critically analyzed its substrate specificity and biochemical properties,
determined its crystal structure at 1.75 Angstrom resolution, and evaluated the
roles residues T82 and H192 play in substrate binding and enzyme catalysis
through site-directed mutagenesis of the enzyme. Our results establish that this
DDC functions exclusively on the production of dopamine and serotonin, with no
activity to tyrosine or tryptophan and catalyzes the formation of serotonin more
efficiently than dopamine. CONCLUSIONS: The crystal structure of Drosophila DDC
and the site-directed mutagenesis study of the enzyme demonstrate that T82 is
involved in substrate binding and that H192 is used not only for substrate
interaction, but for cofactor binding of drDDC as well. Through comparative
analysis, the results also provide insight into the structure-function
relationship of other insect DDC-like proteins.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

