 |
PDBsum entry 2qv7

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.107
- diacylglycerol kinase (ATP).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + ATP = a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
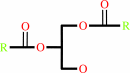 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
16:1036-1046
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Analysis of the Staphylococcus aureus DgkB structure reveals a common catalytic mechanism for the soluble diacylglycerol kinases.
|
|
D.J.Miller,
A.Jerga,
C.O.Rock,
S.W.White.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Soluble diacylglycerol (DAG) kinases function as regulators of diacylglycerol
metabolism in cell signaling and intermediary metabolism. We report the
structure of a DAG kinase, DgkB from Staphylococcus aureus, both as the free
enzyme and in complex with ADP. The molecule is a tight homodimer, and each
monomer comprises two domains with the catalytic center located within the
interdomain cleft. Two distinctive features of DkgB are a structural Mg2+ site
and an associated Asp*water*Mg2+ network that extends toward the active site
locale. Site-directed mutagenesis revealed that these features play important
roles in the catalytic mechanism. The key active site residues and the
components of the Asp*water*Mg2+ network are conserved in the catalytic cores of
the mammalian signaling DAG kinases, indicating that these enzymes use the same
mechanism and have similar structures as DgkB.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Overall Structure of DgkB and a Close-Up of the
Nucleotide-Binding Site
(A) Cartoon diagram of the DgkB
monomer in the asymmetric unit. α helices are gray, and β
strands and loops are green. ADP carbons and Mg1 (sphere) are
cyan. Secondary structure elements are labeled. Disordered
residues 145–157 are absent in the final model and are
indicated with a broken line. The predicted locations of the
insertions in human diacylglycerol kinases (see Figure 2) are
labeled IN1–3.
(B) Stereo cartoon of the YegS structure
(PDB code: 2BON, chain A) superimposed on DgkB. The orientations
of domains 1 and 2 differ slightly in the two structures, and,
to highlight their structural similarity, each domain of YegS
was superimposed independently onto the DgkB structure. DgkB is
colored as shown in (A), and YegS is tan. Disordered residues
are indicated with broken lines. Significant differences reside
in the predicted DgkB substrate-binding region (β8-α6 loop),
which is highlighted in bright green, and the corresponding YegS
region is brown.
(C) Stereo close-up view of the DgkB
nucleotide-binding site with omit electron density for ADP
contoured to 3σ. Bound waters are shown as red spheres.
Hydrogen bonds are indicated by broken lines.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Properties of the DgkB Dimer
(A)
Gel-filtration chromatography of DgkB with a Sephadex-200 10/300
GL column. DgkB eluted with a Stokes radius (Rs) of 41 Å
based on calibration of the column with eight protein standards
(left inset). SDS gel electrophoresis (right inset) showed the
presence of a single protein with an apparent subunit molecular
weight of 42 kDa. The molecular weight calculated from the DNA
sequence was 37,333.
(B) Sedimentation velocity analysis of
DgkB. The protein characteristics determined from the velocity
sedimentation experiment are shown as an inset in the figure.
(C) The structure of the DgkB dimer. The green monomer is
the observed molecule in the asymmetric unit shown in Figure 1A,
tilted backward 45°. The sand-colored monomer is generated
by two-fold symmetry. ADP carbons and Mg1 (sphere) are cyan.
(D) The conserved DgkB dimerization interface. Only the
residues involved in salt bridges are shown as sticks. Hydrogen
bonds are indicated with broken lines.
(E) A representative
sequence alignment of the amino-terminal residues in known
bacterial DgkBs involved in dimer formation. Residues
responsible for salt bridges and van der Waals interactions are
indicated with an “x” and black spheres, respectively.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2008,
16,
1036-1046)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Pitson
(2011).
Regulation of sphingosine kinase and sphingolipid signaling.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
36,
97.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ramboarina,
J.A.Garnett,
M.Zhou,
Y.Li,
Z.Peng,
J.D.Taylor,
W.C.Lee,
A.Bodey,
J.W.Murray,
Y.Alguel,
J.Bergeron,
B.Bardiaux,
E.Sawyer,
R.Isaacson,
C.Tagliaferri,
E.Cota,
M.Nilges,
P.Simpson,
T.Ruiz,
H.Wu,
and
S.Matthews
(2010).
Structural insights into serine-rich fimbriae from Gram-positive bacteria.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
32446-32457.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Jerga,
D.J.Miller,
S.W.White,
and
C.O.Rock
(2009).
Molecular determinants for interfacial binding and conformational change in a soluble diacylglycerol kinase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
7246-7254.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.M.Raben,
and
B.W.Wattenberg
(2009).
Signaling at the membrane interface by the DGK/SK enzyme family.
|
| |
J Lipid Res,
50,
S35-S39.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.D.Van Horn,
H.J.Kim,
C.D.Ellis,
A.Hadziselimovic,
E.S.Sulistijo,
M.D.Karra,
C.Tian,
F.D.Sönnichsen,
and
C.R.Sanders
(2009).
Solution nuclear magnetic resonance structure of membrane-integral diacylglycerol kinase.
|
| |
Science,
324,
1726-1729.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

