 |
PDBsum entry 1dyn

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signal transduction protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1dyn
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.6.5.5
- dynamin GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 GTP
GTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
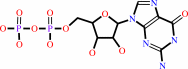 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Cell
79:199-209
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of the pleckstrin homology domain from human dynamin.
|
|
K.M.Ferguson,
M.A.Lemmon,
J.Schlessinger,
P.B.Sigler.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The X-ray crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain from human
dynamin has been refined to 2.2 A resolution. A seven-stranded beta sandwich of
two orthogonal antiparallel beta sheets is closed at one corner by a C-terminal
alpha helix. Opposite this helix are the three loops that vary most among PH
domains. The basic fold is very similar to that of two other PH domains recently
determined by nuclear magnetic resonance, confirming that PH domain with known
structure is electrostatically polarized, with the three variable loops forming
a positively charged surface. This surface includes the position of the X-linked
immunodeficiency mutation in the Btk PH domain and may serve as a ligand-binding
surface.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Ferguson,
and
P.De Camilli
(2012).
Dynamin, a membrane-remodelling GTPase.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
13,
75-88.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Manford,
T.Xia,
A.K.Saxena,
C.Stefan,
F.Hu,
S.D.Emr,
and
Y.Mao
(2010).
Crystal structure of the yeast Sac1: implications for its phosphoinositide phosphatase function.
|
| |
EMBO J,
29,
1489-1498.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Kenniston,
and
M.A.Lemmon
(2010).
Dynamin GTPase regulation is altered by PH domain mutations found in centronuclear myopathy patients.
|
| |
EMBO J,
29,
3054-3067.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Xu,
A.Bateman,
R.D.Finn,
P.Abdubek,
T.Astakhova,
H.L.Axelrod,
C.Bakolitsa,
D.Carlton,
C.Chen,
H.J.Chiu,
M.Chiu,
T.Clayton,
D.Das,
M.C.Deller,
L.Duan,
K.Ellrott,
D.Ernst,
C.L.Farr,
J.Feuerhelm,
J.C.Grant,
A.Grzechnik,
G.W.Han,
L.Jaroszewski,
K.K.Jin,
H.E.Klock,
M.W.Knuth,
P.Kozbial,
S.S.Krishna,
A.Kumar,
D.Marciano,
D.McMullan,
M.D.Miller,
A.T.Morse,
E.Nigoghossian,
A.Nopakun,
L.Okach,
C.Puckett,
R.Reyes,
C.L.Rife,
N.Sefcovic,
H.J.Tien,
C.B.Trame,
H.van den Bedem,
D.Weekes,
T.Wooten,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
M.A.Elsliger,
A.M.Deacon,
A.Godzik,
S.A.Lesley,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2010).
Bacterial pleckstrin homology domains: a prokaryotic origin for the PH domain.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
396,
31-46.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Huang,
and
K.Sauer
(2010).
Lipid signaling in T-cell development and function.
|
| |
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol,
2,
a002428.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Carland,
and
T.Nelson
(2009).
CVP2- and CVL1-mediated phosphoinositide signaling as a regulator of the ARF GAP SFC/VAN3 in establishment of foliar vein patterns.
|
| |
Plant J,
59,
895-907.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.H.Low,
C.Sachse,
L.A.Amos,
and
J.Löwe
(2009).
Structure of a bacterial dynamin-like protein lipid tube provides a mechanism for assembly and membrane curving.
|
| |
Cell,
139,
1342-1352.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Heymann,
and
J.E.Hinshaw
(2009).
Dynamins at a glance.
|
| |
J Cell Sci,
122,
3427-3431.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.McKenna,
and
E.M.Ostap
(2009).
Kinetics of the interaction of myo1c with phosphoinositides.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
28650-28659.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Lian,
Y.Wang,
M.Flick,
J.Choi,
E.W.Scott,
J.Degen,
M.A.Lemmon,
and
C.S.Abrams
(2009).
Loss of pleckstrin defines a novel pathway for PKC-mediated exocytosis.
|
| |
Blood,
113,
3577-3584.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Ramachandran,
T.J.Pucadyil,
Y.W.Liu,
S.Acharya,
M.Leonard,
V.Lukiyanchuk,
and
S.L.Schmid
(2009).
Membrane insertion of the pleckstrin homology domain variable loop 1 is critical for dynamin-catalyzed vesicle scission.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
20,
4630-4639.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Pucadyil,
and
S.L.Schmid
(2009).
Conserved functions of membrane active GTPases in coated vesicle formation.
|
| |
Science,
325,
1217-1220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kawasaki,
S.Tsuji,
M.Sagara,
K.Echizen,
Y.Shibata,
and
T.Akiyama
(2009).
Adenomatous polyposis coli and Asef function downstream of hepatocyte growth factor and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
22436-22443.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Ben Rebeh,
Z.Benzina,
H.Dhouib,
I.Hadjamor,
M.Amyere,
L.Ayadi,
K.Turki,
B.Hammami,
N.Kmiha,
H.Kammoun,
B.Hakim,
I.Charfedine,
M.Vikkula,
A.Ghorbel,
H.Ayadi,
and
S.Masmoudi
(2008).
Identification of candidate regions for a novel Usher syndrome type II locus.
|
| |
Mol Vis,
14,
1719-1726.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Osawa,
S.Funamoto,
M.Nobuhara,
S.Wada-Kakuda,
M.Shimojo,
S.Yagishita,
and
Y.Ihara
(2008).
Phosphoinositides suppress gamma-secretase in both the detergent-soluble and -insoluble states.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
19283-19292.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Mears,
P.Ray,
and
J.E.Hinshaw
(2007).
A corkscrew model for dynamin constriction.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
1190-1202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Hokanson,
and
E.M.Ostap
(2006).
Myo1c binds tightly and specifically to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
3118-3123.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.H.Low,
and
J.Löwe
(2006).
A bacterial dynamin-like protein.
|
| |
Nature,
444,
766-769.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Hurley
(2006).
Membrane binding domains.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1761,
805-811.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Wen,
J.Yan,
and
M.Zhang
(2006).
Structural characterization of the split pleckstrin homology domain in phospholipase C-gamma1 and its interaction with TRPC3.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
12060-12068.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Wang,
X.N.Du,
Q.Z.Jia,
and
H.L.Zhang
(2005).
Binding of PLCdelta1PH-GFP to PtdIns(4,5)P2 prevents inhibition of phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 by neomycin.
|
| |
Acta Pharmacol Sin,
26,
1485-1491.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Yan,
W.Wen,
W.Xu,
J.F.Long,
M.E.Adams,
S.C.Froehner,
and
M.Zhang
(2005).
Structure of the split PH domain and distinct lipid-binding properties of the PH-PDZ supramodule of alpha-syntrophin.
|
| |
EMBO J,
24,
3985-3995.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Komander,
A.Fairservice,
M.Deak,
G.S.Kular,
A.R.Prescott,
C.Peter Downes,
S.T.Safrany,
D.R.Alessi,
and
D.M.van Aalten
(2004).
Structural insights into the regulation of PDK1 by phosphoinositides and inositol phosphates.
|
| |
EMBO J,
23,
3918-3928.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.van Leeuwen,
L.Okrész,
L.Bögre,
and
T.Munnik
(2004).
Learning the lipid language of plant signalling.
|
| |
Trends Plant Sci,
9,
378-384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.E.Cozier,
D.Bouyoucef,
and
P.J.Cullen
(2003).
Engineering the phosphoinositide-binding profile of a class I pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
39489-39496.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.J.Smith,
N.Nassar,
A.Bretscher,
R.A.Cerione,
and
P.A.Karplus
(2003).
Structure of the active N-terminal domain of Ezrin. Conformational and mobility changes identify keystone interactions.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
4949-4956.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Guo,
F.Philip,
and
S.Scarlata
(2003).
The Pleckstrin homology domains of phospholipases C-beta and -delta confer activation through a common site.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
29995-30004.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Xiao,
T.Yin,
X.Y.Wang,
T.Uchida,
J.Chung,
M.F.White,
and
Y.C.Yang
(2002).
Specificity of interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain superfamily cytokines is mediated by insulin receptor substrate-dependent pathway.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
8091-8098.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Várnai,
X.Lin,
S.B.Lee,
G.Tuymetova,
T.Bondeva,
A.Spät,
S.G.Rhee,
G.Hajnóczky,
and
T.Balla
(2002).
Inositol lipid binding and membrane localization of isolated pleckstrin homology (PH) domains. Studies on the PH domains of phospholipase C delta 1 and p130.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
27412-27422.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Vanhaesebroeck,
S.J.Leevers,
K.Ahmadi,
J.Timms,
R.Katso,
P.C.Driscoll,
R.Woscholski,
P.J.Parker,
and
M.D.Waterfield
(2001).
Synthesis and function of 3-phosphorylated inositol lipids.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
70,
535-602.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Zhang,
and
J.E.Hinshaw
(2001).
Three-dimensional reconstruction of dynamin in the constricted state.
|
| |
Nat Cell Biol,
3,
922-926.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.V.Carman,
L.S.Barak,
C.Chen,
L.Y.Liu-Chen,
J.J.Onorato,
S.P.Kennedy,
M.G.Caron,
and
J.L.Benovic
(2000).
Mutational analysis of Gbetagamma and phospholipid interaction with G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
10443-10452.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Wakeham,
J.A.Ybe,
F.M.Brodsky,
and
P.K.Hwang
(2000).
Molecular structures of proteins involved in vesicle coat formation.
|
| |
Traffic,
1,
393-398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Beneken,
J.C.Tu,
B.Xiao,
M.Nuriya,
J.P.Yuan,
P.F.Worley,
and
D.J.Leahy
(2000).
Structure of the Homer EVH1 domain-peptide complex reveals a new twist in polyproline recognition.
|
| |
Neuron,
26,
143-154.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Hinshaw
(2000).
Dynamin and its role in membrane fission.
|
| |
Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol,
16,
483-519.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Hurley,
and
S.Misra
(2000).
Signaling and subcellular targeting by membrane-binding domains.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
29,
49-79.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Ferguson,
J.M.Kavran,
V.G.Sankaran,
E.Fournier,
S.J.Isakoff,
E.Y.Skolnik,
and
M.A.Lemmon
(2000).
Structural basis for discrimination of 3-phosphoinositides by pleckstrin homology domains.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
6,
373-384.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ogasawara,
S.C.Kim,
R.Adamik,
A.Togawa,
V.J.Ferrans,
K.Takeda,
M.Kirby,
J.Moss,
and
M.Vaughan
(2000).
Similarities in function and gene structure of cytohesin-4 and cytohesin-1, guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
3221-3230.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Blomberg,
E.Baraldi,
M.Sattler,
M.Saraste,
and
M.Nilges
(2000).
Structure of a PH domain from the C. elegans muscle protein UNC-89 suggests a novel function.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
1079-1087.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Santoni,
S.Kieffer,
D.Desclaux,
F.Masson,
and
T.Rabilloud
(2000).
Membrane proteomics: use of additive main effects with multiplicative interaction model to classify plasma membrane proteins according to their solubility and electrophoretic properties.
|
| |
Electrophoresis,
21,
3329-3344.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Ma,
and
C.S.Abrams
(1999).
Pleckstrin induces cytoskeletal reorganization via a Rac-dependent pathway.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
28730-28735.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Galetic,
M.Andjelkovic,
R.Meier,
D.Brodbeck,
J.Park,
and
B.A.Hemmings
(1999).
Mechanism of protein kinase B activation by insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 revealed by specific inhibitors of phosphoinositide 3-kinase--significance for diabetes and cancer.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
82,
409-425.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Hinshaw
(1999).
Dynamin spirals.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
9,
260-267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Yao,
P.Janmey,
L.G.Frigeri,
W.Han,
J.Fujita,
Y.Kawakami,
J.R.Apgar,
and
T.Kawakami
(1999).
Pleckstrin homology domains interact with filamentous actin.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
19752-19761.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Achiriloaie,
B.Barylko,
and
J.P.Albanesi
(1999).
Essential role of the dynamin pleckstrin homology domain in receptor-mediated endocytosis.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
19,
1410-1415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Marsh,
and
H.T.McMahon
(1999).
The structural era of endocytosis.
|
| |
Science,
285,
215-220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Movilla,
and
X.R.Bustelo
(1999).
Biological and regulatory properties of Vav-3, a new member of the Vav family of oncoproteins.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
19,
7870-7885.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ahn,
S.Maudsley,
L.M.Luttrell,
R.J.Lefkowitz,
and
Y.Daaka
(1999).
Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of dynamin is required for beta2-adrenergic receptor internalization and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
1185-1188.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Pawelczyk,
and
A.Matecki
(1999).
Phospholipase C-delta3 binds with high specificity to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidic acid in bilayer membranes.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
262,
291-298.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Vallis,
P.Wigge,
B.Marks,
P.R.Evans,
and
H.T.McMahon
(1999).
Importance of the pleckstrin homology domain of dynamin in clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
9,
257-260.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Barylko,
D.Binns,
K.M.Lin,
M.A.Atkinson,
D.M.Jameson,
H.L.Yin,
and
J.P.Albanesi
(1998).
Synergistic activation of dynamin GTPase by Grb2 and phosphoinositides.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
3791-3797.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Parent,
B.J.Blacklock,
W.M.Froehlich,
D.B.Murphy,
and
P.N.Devreotes
(1998).
G protein signaling events are activated at the leading edge of chemotactic cells.
|
| |
Cell,
95,
81-91.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Klein,
A.Lee,
D.W.Frank,
M.S.Marks,
and
M.A.Lemmon
(1998).
The pleckstrin homology domains of dynamin isoforms require oligomerization for high affinity phosphoinositide binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
27725-27733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Fushman,
T.Najmabadi-Haske,
S.Cahill,
J.Zheng,
H.LeVine,
and
D.Cowburn
(1998).
The solution structure and dynamics of the pleckstrin homology domain of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1). A binding partner of Gbetagamma subunits.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
2835-2843.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Burks,
J.Wang,
H.Towery,
O.Ishibashi,
D.Lowe,
H.Riedel,
and
M.F.White
(1998).
IRS pleckstrin homology domains bind to acidic motifs in proteins.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
31061-31067.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Pitcher,
N.J.Freedman,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1998).
G protein-coupled receptor kinases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
67,
653-692.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Kavran,
D.E.Klein,
A.Lee,
M.Falasca,
S.J.Isakoff,
E.Y.Skolnik,
and
M.A.Lemmon
(1998).
Specificity and promiscuity in phosphoinositide binding by pleckstrin homology domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
30497-30508.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hirata,
T.Kanematsu,
H.Takeuchi,
and
H.Yagisawa
(1998).
Pleckstrin homology domain as an inositol compound binding module.
|
| |
Jpn J Pharmacol,
76,
255-263.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Bottomley,
K.Salim,
and
G.Panayotou
(1998).
Phospholipid-binding protein domains.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1436,
165-183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Rebecchi,
and
S.Scarlata
(1998).
Pleckstrin homology domains: a common fold with diverse functions.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
27,
503-528.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Várnai,
and
T.Balla
(1998).
Visualization of phosphoinositides that bind pleckstrin homology domains: calcium- and agonist-induced dynamic changes and relationship to myo-[3H]inositol-labeled phosphoinositide pools.
|
| |
J Cell Biol,
143,
501-510.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Alberti
(1998).
A phosphoinositide-binding sequence is shared by PH domain target molecules--a model for the binding of PH domains to proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
31,
1-9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Schmid,
M.A.McNiven,
and
P.De Camilli
(1998).
Dynamin and its partners: a progress report.
|
| |
Curr Opin Cell Biol,
10,
504-512.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kamimoto,
Y.Nagai,
H.Onogi,
Y.Muro,
T.Wakabayashi,
and
M.Hagiwara
(1998).
Dymple, a novel dynamin-like high molecular weight GTPase lacking a proline-rich carboxyl-terminal domain in mammalian cells.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
1044-1051.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Liu,
H.Wang,
M.Eberstadt,
A.Schnuchel,
E.T.Olejniczak,
R.P.Meadows,
J.M.Schkeryantz,
D.A.Janowick,
J.E.Harlan,
E.A.Harris,
D.E.Staunton,
and
S.W.Fesik
(1998).
NMR structure and mutagenesis of the N-terminal Dbl homology domain of the nucleotide exchange factor Trio.
|
| |
Cell,
95,
269-277.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yoon,
K.R.Pitts,
S.Dahan,
and
M.A.McNiven
(1998).
A novel dynamin-like protein associates with cytoplasmic vesicles and tubules of the endoplasmic reticulum in mammalian cells.
|
| |
J Cell Biol,
140,
779-793.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.August,
A.Sadra,
B.Dupont,
and
H.Hanafusa
(1997).
Src-induced activation of inducible T cell kinase (ITK) requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and the Pleckstrin homology domain of inducible T cell kinase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
94,
11227-11232.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Ma,
L.F.Brass,
and
C.S.Abrams
(1997).
Pleckstrin associates with plasma membranes and induces the formation of membrane projections: requirements for phosphorylation and the NH2-terminal PH domain.
|
| |
J Cell Biol,
136,
1071-1079.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.K.Saha,
S.K.Curtis,
L.B.Vogler,
and
M.Vihinen
(1997).
Molecular and structural characterization of five novel mutations in the Bruton's tyrosine kinase gene from patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia.
|
| |
Mol Med,
3,
477-485.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.R.Artalejo,
M.A.Lemmon,
J.Schlessinger,
and
H.C.Palfrey
(1997).
Specific role for the PH domain of dynamin-1 in the regulation of rapid endocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells.
|
| |
EMBO J,
16,
1565-1574.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Clapham,
and
E.J.Neer
(1997).
G protein beta gamma subunits.
|
| |
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,
37,
167-203.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Burks,
S.Pons,
H.Towery,
J.Smith-Hall,
M.G.Myers,
L.Yenush,
and
M.F.White
(1997).
Heterologous pleckstrin homology domains do not couple IRS-1 to the insulin receptor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
27716-27721.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Tall,
G.Dormán,
P.Garcia,
L.Runnels,
S.Shah,
J.Chen,
A.Profit,
Q.M.Gu,
A.Chaudhary,
G.D.Prestwich,
and
M.J.Rebecchi
(1997).
Phosphoinositide binding specificity among phospholipase C isozymes as determined by photo-cross-linking to novel substrate and product analogs.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
7239-7248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.C.Lin,
B.Barylko,
M.Achiriloaie,
and
J.P.Albanesi
(1997).
Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate-dependent activation of dynamins I and II lacking the proline/arginine-rich domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
25999-26004.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.P.Whitehead,
S.Campbell,
K.L.Rossman,
and
C.J.Der
(1997).
Dbl family proteins.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1332,
F1-23.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zheng,
R.H.Chen,
S.Corblan-Garcia,
S.M.Cahill,
D.Bar-Sagi,
and
D.Cowburn
(1997).
The solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of human SOS1. A possible structural role for the sequential association of diffuse B cell lymphoma and pleckstrin homology domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
30340-30344.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Rameh,
A.Arvidsson,
K.L.Carraway,
A.D.Couvillon,
G.Rathbun,
A.Crompton,
B.VanRenterghem,
M.P.Czech,
K.S.Ravichandran,
S.J.Burakoff,
D.S.Wang,
C.S.Chen,
and
L.C.Cantley
(1997).
A comparative analysis of the phosphoinositide binding specificity of pleckstrin homology domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
22059-22066.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Yao,
H.Suzuki,
K.Ozawa,
J.Deng,
C.Lehel,
H.Fukamachi,
W.B.Anderson,
Y.Kawakami,
and
T.Kawakami
(1997).
Interactions between protein kinase C and pleckstrin homology domains. Inhibition by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
13033-13039.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hyvönen,
and
M.Saraste
(1997).
Structure of the PH domain and Btk motif from Bruton's tyrosine kinase: molecular explanations for X-linked agammaglobulinaemia.
|
| |
EMBO J,
16,
3396-3404.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Safo,
W.Z.Yang,
L.Corselli,
S.E.Cramton,
H.S.Yuan,
and
R.C.Johnson
(1997).
The transactivation region of the fis protein that controls site-specific DNA inversion contains extended mobile beta-hairpin arms.
|
| |
EMBO J,
16,
6860-6873.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Scaife,
and
R.L.Margolis
(1997).
The role of the PH domain and SH3 binding domains in dynamin function.
|
| |
Cell Signal,
9,
395-401.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.D.Singer,
H.A.Brown,
and
P.C.Sternweis
(1997).
Regulation of eukaryotic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and phospholipase D.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
66,
475-509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Abrams,
W.Zhao,
and
L.F.Brass
(1996).
A site of interaction between pleckstrin's PH domains and G beta gamma.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1314,
233-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Cowburn
(1996).
Adaptors and integrators.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
1005-1008.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Warnock,
and
S.L.Schmid
(1996).
Dynamin GTPase, a force-generating molecular switch.
|
| |
Bioessays,
18,
885-893.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Shaw
(1996).
The pleckstrin homology domain: an intriguing multifunctional protein module.
|
| |
Bioessays,
18,
35-46.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Pitcher,
Z.L.Fredericks,
W.C.Stone,
R.T.Premont,
R.H.Stoffel,
W.J.Koch,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1996).
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2)-enhanced G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) activity. Location, structure, and regulation of the PIP2 binding site distinguishes the GRK subfamilies.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
24907-24913.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Font de Mora,
C.Guerrero,
D.Mahadevan,
J.J.Coque,
J.M.Rojas,
L.M.Esteban,
M.Rebecchi,
and
E.Santos
(1996).
Isolated Sos1 PH domain exhibits germinal vesicle breakdown-inducing activity in Xenopus oocytes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
18272-18276.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Lomasney,
H.F.Cheng,
L.P.Wang,
Y.Kuan,
S.Liu,
S.W.Fesik,
and
K.King
(1996).
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binding to the pleckstrin homology domain of phospholipase C-delta1 enhances enzyme activity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
25316-25326.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Salim,
M.J.Bottomley,
E.Querfurth,
M.J.Zvelebil,
I.Gout,
R.Scaife,
R.L.Margolis,
R.Gigg,
C.I.Smith,
P.C.Driscoll,
M.D.Waterfield,
and
G.Panayotou
(1996).
Distinct specificity in the recognition of phosphoinositides by the pleckstrin homology domains of dynamin and Bruton's tyrosine kinase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
15,
6241-6250.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Runnels,
J.Jenco,
A.Morris,
and
S.Scarlata
(1996).
Membrane binding of phospholipases C-beta 1 and C-beta 2 is independent of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and the alpha and beta gamma subunits of G proteins.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
16824-16832.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Zhou,
B.Huang,
E.T.Olejniczak,
R.P.Meadows,
S.B.Shuker,
M.Miyazaki,
T.Trüb,
S.E.Shoelson,
and
S.W.Fesik
(1996).
Structural basis for IL-4 receptor phosphopeptide recognition by the IRS-1 PTB domain.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
3,
388-393.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Bonnefoy-Bérard,
A.Munshi,
I.Yron,
S.Wu,
T.L.Collins,
M.Deckert,
T.Shalom-Barak,
L.Giampa,
E.Herbert,
J.Hernandez,
N.Meller,
C.Couture,
and
A.Altman
(1996).
Vav: function and regulation in hematopoietic cell signaling.
|
| |
Stem Cells,
14,
250-268.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Cerione,
and
Y.Zheng
(1996).
The Dbl family of oncogenes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Cell Biol,
8,
216-222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Daly,
G.M.Sanderson,
P.W.Janes,
and
R.L.Sutherland
(1996).
Cloning and characterization of GRB14, a novel member of the GRB7 gene family.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
12502-12510.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.McClure,
and
P.J.Robinson
(1996).
Dynamin, endocytosis and intracellular signalling (review).
|
| |
Mol Membr Biol,
13,
189-215.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kawakami,
L.Yao,
W.Han,
and
T.Kawakami
(1996).
Tec family protein-tyrosine kinases and pleckstrin homology domains in mast cells.
|
| |
Immunol Lett,
54,
113-117.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zheng,
D.Zangrilli,
R.A.Cerione,
and
A.Eva
(1996).
The pleckstrin homology domain mediates transformation by oncogenic dbl through specific intracellular targeting.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
19017-19020.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Gammie,
L.J.Kurihara,
R.B.Vallee,
and
M.D.Rose
(1995).
DNM1, a dynamin-related gene, participates in endosomal trafficking in yeast.
|
| |
J Cell Biol,
130,
553-566.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Orengo,
M.B.Swindells,
A.D.Michie,
M.J.Zvelebil,
P.C.Driscoll,
M.D.Waterfield,
and
J.M.Thornton
(1995).
Structural similarity between the pleckstrin homology domain and verotoxin: the problem of measuring and evaluating structural similarity.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
1977-1983.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Abrams,
H.Wu,
W.Zhao,
E.Belmonte,
D.White,
and
L.F.Brass
(1995).
Pleckstrin inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis initiated by G-protein-coupled and growth factor receptors. A role for pleckstrin's PH domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
14485-14492.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Abrams,
W.Zhao,
E.Belmonte,
and
L.F.Brass
(1995).
Protein kinase C regulates pleckstrin by phosphorylation of sites adjacent to the N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
23317-23321.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Fushman,
S.Cahill,
M.A.Lemmon,
J.Schlessinger,
and
D.Cowburn
(1995).
Solution structure of pleckstrin homology domain of dynamin by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
816-820.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.B.Cohen,
R.Ren,
and
D.Baltimore
(1995).
Modular binding domains in signal transduction proteins.
|
| |
Cell,
80,
237-248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Pitcher,
K.Touhara,
E.S.Payne,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1995).
Pleckstrin homology domain-mediated membrane association and activation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase requires coordinate interaction with G beta gamma subunits and lipid.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
11707-11710.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Kerner,
M.W.Appleby,
R.N.Mohr,
S.Chien,
D.J.Rawlings,
C.R.Maliszewski,
O.N.Witte,
and
R.M.Perlmutter
(1995).
Impaired expansion of mouse B cell progenitors lacking Btk.
|
| |
Immunity,
3,
301-312.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Ferguson,
M.A.Lemmon,
J.Schlessinger,
and
P.B.Sigler
(1995).
Structure of the high affinity complex of inositol trisphosphate with a phospholipase C pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
Cell,
83,
1037-1046.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Ferguson,
M.A.Lemmon,
P.B.Sigler,
and
J.Schlessinger
(1995).
Scratching the surface with the PH domain.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
2,
715-718.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Touhara,
W.J.Koch,
B.E.Hawes,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1995).
Mutational analysis of the pleckstrin homology domain of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Differential effects on G beta gamma and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
17000-17005.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Luttrell,
B.E.Hawes,
K.Touhara,
T.van Biesen,
W.J.Koch,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1995).
Effect of cellular expression of pleckstrin homology domains on Gi-coupled receptor signaling.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
12984-12989.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Lemmon,
K.M.Ferguson,
R.O'Brien,
P.B.Sigler,
and
J.Schlessinger
(1995).
Specific and high-affinity binding of inositol phosphates to an isolated pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
10472-10476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Adams,
T.M.Dwyer,
L.L.Dowler,
R.A.White,
and
S.C.Froehner
(1995).
Mouse alpha 1- and beta 2-syntrophin gene structure, chromosome localization, and homology with a discs large domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
25859-25865.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hyvönen,
M.J.Macias,
M.Nilges,
H.Oschkinat,
M.Saraste,
and
M.Wilmanns
(1995).
Structure of the binding site for inositol phosphates in a PH domain.
|
| |
EMBO J,
14,
4676-4685.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Saraste,
and
M.Hyvönen
(1995).
Pleckstrin homology domains: a fact file.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
5,
403-408.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.De Camilli,
K.Takei,
and
P.S.McPherson
(1995).
The function of dynamin in endocytosis.
|
| |
Curr Opin Neurobiol,
5,
559-565.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Zhang,
S.Talluri,
H.Deng,
D.Branton,
and
G.Wagner
(1995).
Solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of Drosophila beta-spectrin.
|
| |
Structure,
3,
1185-1195.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.B.Vallee,
and
P.M.Okamoto
(1995).
The regulation of endocytosis: identifying dynamin's binding partners.
|
| |
Trends Cell Biol,
5,
43-47.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Langhans-Rajasekaran,
Y.Wan,
and
X.Y.Huang
(1995).
Activation of Tsk and Btk tyrosine kinases by G protein beta gamma subunits.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
8601-8605.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Li,
S.Tsukada,
A.Satterthwaite,
M.H.Havlik,
H.Park,
K.Takatsu,
and
O.N.Witte
(1995).
Activation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) by a point mutation in its pleckstrin homology (PH) domain.
|
| |
Immunity,
2,
451-460.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

