 |
PDBsum entry 4zqc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zqc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.4.2.1.20
- tryptophan synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Tryptophan Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate + L-serine = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + L-tryptophan + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
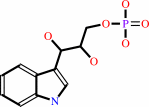 (1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate
(1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate
|
+
|
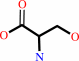 L-serine
L-serine
|
=
|
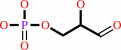 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
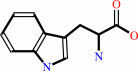 L-tryptophan
L-tryptophan
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochim Biophys Acta
1864:268-279
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Visualizing the tunnel in tryptophan synthase with crystallography: Insights into a selective filter for accommodating indole and rejecting water.
|
|
E.Hilario,
B.G.Caulkins,
Y.M.Huang,
W.You,
C.E.Chang,
L.J.Mueller,
M.F.Dunn,
L.Fan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Four new X-ray structures of tryptophan synthase (TS) crystallized with varying
numbers of the amphipathic N-(4'-trifluoromethoxybenzoyl)-2-aminoethyl phosphate
(F6) molecule are presented. These structures show one of the F6 ligands
threaded into the tunnel from the β-site and reveal a distinct hydrophobic
region. Over this expanse, the interactions between F6 and the tunnel are
primarily nonpolar, while the F6 phosphoryl group fits into a polar pocket of
the β-subunit active site. Further examination of TS structures reveals that
one portion of the tunnel (T1) binds clusters of water molecules, whereas waters
are not observed in the nonpolar F6 binding region of the tunnel (T2). MD
simulation of another TS structure with an unobstructed tunnel also indicates
the T2 region of the tunnel excludes water, consistent with a dewetted state
that presents a significant barrier to the transfer of water into the closed
β-site. We conclude that hydrophobic molecules can freely diffuse between the
α- and β-sites via the tunnel, while water does not. We propose that exclusion
of water serves to inhibit reaction of water with the α-aminoacrylate
intermediate to form ammonium ion and pyruvate, a deleterious side reaction in
the αβ-catalytic cycle. Finally, while most TS structures show βPhe280
partially blocking the tunnel between the α- and β-sites, new structures show
an open tunnel, suggesting the flexibility of the βPhe280 side chain. Flexible
docking studies and MD simulations confirm that the dynamic behavior of βPhe280
allows unhindered transfer of indole through the tunnel, therefore excluding a
gating role for this residue.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

