 |
PDBsum entry 4xec

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4xec
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.1.3
- dihydrofolate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + NADP+ = 7,8-dihydrofolate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
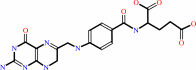 7,8-dihydrofolate
7,8-dihydrofolate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
137:8983-8990
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Nonracemic Antifolates Stereoselectively Recruit Alternate Cofactors and Overcome Resistance in S. aureus.
|
|
S.Keshipeddy,
S.M.Reeve,
A.C.Anderson,
D.L.Wright.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
While antifolates such as Bactrim (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; TMP-SMX)
continue to play an important role in treating community-acquired
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA), resistance-conferring
mutations, specifically F98Y of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), have arisen and
compromise continued use. In an attempt to extend the lifetime of this important
class, we have developed a class of propargyl-linked antifolates (PLAs) that
exhibit potent inhibition of the enzyme and bacterial strains. Probing the role
of the configuration at the single propargylic stereocenter in these inhibitors
required us to develop a new approach to nonracemic 3-aryl-1-butyne building
blocks by the pairwise use of asymmetric conjugate addition and aldehyde
dehydration protocols. Using this new route, a series of nonracemic PLA
inhibitors was prepared and shown to possess potent enzyme inhibition (IC50
values <50 nM), antibacterial effects (several with MIC values <1 μg/mL)
and to form stable ternary complexes with both wild-type and resistant mutants.
Unexpectedly, crystal structures of a pair of individual enantiomers in the
wild-type DHFR revealed that the single change in configuration of the
stereocenter drove the selection of an alternative NADPH cofactor, with the
minor α-anomer appearing with R-27. Remarkably, this cofactor switching becomes
much more prevalent when the F98Y mutation is present. The observation of
cofactor site plasticity leads to a postulate for the structural basis of TMP
resistance in DHFR and also suggests design strategies that can be used to
target these resistant enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

