 |
PDBsum entry 4n4t

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4n4t
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Co-crystal structure of tankyrase 1 with compound 3 [(4s)-3-{4-[6- amino-5-(pyrimidin-2-yl)pyridin-3-yl]phenyl}-5,5-dimethyl-4-phenyl-1, 3-oxazolidin-2-one]
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Tankyrase-1. Chain: a, b. Fragment: unp residues 1104-1314. Synonym: tank1, adp-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 5, artd5, trf1-interacting ankyrin-related adp-ribose polymerase 1, tankyrase i. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. Mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Gene: tnks, tnks1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.32Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.251
|
R-free:
|
0.275
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
X.Huang
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.Huang
et al.
(2013).
Structure-based design of 2-aminopyridine oxazolidinones as potent and selective tankyrase inhibitors.
Acs Med Chem Lett,
4,
1218-1223.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
08-Oct-13
|
Release date:
|
11-Dec-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.4.2.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.4.2.30
- NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + (ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor = nicotinamide + (ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
(ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor
|
=
|
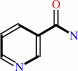 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
(ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acs Med Chem Lett
4:1218-1223
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure-based design of 2-aminopyridine oxazolidinones as potent and selective tankyrase inhibitors.
|
|
H.Huang,
A.Guzman-Perez,
L.Acquaviva,
V.Berry,
H.Bregman,
J.Dovey,
H.Gunaydin,
X.Huang,
L.Huang,
D.Saffran,
R.Serafino,
S.Schneider,
C.Wilson,
E.F.DiMauro.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aberrant activation of the Wnt pathway has been implicated in the development
and formation of many cancers. TNKS inhibition has been shown to antagonize Wnt
signaling via Axin stabilization in APC mutant colon cancer cell lines. We
employed structure-based design to identify a series of 2-aminopyridine
oxazolidinones as potent and selective TNKS inhibitors. These compounds
exhibited good enzyme and cell potency as well as selectivity over other PARP
isoforms. Co-crystal structures of these 2-aminopyridine oxazolidinones
complexed to TNKS reveal an induced-pocket binding mode that does not involve
interactions with the nicotinamide binding pocket. Oral dosing of lead compounds
3 and 4 resulted in significant effects on several Wnt-pathway biomarkers in a
three day DLD-1 mouse tumor PD model.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

