 |
PDBsum entry 3b8h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Biosynthetic protein/transferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3b8h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Biosynthetic protein/transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of the eef2-exoa(e546a)-NAD+ complex
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Elongation factor 2. Chain: a, c, e. Synonym: ef-2, translation elongation factor 2, eukaryotic elongation factor 2, eef2, ribosomal translocase. Exotoxin a. Chain: b, d, f. Fragment: catalytic domain. Synonym: NAD-dependent adp-ribosyltransferase. Engineered: yes.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Baker's yeast. Organism_taxid: 4932. Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Organism_taxid: 287. Gene: eta. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.214
|
R-free:
|
0.256
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Jorgensen,A.R.Merrill
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.Jørgensen
et al.
(2008).
The nature and character of the transition state for the ADP-ribosyltransferase reaction.
Embo Rep,
9,
802-809.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-Nov-07
|
Release date:
|
17-Jun-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, C, E:
E.C.3.6.5.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, D, F:
E.C.2.4.2.36
- NAD(+)--diphthamide ADP-ribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2] + NAD+ = N-(ADP-D- ribosyl)diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2] + nicotinamide + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2]
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
N-(ADP-D- ribosyl)diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2]
|
+
|
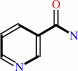 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Embo Rep
9:802-809
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The nature and character of the transition state for the ADP-ribosyltransferase reaction.
|
|
R.Jørgensen,
Y.Wang,
D.Visschedyk,
A.R.Merrill.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Exotoxin A (ExoA) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an important virulence factor
that belongs to a class of exotoxins that are secreted by pathogenic bacteria
which cause human diseases such as cholera, diphtheria, pneumonia and whooping
cough. We present the first crystal structures, to our knowledge, of ExoA in
complex with elongation factor 2 (eEF2) and intact NAD(+), which indicate a
direct role of two active-site loops in ExoA during the catalytic cycle. One
loop moves to form a solvent cover for the active site of the enzyme and reaches
towards the target residue (diphthamide) in eEF2 forming an important hydrogen
bond. The NAD(+) substrate adopts a conformation remarkably different from that
of the NAD(+) analogue, betaTAD, observed in previous structures, and fails to
trigger any loop movements. Mutational studies of the two loops in the toxin
identify several residues important for catalytic activity, in particular Glu
546 and Arg 551, clearly supporting the new complex structures. On the basis of
these data, we propose a transition-state model for the toxin-catalysed reaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.O.Hottiger,
P.O.Hassa,
B.Lüscher,
H.Schüler,
and
F.Koch-Nolte
(2010).
Toward a unified nomenclature for mammalian ADP-ribosyltransferases.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
35,
208-219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Fieldhouse,
Z.Turgeon,
D.White,
and
A.R.Merrill
(2010).
Cholera- and anthrax-like toxins are among several new ADP-ribosyltransferases.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
6,
e1001029.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

