 |
PDBsum entry 1s1m

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of e. Coli ctp synthetase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Ctp synthase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: utp--ammonia ligase, ctp synthetase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: pyrg, b2780, c3345, z4095, ecs3640, sf2795, s2989. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.214
|
R-free:
|
0.281
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.A.Endrizzi,H.Kim,P.M.Anderson,E.P.Baldwin
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.A.Endrizzi
et al.
(2004).
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli cytidine triphosphate synthetase, a nucleotide-regulated glutamine amidotransferase/ATP-dependent amidoligase fusion protein and homologue of anticancer and antiparasitic drug targets.
Biochemistry,
43,
6447-6463.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
06-Jan-04
|
Release date:
|
15-Jun-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A7E5
(PYRG_ECOLI) -
CTP synthase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
545 a.a.
534 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.4.2
- Ctp synthase (glutamine hydrolyzing).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
UTP + L-glutamine + ATP + H2O = CTP + L-glutamate + ADP + phosphate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
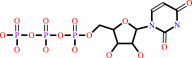 UTP
UTP
|
+
|
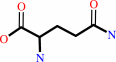 L-glutamine
L-glutamine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
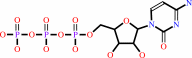 CTP
CTP
|
+
|
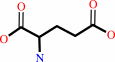 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
43:6447-6463
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli cytidine triphosphate synthetase, a nucleotide-regulated glutamine amidotransferase/ATP-dependent amidoligase fusion protein and homologue of anticancer and antiparasitic drug targets.
|
|
J.A.Endrizzi,
H.Kim,
P.M.Anderson,
E.P.Baldwin.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cytidine triphosphate synthetases (CTPSs) produce CTP from UTP and glutamine,
and regulate intracellular CTP levels through interactions with the four
ribonucleotide triphosphates. We solved the 2.3-A resolution crystal structure
of Escherichia coli CTPS using Hg-MAD phasing. The structure reveals a nearly
symmetric 222 tetramer, in which each bifunctional monomer contains a
dethiobiotin synthetase-like amidoligase N-terminal domain and a Type 1
glutamine amidotransferase C-terminal domain. For each amidoligase active site,
essential ATP- and UTP-binding surfaces are contributed by three monomers,
suggesting that activity requires tetramer formation, and that a
nucleotide-dependent dimer-tetramer equilibrium contributes to the observed
positive cooperativity. A gated channel that spans 25 A between the glutamine
hydrolysis and amidoligase active sites provides a path for ammonia diffusion.
The channel is accessible to solvent at the base of a cleft adjoining the
glutamine hydrolysis active site, providing an entry point for exogenous
ammonia. Guanine nucleotide binding sites of structurally related GTPases
superimpose on this cleft, providing insights into allosteric regulation by GTP.
Mutations that confer nucleoside drug resistance and release CTP inhibition map
to a pocket that neighbors the UTP-binding site and can accommodate a pyrimidine
ring. Its location suggests that competitive feedback inhibition is affected via
a distinct product/drug binding site that overlaps the substrate triphosphate
binding site. Overall, the E. coli structure provides a framework for homology
modeling of other CTPSs and structure-based design of anti-CTPS therapeutics.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Liu
(2011).
The enigmatic cytoophidium: Compartmentation of CTP synthase via filament formation.
|
| |
Bioessays,
33,
159-164.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ingerson-Mahar,
A.Briegel,
J.N.Werner,
G.J.Jensen,
and
Z.Gitai
(2010).
The metabolic enzyme CTP synthase forms cytoskeletal filaments.
|
| |
Nat Cell Biol,
12,
739-746.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.LaRonde-LeBlanc,
M.Resto,
and
B.Gerratana
(2009).
Regulation of active site coupling in glutamine-dependent NAD(+) synthetase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
16,
421-429.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.J.Hart,
and
S.G.Powers-Lee
(2008).
Mutation analysis of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: does the structurally conserved glutamine amidotransferase triad act as a functional dyad?
|
| |
Protein Sci,
17,
1120-1128.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.A.Lunn,
J.E.Macdonnell,
and
S.L.Bearne
(2008).
Structural Requirements for the Activation of Escherichia coli CTP Synthase by the Allosteric Effector GTP Are Stringent, but Requirements for Inhibition Are Lax.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
2010-2020.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Taylor,
F.A.Lunn,
and
S.L.Bearne
(2008).
Ground state, intermediate, and multivalent nucleotide analogue inhibitors of cytidine 5'-triphosphate synthase.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
3,
1853-1857.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Agari,
S.Sato,
T.Wakamatsu,
Y.Bessho,
A.Ebihara,
S.Yokoyama,
S.Kuramitsu,
and
A.Shinkai
(2008).
X-ray crystal structure of a hypothetical Sua5 protein from Sulfolobus tokodaii strain 7.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
1108-1111.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.F.Chang,
and
G.M.Carman
(2008).
CTP synthetase and its role in phospholipid synthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
47,
333-339.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Fijolek,
A.Hofer,
and
L.Thelander
(2007).
Expression, purification, characterization, and in vivo targeting of trypanosome CTP synthetase for treatment of African sleeping sickness.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
11858-11865.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Evrin,
M.Straut,
N.Slavova-Azmanova,
N.Bucurenci,
A.Onu,
L.Assairi,
M.Ionescu,
N.Palibroda,
O.Bârzu,
and
A.M.Gilles
(2007).
Regulatory mechanisms differ in UMP kinases from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
7242-7253.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Choi,
and
G.M.Carman
(2007).
Phosphorylation of human CTP synthetase 1 by protein kinase A: identification of Thr455 as a major site of phosphorylation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
5367-5377.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Higgins,
P.R.Graves,
and
L.M.Graves
(2007).
Regulation of human cytidine triphosphate synthetase 1 by glycogen synthase kinase 3.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
29493-29503.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Braun,
M.Knipp,
S.Chesnov,
and
M.Vasák
(2007).
Specific reactions of S-nitrosothiols with cysteine hydrolases: A comparative study between dimethylargininase-1 and CTP synthetase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
1522-1534.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mouilleron,
and
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau
(2007).
Conformational changes in ammonia-channeling glutamine amidotransferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
17,
653-664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.F.Chang,
S.S.Martin,
E.P.Baldwin,
and
G.M.Carman
(2007).
Phosphorylation of human CTP synthetase 1 by protein kinase C: identification of Ser(462) and Thr(455) as major sites of phosphorylation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
17613-17622.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.G.Richards,
and
M.S.Kilberg
(2006).
Asparagine synthetase chemotherapy.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
75,
629-654.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Kursula,
S.Flodin,
M.Ehn,
M.Hammarström,
H.Schüler,
P.Nordlund,
and
P.Stenmark
(2006).
Structure of the synthetase domain of human CTP synthetase, a target for anticancer therapy.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
613-617.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.S.Han,
A.Sreenivas,
M.G.Choi,
Y.F.Chang,
S.S.Martin,
E.P.Baldwin,
and
G.M.Carman
(2005).
Expression of Human CTP synthetase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals phosphorylation by protein kinase A.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
38328-38336.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Endrizzi,
H.Kim,
P.M.Anderson,
and
E.P.Baldwin
(2005).
Mechanisms of product feedback regulation and drug resistance in cytidine triphosphate synthetases from the structure of a CTP-inhibited complex.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
44,
13491-13499.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Willemoës,
A.Mølgaard,
E.Johansson,
and
J.Martinussen
(2005).
Lid L11 of the glutamine amidotransferase domain of CTP synthase mediates allosteric GTP activation of glutaminase activity.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
856-864.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.A.Lunn,
and
S.L.Bearne
(2004).
Alternative substrates for wild-type and L109A E. coli CTP synthases: kinetic evidence for a constricted ammonia tunnel.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
4204-4212.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Goto,
R.Omi,
N.Nakagawa,
I.Miyahara,
and
K.Hirotsu
(2004).
Crystal structures of CTP synthetase reveal ATP, UTP, and glutamine binding sites.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
1413-1423.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.L.Yang,
and
G.M.Carman
(1995).
Phosphorylation of CTP synthetase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by protein kinase C.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
14983-14988.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

