 |
PDBsum entry 1mj4

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1mj4
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.8.3.1
- sulfite oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
sulfite + O2 + H2O = sulfate + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
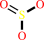 sulfite
sulfite
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
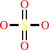 sulfate
sulfate
|
+
|
H2O2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Heme; Mo cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Heme
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
HEM)
matches with 95.45% similarity
|
Mo cation
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
59:1183-1191
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The 1.2 A structure of the human sulfite oxidase cytochrome b(5) domain.
|
|
M.J.Rudolph,
J.L.Johnson,
K.V.Rajagopalan,
C.Kisker.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The molybdenum- and iron-containing enzyme sulfite oxidase catalyzes the
physiologically vital oxidation of sulfite to sulfate. Sulfite oxidase contains
three domains: an N-terminal cytochrome b(5) domain, a central domain harboring
the molybdenum cofactor (Moco) and a C-terminal dimerization domain. Oxidation
of the substrate sulfite is coupled to the transfer of two electrons to the
molybdenum cofactor. Subsequently, these electrons are passed on, one at a time,
to the b(5) heme of sulfite oxidase and from there to the soluble electron
carrier cytochrome c. The crystal structure of the oxidized human sulfite
oxidase cytochrome b(5) domain has been determined at 1.2 A resolution and has
been refined to a crystallographic R factor of 0.107 (R(free) = 0.137). A
comparison of this structure with other b(5)-type cytochromes reveals distinct
structural features present in the sulfite oxidase b(5) domain which promote
optimal electron transport between the Moco of sulfite oxidase and the heme of
cytochrome c.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1 Sulfite oxidase-catalyzed reaction. The reaction
consists of the oxidation of sulfite to sulfate coupled with the
subsequent reduction of two equivalents of ferricytochrome c to
ferrocytochrome c.
|
 |
Figure 8.
Figure 8 Representation of the HSO b[5] (a) and CYT b[5] (b)
heme axial ligand environments. The heme is shown in all-bonds
representation, with the iron in green. The axial histidines are
in all-bonds representation, with the red dots depicting the
interactions between the Fe atom and the N  2
atoms of the axial histidines as well as the hydrogen bonds
between the carbonyl O atoms and the N 2
atoms of the axial histidines as well as the hydrogen bonds
between the carbonyl O atoms and the N  1
atoms from the axial histidines. 1
atoms from the axial histidines.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2003,
59,
1183-1191)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.T.Lecomte,
K.Mukhopadhyay,
and
M.P.Pond
(2008).
Structural and thermodynamic encoding in the sequence of rat microsomal cytochrome b(5).
|
| |
Biopolymers,
89,
428-442.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Feng,
G.Tollin,
and
J.H.Enemark
(2007).
Sulfite oxidizing enzymes.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1774,
527-539.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Hoy,
S.Kundu,
J.T.Trent,
S.Ramaswamy,
and
M.S.Hargrove
(2004).
The crystal structure of Synechocystis hemoglobin with a covalent heme linkage.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
16535-16542.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

