 |
PDBsum entry 1kko

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.2
- methylaspartate ammonia-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2S,3S)-3-methyl-L-aspartate = mesaconate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2S,3S)-3-methyl-L-aspartate
|
=
|
 mesaconate
mesaconate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Cob(II)alamin
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
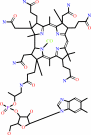 Cob(II)alamin
Cob(II)alamin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
10:105-113
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insights into enzyme evolution revealed by the structure of methylaspartate ammonia lyase.
|
|
C.W.Levy,
P.A.Buckley,
S.Sedelnikova,
Y.Kato,
Y.Asano,
D.W.Rice,
P.J.Baker.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Methylaspartate ammonia lyase (MAL) catalyzes the magnesium-dependent reversible
alpha,beta-elimination of ammonia from L-threo-(2S,3S)-3-methylaspartic acid to
mesaconic acid. The 1.3 A MAD crystal structure of the dimeric Citrobacter
amalonaticus MAL shows that each subunit comprises two domains, one of which
adopts the classical TIM barrel fold, with the active site at the C-terminal end
of the barrel. Despite very low sequence similarity, the structure of MAL is
closely related to those of representative members of the enolase superfamily,
indicating that the mechanism of MAL involves the initial abstraction of a
proton alpha to the 3-carboxyl of (2S,3S)-3-methylasparic acid to yield an
enolic intermediate. This analysis resolves the conflict that had linked MAL to
the histidine and phenylalanine ammonia lyase family of enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. A Schematic of the Proposed Reaction Mechanism of
MALThe 3-proton of (2S,3S)-3-methyl aspartic acid is abstracted
by Lys-331 acting as a base to give the enolic intermediate
shown in the middle panel. The negative charge on the
aci-carboxylate is stabilized by the metal ion and possibly by
His-194 acting as an electrophile. The enolic intermediate
collapses with the elimination of ammonia to yield mesaconic
acid (right hand panel).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2002,
10,
105-113)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Raj,
B.Weiner,
V.P.Veetil,
C.R.Reis,
W.J.Quax,
D.B.Janssen,
B.L.Feringa,
and
G.J.Poelarends
(2009).
Alteration of the diastereoselectivity of 3-methylaspartate ammonia lyase by using structure-based mutagenesis.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
2236-2245.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Buckel,
and
B.T.Golding
(2006).
Radical enzymes in anaerobes.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
60,
27-49.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Asano,
I.Kira,
and
K.Yokozeki
(2005).
Alteration of substrate specificity of aspartase by directed evolution.
|
| |
Biomol Eng,
22,
95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Meng,
B.J.Polacco,
and
P.C.Babbitt
(2004).
Superfamily active site templates.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
962-976.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.N.Chaudhuri,
M.R.Sawaya,
C.Y.Kim,
G.S.Waldo,
M.S.Park,
T.C.Terwilliger,
and
T.O.Yeates
(2003).
The crystal structure of the first enzyme in the pantothenate biosynthetic pathway, ketopantoate hydroxymethyltransferase, from M tuberculosis.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
753-764.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kajander,
L.Lehtiö,
M.Schlömann,
and
A.Goldman
(2003).
The structure of Pseudomonas P51 Cl-muconate lactonizing enzyme: co-evolution of structure and dynamics with the dehalogenation function.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
1855-1864.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

