 |
PDBsum entry 1g0s

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.6.1.13
- ADP-ribose diphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ADP-D-ribose + H2O = D-ribose 5-phosphate + AMP + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
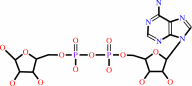 ADP-D-ribose
ADP-D-ribose
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 D-ribose 5-phosphate
D-ribose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Struct Biol
8:467-472
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase reveals the structural basis for the versatility of the Nudix family.
|
|
S.B.Gabelli,
M.A.Bianchet,
M.J.Bessman,
L.M.Amzel.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Regulation of cellular levels of ADP-ribose is important in preventing
nonenzymatic ADP-ribosylation of proteins. The Escherichia coli ADP-ribose
pyrophosphatase, a Nudix enzyme, catalyzes the hydrolysis of ADP-ribose to
ribose-5-P and AMP, compounds that can be recycled as part of nucleotide
metabolism. The structures of the apo enzyme, the active enzyme and the complex
with ADP-ribose were determined to 1.9 A, 2.7 A and 2.3 A, respectively. The
structures reveal a symmetric homodimer with two equivalent catalytic sites,
each formed by residues of both monomers, requiring dimerization through domain
swapping for substrate recognition and catalytic activity. The structures also
suggest a role for the residues conserved in each Nudix subfamily. The Nudix
motif residues, folded as a loop-helix-loop tailored for pyrophosphate
hydrolysis, compose the catalytic center; residues conferring substrate
specificity occur in regions of the sequence removed from the Nudix motif. This
segregation of catalytic and recognition roles provides versatility to the Nudix
family.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Coordination of the Gd^3+ in ADPRase. The side
chains of the residues involved in ion coordination are shown in
all-atom representation. The corresponding portion of the 2F[o]
- F[c] electron density map is shown in sky blue. The metal ion
is shown in green, and the metal-coordinating waters as red
spheres.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Substrate binding to ADPRase. a, Location of the
two equivalent ADPR binding sites in the ADPRase dimer. In each
binding site, loop L8 of the opposite monomer is in close
proximity to the ribose moiety of ADPR. b, Stereo diagram of one
ADPR binding site. Residues of the two monomers contributing to
binding are labeled (B: main monomer, A: second monomer). The
2F[o] - F[c] electron density of the ADPR is shown in light
blue. Carbons are gray, oxygens red, nitrogens blue, phosphorous
yellow, and sulfur green; bound waters (labeled W3 and W4) are
shown as red spheres. The adenosine group of the substrate binds
to the enzyme in anti conformation (dihedral glycosylic bond is
-143°); the adenine ribose ring has C3'-endo puckering and the
terminal ribose binds with C2'-endo puckering. c, Interactions
between ADPR and ADPRase. The ADPR molecule is drawn with heavy
lines. Hydrogen bonds are shown with dashed blue lines; the
distances between donors and acceptors are indicated. Amino
acids providing van der Waals interactions are shown as
decorated arcs. Residue numbers are followed by a letter (A or
B) to indicate the monomer. Water molecules W1 to W4 are shown
as spheres.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nat Struct Biol
(2001,
8,
467-472)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Isogai,
S.Kanno,
M.Ariyoshi,
H.Tochio,
Y.Ito,
A.Yasui,
and
M.Shirakawa
(2010).
Solution structure of a zinc-finger domain that binds to poly-ADP-ribose.
|
| |
Genes Cells,
15,
101-110.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.N.Floor,
B.N.Jones,
G.A.Hernandez,
and
J.D.Gross
(2010).
A split active site couples cap recognition by Dcp2 to activation.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
17,
1096-1101.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Nakamura,
S.Meshitsuka,
S.Kitagawa,
N.Abe,
J.Yamada,
T.Ishino,
H.Nakano,
T.Tsuzuki,
T.Doi,
Y.Kobayashi,
S.Fujii,
M.Sekiguchi,
and
Y.Yamagata
(2010).
Structural and dynamic features of the MutT protein in the recognition of nucleotides with the mutagenic 8-oxoguanine base.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
444-452.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Huang,
J.De Ingeniis,
L.Galeazzi,
C.Mancini,
Y.D.Korostelev,
A.B.Rakhmaninova,
M.S.Gelfand,
D.A.Rodionov,
N.Raffaelli,
and
H.Zhang
(2009).
Structure and function of an ADP-ribose-dependent transcriptional regulator of NAD metabolism.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
939-951.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Messing,
S.B.Gabelli,
Q.Liu,
H.Celesnik,
J.G.Belasco,
S.A.Piñeiro,
and
L.M.Amzel
(2009).
Structure and biological function of the RNA pyrophosphohydrolase BdRppH from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
472-481.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.W.Buchko,
O.Litvinova,
H.Robinson,
A.F.Yakunin,
and
M.A.Kennedy
(2008).
Functional and structural characterization of DR_0079 from Deinococcus radiodurans, a novel Nudix hydrolase with a preference for cytosine (deoxy)ribonucleoside 5'-Di- and triphosphates.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
6571-6582.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zhang,
F.Gao,
Q.Zhang,
Q.Chen,
J.Qi,
and
J.Yan
(2008).
Crystallization and crystallographic analysis of human NUDT16.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
639-640.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Coseno,
G.Martin,
C.Berger,
G.Gilmartin,
W.Keller,
and
S.Doublié
(2008).
Crystal structure of the 25 kDa subunit of human cleavage factor Im.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
3474-3483.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.V.Deshmukh,
B.N.Jones,
D.U.Quang-Dang,
J.Flinders,
S.N.Floor,
C.Kim,
J.Jemielity,
M.Kalek,
E.Darzynkiewicz,
and
J.D.Gross
(2008).
mRNA decapping is promoted by an RNA-binding channel in Dcp2.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
29,
324-336.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Huang,
L.Sorci,
X.Zhang,
C.A.Brautigam,
X.Li,
N.Raffaelli,
G.Magni,
N.V.Grishin,
A.L.Osterman,
and
H.Zhang
(2008).
Bifunctional NMN adenylyltransferase/ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase: structure and function in bacterial NAD metabolism.
|
| |
Structure,
16,
196-209.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Zhang,
K.A.MacDonald,
M.Baguma-Nibasheka,
L.Geldenhuys,
A.G.Casson,
and
P.R.Murphy
(2008).
Alternative splicing and differential subcellular localization of the rat FGF antisense gene product.
|
| |
BMC Mol Biol,
9,
10.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Steyert,
S.A.Messing,
L.M.Amzel,
S.B.Gabelli,
and
S.A.Piñeiro
(2008).
Identification of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus HD100 Bd0714 as a Nudix dGTPase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
8215-8219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Wakamatsu,
N.Nakagawa,
S.Kuramitsu,
and
R.Masui
(2008).
Structural basis for different substrate specificities of two ADP-ribose pyrophosphatases from Thermus thermophilus HB8.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
1108-1117.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Gabelli,
M.A.Bianchet,
W.Xu,
C.A.Dunn,
Z.D.Niu,
L.M.Amzel,
and
M.J.Bessman
(2007).
Structure and function of the E. coli dihydroneopterin triphosphate pyrophosphatase: a Nudix enzyme involved in folate biosynthesis.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
1014-1022.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Zhang,
C.Barclay,
L.A.Alexander,
L.Geldenhuys,
G.A.Porter,
A.G.Casson,
and
P.R.Murphy
(2007).
Alternative splicing of the FGF antisense gene: differential subcellular localization in human tissues and esophageal adenocarcinoma.
|
| |
J Mol Med,
85,
1215-1228.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Tossavainen,
T.Pihlajamaa,
T.K.Huttunen,
E.Raulo,
H.Rauvala,
P.Permi,
and
I.Kilpeläinen
(2006).
The layered fold of the TSR domain of P. falciparum TRAP contains a heparin binding site.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
1760-1768.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.She,
C.J.Decker,
N.Chen,
S.Tumati,
R.Parker,
and
H.Song
(2006).
Crystal structure and functional analysis of Dcp2p from Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
13,
63-70.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Kumaran,
S.Eswaramoorthy,
F.W.Studier,
and
S.Swaminathan
(2005).
Structure and mechanism of ADP-ribose-1''-monophosphatase (Appr-1''-pase), a ubiquitous cellular processing enzyme.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
719-726.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.J.Kühn,
I.Heiner,
and
A.Lückhoff
(2005).
TRPM2: a calcium influx pathway regulated by oxidative stress and the novel second messenger ADP-ribose.
|
| |
Pflugers Arch,
451,
212-219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Badger,
J.M.Sauder,
J.M.Adams,
S.Antonysamy,
K.Bain,
M.G.Bergseid,
S.G.Buchanan,
M.D.Buchanan,
Y.Batiyenko,
J.A.Christopher,
S.Emtage,
A.Eroshkina,
I.Feil,
E.B.Furlong,
K.S.Gajiwala,
X.Gao,
D.He,
J.Hendle,
A.Huber,
K.Hoda,
P.Kearins,
C.Kissinger,
B.Laubert,
H.A.Lewis,
J.Lin,
K.Loomis,
D.Lorimer,
G.Louie,
M.Maletic,
C.D.Marsh,
I.Miller,
J.Molinari,
H.J.Muller-Dieckmann,
J.M.Newman,
B.W.Noland,
B.Pagarigan,
F.Park,
T.S.Peat,
K.W.Post,
S.Radojicic,
A.Ramos,
R.Romero,
M.E.Rutter,
W.E.Sanderson,
K.D.Schwinn,
J.Tresser,
J.Winhoven,
T.A.Wright,
L.Wu,
J.Xu,
and
T.J.Harris
(2005).
Structural analysis of a set of proteins resulting from a bacterial genomics project.
|
| |
Proteins,
60,
787-796.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Swarbrick,
S.Buyya,
D.Gunawardana,
K.R.Gayler,
A.G.McLennan,
and
P.R.Gooley
(2005).
Structure and substrate-binding mechanism of human Ap4A hydrolase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
8471-8481.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Okuda,
H.Hayashi,
and
Y.Nishiyama
(2005).
Systematic characterization of the ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase family in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
187,
4984-4991.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Zachariah,
G.E.Crooks,
S.R.Holbrook,
and
S.E.Brenner
(2005).
A generalized affine gap model significantly improves protein sequence alignment accuracy.
|
| |
Proteins,
58,
329-338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.J.Kühn,
and
A.Lückhoff
(2004).
Sites of the NUDT9-H domain critical for ADP-ribose activation of the cation channel TRPM2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
46431-46437.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.W.Buchko,
S.Ni,
S.R.Holbrook,
and
M.A.Kennedy
(2004).
Solution structure of hypothetical Nudix hydrolase DR0079 from extremely radiation-resistant Deinococcus radiodurans bacterium.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
28-39.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Gabelli,
M.A.Bianchet,
H.F.Azurmendi,
Z.Xia,
V.Sarawat,
A.S.Mildvan,
and
L.M.Amzel
(2004).
Structure and mechanism of GDP-mannose glycosyl hydrolase, a Nudix enzyme that cleaves at carbon instead of phosphorus.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
927-935.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ghosh,
B.Peterson,
N.Tomasevic,
and
B.A.Peculis
(2004).
Xenopus U8 snoRNA binding protein is a conserved nuclear decapping enzyme.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
13,
817-828.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Iwai,
S.Kuramitsu,
and
R.Masui
(2004).
The Nudix hydrolase Ndx1 from Thermus thermophilus HB8 is a diadenosine hexaphosphate hydrolase with a novel activity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
21732-21739.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Perraud,
B.Shen,
C.A.Dunn,
K.Rippe,
M.K.Smith,
M.J.Bessman,
B.L.Stoddard,
and
A.M.Scharenberg
(2003).
NUDT9, a member of the Nudix hydrolase family, is an evolutionarily conserved mitochondrial ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
1794-1801.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.J.Sheehan,
J.T.Bossé,
A.J.Beddek,
A.N.Rycroft,
J.S.Kroll,
and
P.R.Langford
(2003).
Identification of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae genes important for survival during infection in its natural host.
|
| |
Infect Immun,
71,
3960-3970.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Piccirillo,
R.Khanna,
and
M.Kiledjian
(2003).
Functional characterization of the mammalian mRNA decapping enzyme hDcp2.
|
| |
RNA,
9,
1138-1147.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.K.Kim,
J.H.Kim,
E.K.Song,
M.K.Han,
and
J.S.Kim
(2003).
Polymerization of ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase: conversion mechanism of Mg(2+)-dependent ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase into Mg(2+)-independent form.
|
| |
Arch Pharm Res,
26,
826-831.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.M.Abdelghany,
S.Bailey,
G.M.Blackburn,
J.B.Rafferty,
and
A.G.McLennan
(2003).
Analysis of the catalytic and binding residues of the diadenosine tetraphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase from Caenorhabditis elegans by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
4435-4439.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Kang,
S.B.Gabelli,
J.E.Cunningham,
S.F.O'Handley,
and
L.M.Amzel
(2003).
Structure and mechanism of MT-ADPRase, a nudix hydrolase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
1015-1023.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Kang,
S.B.Gabelli,
M.A.Bianchet,
W.L.Xu,
M.J.Bessman,
and
L.M.Amzel
(2003).
Structure of a coenzyme A pyrophosphatase from Deinococcus radiodurans: a member of the Nudix family.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
185,
4110-4118.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Xu,
J.Shen,
C.A.Dunn,
and
M.J.Bessman
(2003).
A new subfamily of the Nudix hydrolase superfamily active on 5-methyl-UTP (ribo-TTP) and UTP.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
37492-37496.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Tsuchiya,
N.Kunishima,
N.Kamiya,
H.Jingami,
and
K.Morikawa
(2002).
Structural views of the ligand-binding cores of a metabotropic glutamate receptor complexed with an antagonist and both glutamate and Gd3+.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
2660-2665.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.I.Fletcher,
J.D.Swarbrick,
D.Maksel,
K.R.Gayler,
and
P.R.Gooley
(2002).
The structure of Ap(4)A hydrolase complexed with ATP-MgF(x) reveals the basis of substrate binding.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
205-213.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.A.Rafty,
M.T.Schmidt,
A.L.Perraud,
A.M.Scharenberg,
and
J.M.Denu
(2002).
Analysis of O-acetyl-ADP-ribose as a target for Nudix ADP-ribose hydrolases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
47114-47122.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Dobrzanska,
B.Szurmak,
A.Wyslouch-Cieszynska,
and
E.Kraszewska
(2002).
Cloning and characterization of the first member of the Nudix family from Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
50482-50486.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bailey,
S.E.Sedelnikova,
G.M.Blackburn,
H.M.Abdelghany,
P.J.Baker,
A.G.McLennan,
and
J.B.Rafferty
(2002).
The crystal structure of diadenosine tetraphosphate hydrolase from Caenorhabditis elegans in free and binary complex forms.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
589-600.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Wang,
X.Jiao,
A.Carr-Schmid,
and
M.Kiledjian
(2002).
The hDcp2 protein is a mammalian mRNA decapping enzyme.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
12663-12668.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

