 |
PDBsum entry 1f1h

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of glutamine synthetase from salmonella typhimurium with thallium ions
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Protein (glutamine synthetase). Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l. Ec: 6.3.1.2
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Salmonella typhimurium. Organism_taxid: 602. Other_details: gram negative bacteria
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dodecamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.67Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.232
|
R-free:
|
0.263
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.S.Gill,D.Eisenberg
|
Key ref:

|
 |
H.S.Gill
and
D.Eisenberg
(2001).
The crystal structure of phosphinothricin in the active site of glutamine synthetase illuminates the mechanism of enzymatic inhibition.
Biochemistry,
40,
1903-1912.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-May-00
|
Release date:
|
04-Apr-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A1P6
(GLN1B_SALTY) -
Glutamine synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
469 a.a.
468 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.1.2
- glutamine synthetase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-glutamate + NH4+ + ATP = L-glutamine + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
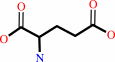 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
L-glutamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
40:1903-1912
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of phosphinothricin in the active site of glutamine synthetase illuminates the mechanism of enzymatic inhibition.
|
|
H.S.Gill,
D.Eisenberg.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Phosphinothricin is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme glutamine synthetase (GS).
The resolution of the native structure of GS from Salmonella typhimurium has
been extended to 2.5 A resolution, and the improved model is used to determine
the structure of phosphinothricin complexed to GS by difference Fourier methods.
The structure suggests a noncovalent, dead-end mechanism of inhibition.
Phosphinothricin occupies the glutamate substrate pocket and stabilizes the
Glu327 flap in a position which blocks the glutamate entrance to the active
site, trapping the inhibitor on the enzyme. One oxygen of the phosphinyl group
of phosphinothricin appears to be protonated, because of its proximity to the
carboxylate group of Glu327. The other phosphinyl oxygen protrudes into the
negatively charged binding pocket for the substrate ammonium, disrupting that
pocket. The distribution of charges in the glutamate binding pocket is
complementary to those of phosphinothricin. The presence of a second ammonium
binding site within the active site is confirmed by its analogue thallous ion,
marking the ammonium site and its protein ligands. The inhibition of GS by
methionine sulfoximine can be explained by the same mechanism. These models of
inhibited GS further illuminate its catalytic mechanism.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.M.van Rooyen,
V.R.Abratt,
H.Belrhali,
and
T.Sewell
(2011).
Crystal Structure of Type III Glutamine Synthetase: Surprising Reversal of the Inter-Ring Interface.
|
| |
Structure,
19,
471-483.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Illingworth,
P.D.Scott,
K.E.Parkes,
C.R.Snell,
M.P.Campbell,
and
C.A.Reynolds
(2010).
Connectivity and binding-site recognition: applications relevant to drug design.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
31,
2677-2688.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.H.Fisher,
and
L.V.Wray
(2009).
Novel trans-Acting Bacillus subtilis glnA mutations that derepress glnRA expression.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
2485-2492.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.B.Inwood,
J.A.Hall,
K.S.Kim,
L.Demirkhanyan,
D.Wemmer,
H.Zgurskaya,
and
S.Kustu
(2009).
Epistatic effects of the protease/chaperone HflB on some damaged forms of the Escherichia coli ammonium channel AmtB.
|
| |
Genetics,
183,
1327-1340.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.X.He,
L.Gui,
Y.Z.Liu,
Y.Du,
Y.Zhou,
P.Li,
and
C.Z.Zhou
(2009).
Crystal structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae glutamine synthetase Gln1 suggests a nanotube-like supramolecular assembly.
|
| |
Proteins,
76,
249-254.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.K.Rana,
P.Mohanpuria,
and
S.K.Yadav
(2008).
Cloning and characterization of a cytosolic glutamine synthetase from Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze that is upregulated by ABA, SA, and H2O2.
|
| |
Mol Biotechnol,
39,
49-56.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jones,
D.J.Studholme,
C.G.Knight,
and
G.M.Preston
(2007).
Integrated bioinformatic and phenotypic analysis of RpoN-dependent traits in the plant growth-promoting bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens SBW25.
|
| |
Environ Microbiol,
9,
3046-3064.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Gold,
L.M.Marky,
M.P.Stone,
and
L.D.Williams
(2006).
A review of the role of the sequence-dependent electrostatic landscape in DNA alkylation patterns.
|
| |
Chem Res Toxicol,
19,
1402-1414.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Wyatt,
H.E.White,
L.Wang,
O.A.Bateman,
C.Slingsby,
E.V.Orlova,
and
G.Wistow
(2006).
Lengsin is a survivor of an ancient family of class I glutamine synthetases re-engineered by evolution for a role in the vertebrate lens.
|
| |
Structure,
14,
1823-1834.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.H.Fisher,
and
L.V.Wray
(2006).
Feedback-resistant mutations in Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase are clustered in the active site.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
5966-5974.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Davies,
R.Tata,
R.Agha,
B.J.Sutton,
and
P.R.Brown
(2005).
Crystal structure of a putative phosphinothricin acetyltransferase (PA4866) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAC1.
|
| |
Proteins,
61,
677-679.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.V.Wray,
and
S.H.Fisher
(2005).
A feedback-resistant mutant of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase with pleiotropic defects in nitrogen-regulated gene expression.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
33298-33304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.W.Krajewski,
T.A.Jones,
and
S.L.Mowbray
(2005).
Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis glutamine synthetase in complex with a transition-state mimic provides functional insights.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
10499-10504.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Lehmann,
V.Doseeva,
S.Pullalarevu,
W.Krajewski,
A.Howard,
and
O.Herzberg
(2004).
YbdK is a carboxylate-amine ligase with a gamma-glutamyl:Cysteine ligase activity: crystal structure and enzymatic assays.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
376-383.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Matsuda,
T.Nishioka,
K.Kinoshita,
T.Kawabata,
and
N.Go
(2003).
Finding evolutionary relations beyond superfamilies: fold-based superfamilies.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
2239-2251.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Howerton,
A.Nagpal,
and
L.D.Williams
(2003).
Surprising roles of electrostatic interactions in DNA-ligand complexes.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
69,
87-99.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Wang,
and
D.Eisenberg
(2003).
Crystal structures of a pantothenate synthetase from M. tuberculosis and its complexes with substrates and a reaction intermediate.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
1097-1108.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.S.Gill,
G.M.Pfluegl,
and
D.Eisenberg
(2002).
Multicopy crystallographic refinement of a relaxed glutamine synthetase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis highlights flexible loops in the enzymatic mechanism and its regulation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9863-9872.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.H.Fisher,
J.L.Brandenburg,
and
L.V.Wray
(2002).
Mutations in Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase that block its interaction with transcription factor TnrA.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
45,
627-635.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Motohashi,
A.Kondoh,
M.T.Stumpp,
and
T.Hisabori
(2001).
Comprehensive survey of proteins targeted by chloroplast thioredoxin.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
11224-11229.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

