 |
PDBsum entry 1e9c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Mutant human thymidylate kinase complexed with tmp and appnp
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Thymidylate kinase. Chain: a. Synonym: dtmp kinase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Homo-Dimer (from PDB file)
Homo-Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.209
|
R-free:
|
0.268
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
N.Ostermann,A.Lavie,S.Padiyar,R.Brundiers,T.Veit,J.Reintein, R.S.Goody,M.Konrad,I.Schlichting
|
Key ref:

|
 |
N.Ostermann
et al.
(2000).
Potentiating AZT activation: structures of wild-type and mutant human thymidylate kinase suggest reasons for the mutants' improved kinetics with the HIV prodrug metabolite AZTMP.
J Mol Biol,
304,
43-53.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Oct-00
|
Release date:
|
11-Oct-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P23919
(KTHY_HUMAN) -
Thymidylate kinase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
212 a.a.
209 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.4.9
- dTMP kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dTMP + ATP = dTDP + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
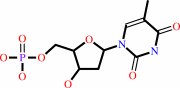 dTMP
dTMP
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
dTDP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
304:43-53
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Potentiating AZT activation: structures of wild-type and mutant human thymidylate kinase suggest reasons for the mutants' improved kinetics with the HIV prodrug metabolite AZTMP.
|
|
N.Ostermann,
A.Lavie,
S.Padiyar,
R.Brundiers,
T.Veit,
J.Reinstein,
R.S.Goody,
M.Konrad,
I.Schlichting.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The 60-fold reduced phosphorylation rate of azidothymidine (AZT) monophosphate
(AZTMP), the partially activated AZT metabolite, by human thymidylate kinase
(TMPK) severely limits the efficacy of this anti-HIV prodrug. Crystal structures
of different TMPK nucleotide complexes indicate that steric hindrance by the
azido group of AZTMP prevents formation of the catalytically active closed
conformation of the P-loop of TMPK. The F105Y mutant and a chimeric mutant that
contains sequences of the human and Escherichia coli enzyme phosphorylate AZTMP
20-fold faster than the wild-type enzyme. The structural basis of the increased
activity is assigned to stabilization of the closed P-loop conformation.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. The 60-fold reduced catalytic rate with AZTMP in
comparison to TMP suggests that TMPK can nevertheless adopt the
partially closed (i.e. active) conformation despite the presence
of the azido group. Overlay of the bisubstrate inhibitor
complexes with either TP[5]A, shown in pink and modeled as TMP
and ATP, and AZTP[5]A (modeled as AZTMP and ATP) reveal that the
side-chain of Asp15 points away from the 3' substituent in the
case of AZTP[5]A, but makes an interaction with the 3'-hydroxyl
group in the case of TP[5]A. Only the fully closed conformation
was observed for the P-loop in the presence of TP[5]A, while
both the open and closed P-loop conformations were observed in
the presence of AZTP[5]A, again suggesting a higher barrier for
reaching the closed conformation in the presence of the azido
group.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. The F105Y mutant adopts a partially closed
conformation even in the presence of ADP. (a) Stereoview of the
overlay between the complex of TMP and ADP with wild-type TMPK
and the F105Y mutant, respectively. In the wild-type complex
structure (depicted in pink), seven interconnected water
molecules are observed to stabilize the open conformation. The
presence of the hydroxyl group of Y105 hinders the formation of
such a water structure, thereby destabilizing the open
conformation. In addition, the hydroxyl moiety interacts with
the side-chain of Gln157, which interacts with the amide
nitrogen atom of the P-loop Asp15 (broken lines), resulting in
the stabilization of the closed conformation. (b) To illustrate
the steric clash that would ensue due to the introduced tyrosine
hydroxyl moiety (instead of Phe), the structure observed in the
open TMP-ADP complex is depicted with its interconnecting water
structure, and the tyrosine residue (pink) from the F105Y
structure.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2000,
304,
43-53)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Ardiani,
M.Sanchez-Bonilla,
and
M.E.Black
(2010).
Fusion enzymes containing HSV-1 thymidine kinase mutants and guanylate kinase enhance prodrug sensitivity in vitro and in vivo.
|
| |
Cancer Gene Ther,
17,
86-96.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Preuss,
A.Treschow,
S.Newrzela,
D.Brücher,
K.Weber,
U.Felldin,
E.Alici,
G.Gahrton,
D.von Laer,
M.S.Dilber,
and
B.Fehse
(2010).
TK.007: A novel, codon-optimized HSVtk(A168H) mutant for suicide gene therapy.
|
| |
Hum Gene Ther,
21,
929-941.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Whittingham,
J.Carrero-Lerida,
J.A.Brannigan,
L.M.Ruiz-Perez,
A.P.Silva,
M.J.Fogg,
A.J.Wilkinson,
I.H.Gilbert,
K.S.Wilson,
and
D.González-Pacanowska
(2010).
Structural basis for the efficient phosphorylation of AZT-MP (3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine monophosphate) and dGMP by Plasmodium falciparum type I thymidylate kinase.
|
| |
Biochem J,
428,
499-509.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Gogolin,
R.Seidel,
M.Engelhard,
R.S.Goody,
and
C.F.Becker
(2010).
Semisynthesis of human thymidine monophosphate kinase.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
94,
433-440.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Lavie,
Y.Su,
M.Ghassemi,
R.M.Novak,
M.Caffrey,
N.Sekulic,
C.Monnerjahn,
M.Konrad,
and
J.L.Cook
(2008).
Restoration of the antiviral activity of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) against AZT-resistant human immunodeficiency virus by delivery of engineered thymidylate kinase to T cells.
|
| |
J Gen Virol,
89,
1672-1679.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.E.Mikkelsen,
B.Munch-Petersen,
and
H.Eklund
(2008).
Structural studies of nucleoside analog and feedback inhibitor binding to Drosophila melanogaster multisubstrate deoxyribonucleoside kinase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
2151-2160.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Sato,
A.Neschadim,
M.Konrad,
D.H.Fowler,
A.Lavie,
and
J.A.Medin
(2007).
Engineered human tmpk/AZT as a novel enzyme/prodrug axis for suicide gene therapy.
|
| |
Mol Ther,
15,
962-970.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Willmon,
E.Krabbenhoft,
and
M.E.Black
(2006).
A guanylate kinase/HSV-1 thymidine kinase fusion protein enhances prodrug-mediated cell killing.
|
| |
Gene Ther,
13,
1309-1312.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Haouz,
V.Vanheusden,
H.Munier-Lehmann,
M.Froeyen,
P.Herdewijn,
S.Van Calenbergh,
and
M.Delarue
(2003).
Enzymatic and structural analysis of inhibitors designed against Mycobacterium tuberculosis thymidylate kinase. New insights into the phosphoryl transfer mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
4963-4971.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Monnerjahn,
and
M.Konrad
(2003).
Modulated nucleoside kinases as tools to improve the activation of therapeutic nucleoside analogues.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
4,
143-146.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.P.Bahadur,
P.Chakrabarti,
F.Rodier,
and
J.Janin
(2003).
Dissecting subunit interfaces in homodimeric proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
53,
708-719.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Sekulic,
L.Shuvalova,
O.Spangenberg,
M.Konrad,
and
A.Lavie
(2002).
Structural characterization of the closed conformation of mouse guanylate kinase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
30236-30243.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

