 |
PDBsum entry 1mrs

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of mycobacterium tuberculosis thymidylate kinase complexed with 5-ch2oh deoxyuridine monophosphate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Thymidylate kinase. Chain: a. Synonym: dtmp kinase, thymidylic acid kinase, tmpk. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Organism_taxid: 1773. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.228
|
R-free:
|
0.265
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Haouz,V.Vanheusden,H.Munier-Lehmann,M.Froeyen,P.Herdewijn,S.Van Calenbergh,M.Delarue
|
Key ref:

|
 |
A.Haouz
et al.
(2003).
Enzymatic and structural analysis of inhibitors designed against Mycobacterium tuberculosis thymidylate kinase. New insights into the phosphoryl transfer mechanism.
J Biol Chem,
278,
4963-4971.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
18-Sep-02
|
Release date:
|
07-Jan-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P9WKE1
(KTHY_MYCTU) -
Thymidylate kinase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
214 a.a.
208 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.4.9
- dTMP kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dTMP + ATP = dTDP + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
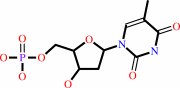 dTMP
dTMP
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 95.45% similarity
|
=
|
 dTDP
dTDP
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
278:4963-4971
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Enzymatic and structural analysis of inhibitors designed against Mycobacterium tuberculosis thymidylate kinase. New insights into the phosphoryl transfer mechanism.
|
|
A.Haouz,
V.Vanheusden,
H.Munier-Lehmann,
M.Froeyen,
P.Herdewijn,
S.Van Calenbergh,
M.Delarue.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The chemical synthesis of new compounds designed as inhibitors of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis TMP kinase (TMPK) is reported. The synthesis concerns TMP analogues
modified at the 5-position of the thymine ring as well as a novel compound with
a six-membered sugar ring. The binding properties of the analogues are compared
with the known inhibitor azido-TMP, which is postulated here to work by
excluding the TMP-bound Mg(2+) ion. The crystallographic structure of the
complex of one of the compounds, 5-CH(2)OH-dUMP, with TMPK has been determined
at 2.0 A. It reveals a major conformation for the hydroxyl group in contact with
a water molecule and a minor conformation pointing toward Ser(99). Looking for a
role for Ser(99), we have identified an unusual catalytic triad, or a proton
wire, made of strictly conserved residues (including Glu(6), Ser(99), Arg(95),
and Asp(9)) that probably serves to protonate the transferred PO(3) group. The
crystallographic structure of the commercially available bisubstrate analogue
P(1)-(adenosine-5')-P(5)-(thymidine-5')-pentaphosphate bound to TMPK is also
reported at 2.45 A and reveals an alternative binding pocket for the adenine
moiety of the molecule compared with what is observed either in the Escherichia
coli or in the yeast enzyme structures. This alternative binding pocket opens a
way for the design of a new family of specific inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Chemical structure of synthesized TMP analogues.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Network of interactions of the analogue 1 in the
active site of TMP kinase (drawn with Chemdraw).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2003,
278,
4963-4971)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.Frecer,
P.Seneci,
and
S.Miertus
(2011).
Computer-assisted combinatorial design of bicyclic thymidine analogs as inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis thymidine monophosphate kinase.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
25,
31-49.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Andrade,
K.F.Pasqualoto,
E.I.Ferreira,
and
A.J.Hopfinger
(2010).
3D-Pharmacophore mapping of thymidine-based inhibitors of TMPK as potential antituberculosis agents.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
24,
157-172.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Whittingham,
J.Carrero-Lerida,
J.A.Brannigan,
L.M.Ruiz-Perez,
A.P.Silva,
M.J.Fogg,
A.J.Wilkinson,
I.H.Gilbert,
K.S.Wilson,
and
D.González-Pacanowska
(2010).
Structural basis for the efficient phosphorylation of AZT-MP (3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine monophosphate) and dGMP by Plasmodium falciparum type I thymidylate kinase.
|
| |
Biochem J,
428,
499-509.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kandeel,
T.Ando,
Y.Kitamura,
M.Abdel-Aziz,
and
Y.Kitade
(2009).
Mutational, inhibitory and microcalorimetric analyses of Plasmodium falciparum TMP kinase. Implications for drug discovery.
|
| |
Parasitology,
136,
11-25.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tzioumaki,
E.Tsoukala,
S.Manta,
G.Agelis,
J.Balzarini,
and
D.Komiotis
(2009).
Synthesis, antiviral and cytostatic evaluation of unsaturated exomethylene and keto D-lyxopyranonucleoside analogues.
|
| |
Arch Pharm (Weinheim),
342,
353-360.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Carnrot,
L.Wang,
D.Topalis,
and
S.Eriksson
(2008).
Mechanisms of substrate selectivity for Bacillus anthracis thymidylate kinase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
17,
1486-1493.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Hible,
P.Christova,
L.Renault,
E.Seclaman,
A.Thompson,
E.Girard,
H.Munier-Lehmann,
and
J.Cherfils
(2006).
Unique GMP-binding site in Mycobacterium tuberculosis guanosine monophosphate kinase.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
489-500.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kotaka,
B.Dhaliwal,
J.Ren,
C.E.Nichols,
R.Angell,
M.Lockyer,
A.R.Hawkins,
and
D.K.Stammers
(2006).
Structures of S. aureus thymidylate kinase reveal an atypical active site configuration and an intermediate conformational state upon substrate binding.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
774-784.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Topalis,
B.Collinet,
C.Gasse,
L.Dugué,
J.Balzarini,
S.Pochet,
and
D.Deville-Bonne
(2005).
Substrate specificity of vaccinia virus thymidylate kinase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
6254-6265.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

