 |
PDBsum entry 1a3f

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Carboxylic ester hydrolase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1a3f
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
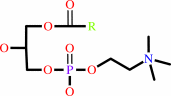 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
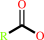 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
279:223-232
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of two novel crystal forms of Naja naja naja phospholipase A2 lacking Ca2+ reveal trimeric packing.
|
|
B.W.Segelke,
D.Nguyen,
R.Chee,
N.H.Xuong,
E.A.Dennis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Three crystal forms of Naja naja naja phospholipase A2 were discovered through
random crystallization screening, including two heretofore uncharacterized
forms. The crystallization conditions for both of these novel crystal forms are
Ca(2+)-free whereas previously reported conditions include Ca2+. One of the new
crystal forms has a cubic lattice in the space group P2(1)3 (a = b = c = 69.24
A), the other has an orthorhombic lattice in the space group P2(1)2(1)2(1) (a =
67.22 A, b = 73.48 A, c = 87.52 A) and a previously characterized crystal belong
to the tetragonal space group P4(3)2(1)2 (a = b = 88.6 A, c = 107.4 A). The
structure from the cubic crystal form has been determined to 1.8 A and refined
to an R-factor of 17% while the structure from the orthorhombic form has been
determined to 2.65 A and has been refined to an R-factor of 21%. The
determination of the cubic structure extends the resolution to which structures
of this molecule have been determined from 2.3 A to 1.8 A. The two newly
determined structures, in combination with the previously determined structure,
generate an informative structural ensemble from which structural changes due to
Ca2+, which is required for catalysis, and the effect of crystal contacts on
side-chain conformations and oligomeric association can be inferred. Both of the
newly determined structures reveal a trimeric oligomer as observed in the
tetragonal structure; this appears to be a unique feature of the Naja naja naja
enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Average deviation of
atomic position for side-chain
atoms versus
����������������
�B=8p
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Conformational changes. (a) Conformational
change at residue 73 due to crystal contacts. A stereo
view of the crystal contact environment for glutamine
73 of subunit B in the tetragonal structure (shown in
yellow) is shown with the cubic structure (shown in
cyan) superimposed. Bonds are shown as thin tubes and
polar or charged atoms of interest are shown as spheres
colored according to atom type (nitrogen blue and
oxygen red). Proposed hydrogen bonds are shown as
broken gray lines. Glutamine 73 from subunit B of the
tetragonal structure is hydrogen bonding with lysine 65
and asparagine 83 of subunit C of a symmetry-related
molecule in the crystal packing of the tetragonal struc-
ture. Glutamine 73 from the cubic structure clashes
severely with atoms in the symmetry-related molecules
in the crystal packing of the tetragonal structure. Gluta-
mine 73 from subunit C (not shown) is also involved in
crystal contacts, hydrogen bonding with asparagine 83
of a symmetry-related subunit A and to a water mol-
ecule hydrogen bonding to lysine 65 of subunit A. This
Figure was generated with MIDAS (UCSF & MGL,
1995). (b) Conformational change at residue 42 due to
crystal contacts. Shown in cyan, residues 39, 42, and 45
are shown with the backbone helical segment and
superimposed with the same residues of the tetragonal
structure (shown in yellow). Backbone C
a
trace is shown
as thick tubes while bonds are shown as thin tubes and
polar or charged atoms of interest are shown as spheres
colored according to atom type (nitrogen blue and oxy-
gen red). Proposed hydrogen bonds are shown as bro-
ken gray lines. Also shown are two symmetry-related
residues 39 and a proposed sodium ion coordinated to
the three acid groups that approach each other in the
crystal packing. A thin green line is shown which is
coincident with the crystallographic 3-fold axis. The con-
formational change in residue 42 is due to shielding of
the charge on the acidic group of aspartate 39 upon
binding to the ammonium ion, which causes the charge
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(1998,
279,
223-232)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Almonacid,
E.R.Yera,
J.B.Mitchell,
and
P.C.Babbitt
(2010).
Quantitative comparison of catalytic mechanisms and overall reactions in convergently evolved enzymes: implications for classification of enzyme function.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
6,
e1000700.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.S.Glazer,
R.J.Radmer,
and
R.B.Altman
(2009).
Improving structure-based function prediction using molecular dynamics.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
919-929.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Burke,
and
E.A.Dennis
(2009).
Phospholipase a(2) biochemistry.
|
| |
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther,
23,
49-59.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Xu,
L.Yi,
Y.Feng,
L.Chen,
and
J.Liu
(2009).
Structural insight into the activation mechanism of human pancreatic prophospholipase A2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
16659-16666.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Burke,
M.J.Karbarz,
R.A.Deems,
S.Li,
V.L.Woods,
and
E.A.Dennis
(2008).
Interaction of group IA phospholipase A2 with metal ions and phospholipid vesicles probed with deuterium exchange mass spectrometry.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
6451-6459.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Hu,
L.Sun,
Z.Q.Zhu,
X.W.Hou,
S.Wang,
S.S.Yu,
H.L.Wang,
P.Zhang,
M.Wang,
L.W.Niu,
M.K.Teng,
and
D.Y.Ruan
(2008).
Crystal structure of Natratoxin, a novel snake secreted phospholipaseA2 neurotoxin from Naja atra venom inhibiting A-type K+ currents.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
673-683.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Jabeen,
N.Singh,
R.K.Singh,
J.Jasti,
S.Sharma,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2006).
Crystal structure of a heterodimer of phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera at 2.3 A resolution reveals the presence of a new PLA2-like protein with a novel cys 32-Cys 49 disulphide bridge with a bound sugar at the substrate-binding site.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
329-337.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Pierce,
W.Tong,
and
Z.Weng
(2005).
M-ZDOCK: a grid-based approach for Cn symmetric multimer docking.
|
| |
Bioinformatics,
21,
1472-1478.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Singh,
S.Gourinath,
K.Saravanan,
S.Sharma,
S.Bhanumathi,
C.h.Betzel,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2005).
Sequence-induced trimerization of phospholipase A2: structure of a trimeric isoform of PLA2 from common krait (Bungarus caeruleus) at 2.5 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
8.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Chandra,
P.Kaur,
J.Jasti,
C.Betzel,
and
T.P.Singh
(2001).
Regulation of catalytic function by molecular association: structure of phospholipase A2 from Daboia russelli pulchella (DPLA2) at 1.9 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
1793-1798.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.H.Lee,
M.T.da Silva Giotto,
S.Marangoni,
M.H.Toyama,
I.Polikarpov,
and
R.C.Garratt
(2001).
Structural basis for low catalytic activity in Lys49 phospholipases A2--a hypothesis: the crystal structure of piratoxin II complexed to fatty acid.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
28-36.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Cartailler,
H.T.Haigler,
and
H.Luecke
(2000).
Annexin XII E105K crystal structure: identification of a pH-dependent switch for mutant hexamerization.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
2475-2483.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Falconi,
A.Desideri,
and
S.Rufini
(2000).
Membrane-perturbing activity of Viperidae myotoxins: an electrostatic surface potential approach to a puzzling problem.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
13,
14-19.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.J.Lefkowitz,
R.A.Deems,
and
E.A.Dennis
(1999).
Expression of group IA phospholipase A2 in Pichia pastoris: identification of a phosphatidylcholine activator site using site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
14174-14184.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

