 |
PDBsum entry 5mvc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5mvc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of potent human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors based on hydroxylated azole scaffolds
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial. Chain: a. Synonym: dhodehase,dihydroorotate oxidase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: dhodh. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.85Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.163
|
R-free:
|
0.189
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
P.Goyal,M.Andersson,A.C.Moritzer,S.Sainas,A.C.Pippione,D.Boschi,S.Al- Kadaraghi,M.Lolli,R.Friemann
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.Sainas
et al.
(2017).
Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and X-ray structural studies of potent human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors based on hydroxylated azole scaffolds.
Eur J Med Chem,
129,
287-302.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Jan-17
|
Release date:
|
08-Mar-17
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q02127
(PYRD_HUMAN) -
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
395 a.a.
352 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.3.5.2
- dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(S)-dihydroorotate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
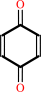 quinone
quinone
|
=
|
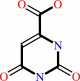 orotate
orotate
|
+
|
quinol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FMN)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Eur J Med Chem
129:287-302
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and X-ray structural studies of potent human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors based on hydroxylated azole scaffolds.
|
|
S.Sainas,
A.C.Pippione,
M.Giorgis,
E.Lupino,
P.Goyal,
C.Ramondetti,
B.Buccinnà,
M.Piccinini,
R.C.Braga,
C.H.Andrade,
M.Andersson,
A.C.Moritzer,
R.Friemann,
S.Mensa,
S.Al-Kadaraghi,
D.Boschi,
M.L.Lolli.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A new generation of potent hDHODH inhibitors designed by a scaffold-hopping
replacement of the quinolinecarboxylate moiety of brequinar, one of the most
potent known hDHODH inhibitors, is presented here. Their general structure is
characterized by a biphenyl moiety joined through an amide bridge with an acidic
hydroxyazole scaffold (hydroxylated thiadiazole, pyrazole and triazole).
Molecular modelling suggested that these structures should adopt a
brequinar-like binding mode involving interactions with subsites 1, 2 and 4 of
the hDHODH binding site. Initially, the inhibitory activity of the compounds was
studied on recombinant hDHODH. The most potent compound of the series in the
enzymatic assays was the thiadiazole analogue 4 (IC50 16 nM). The activity was
found to be dependent on the fluoro substitution pattern at the biphenyl moiety
as well as on the choice/substitution of the heterocyclic ring. Structure
determination of hDHODH co-crystallized with one representative compound from
each series (4, 5 and 6) confirmed the brequinar-like binding mode as suggested
by modelling. The specificity of the observed effects of the compound series was
tested in cell-based assays for antiproliferation activity using Jurkat cells
and PHA-stimulated PBMC. These tests were also verified by addition of exogenous
uridine to the culture medium. In particular, the triazole analogue 6 (IC50
against hDHODH: 45 nM) exerted potent in vitro antiproliferative and
immunosuppressive activity without affecting cell survival.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

