 |
PDBsum entry 4x9s
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of hisap from streptomyces sp. Mg1
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phosphoribosyl isomerase a. Chain: a. Synonym: 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-[(5-phosphoribosylamino) methylideneamino] imidazole-4-carboxamide isomerase,n-(5'- phosphoribosyl)anthranilate isomerase,phosphoribosylformimino-5- aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide isomerase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Streptomyces sp. Mg1. Organism_taxid: 465541. Gene: pria, hisa, ssag_02214. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.156
|
R-free:
|
0.190
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.Michalska,E.A.Verduzco-Castro,M.Endres,F.Barona-Gomez,A.Joachimiak, Midwest Center For Structural Genomics (Mcsg)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
E.A.Verduzco-Castro
et al.
(2016).
Co-occurrence of analogous enzymes determines evolution of a novel (βα)8-isomerase sub-family after non-conserved mutations in flexible loop.
Biochem J,
473,
1141-1152.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
11-Dec-14
|
Release date:
|
24-Dec-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
B4V386
(B4V386_9ACTN) -
Phosphoribosyl isomerase A from Streptomyces sp. Mg1
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
243 a.a.
241 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.16
- 1-(5-phosphoribosyl)-5-
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Histidine Biosynthesis (early stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)-5-[(5-phospho-beta-D- ribosylamino)methylideneamino]imidazole-4-carboxamide = 5-[(5-phospho-1- deoxy-D-ribulos-1-ylimino)methylamino]-1-(5-phospho-beta-D- ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.24
- phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)anthranilate = 1-(2-carboxyphenylamino)-1- deoxy-D-ribulose 5-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
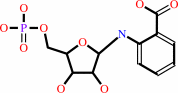 N-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)anthranilate
N-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)anthranilate
|
=
|
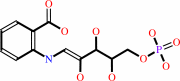 1-(2-carboxyphenylamino)-1- deoxy-D-ribulose 5-phosphate
1-(2-carboxyphenylamino)-1- deoxy-D-ribulose 5-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochem J
473:1141-1152
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Co-occurrence of analogous enzymes determines evolution of a novel (βα)8-isomerase sub-family after non-conserved mutations in flexible loop.
|
|
E.A.Verduzco-Castro,
K.Michalska,
M.Endres,
A.L.Juárez-Vazquez,
L.Noda-García,
C.Chang,
C.S.Henry,
G.Babnigg,
A.Joachimiak,
F.Barona-Gómez.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We investigate the evolution of co-occurring analogous enzymes involved in
L-tryptophan and L-histidine biosynthesis in Actinobacteria Phylogenetic
analysis of trpF homologues, a missing gene in certain clades of this lineage
whose absence is complemented by a dual-substrate HisA homologue, termed PriA,
found that they fall into three categories: (i) trpF-1, an L-tryptophan
biosynthetic gene horizontally acquired by certain Corynebacterium species;
(ii) trpF-2, a paralogue known to be involved in synthesizing a pyrrolopyrrole
moiety and (iii) trpF-3, a variable non-conserved orthologue of trpF-1 We
previously investigated the effect of trpF-1 upon the evolution of PriA
substrate specificity, but nothing is known about the relationship between
trpF-3 and priA After in vitro steady-state enzyme kinetics we found that
trpF-3 encodes a phosphoribosyl anthranilate isomerase. However, mutation of
this gene in Streptomyces sviceus did not lead to auxothrophy, as expected
from the biosynthetic role of trpF-1 Biochemical characterization of a dozen
co-occurring TrpF-2 or TrpF-3, with PriA homologues, explained the prototrophic
phenotype, and unveiled an enzyme activity trade-off between TrpF and PriA.
X-ray structural analysis suggests that the function of these PriA homologues is
mediated by non-conserved mutations in the flexible L5 loop, which may be
responsible for different substrate affinities. Thus, the PriA homologues that
co-occur with TrpF-3 represent a novel enzyme family, termed PriB, which evolved
in response to PRA isomerase activity. The characterization of co-occurring
enzymes provides insights into the influence of functional redundancy on the
evolution of enzyme function, which could be useful for enzyme functional
annotation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

