 |
PDBsum entry 4lz3
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
F95h epi-isozizaene synthase: complex with mg, inorganic pyrophosphate and benzyl triethyl ammonium cation
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Epi-isozizaene synthase. Chain: a. Synonym: eizs, sesquiterpene cyclase, sesquiterpene synthase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Streptomyces coelicolor. Organism_taxid: 100226. Strain: a3(2). Gene: cyc1, sco5222, sc7e4.19. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.164
|
R-free:
|
0.204
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Li,W.Chou,J.A.Himmelberger,K.Litwin,G.Harris,D.E.Cane, D.W.Christianson
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.Li
et al.
(2014).
Reprogramming the chemodiversity of terpenoid cyclization by remolding the active site contour of epi-isozizaene synthase.
Biochemistry,
53,
1155-1168.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
31-Jul-13
|
Release date:
|
18-Dec-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9K499
(CYC1_STRCO) -
Epi-isozizaene synthase from Streptomyces coelicolor (strain ATCC BAA-471 / A3(2) / M145)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
361 a.a.
341 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.3.37
- epi-isozizaene synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate = +-epi-isozizaene + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
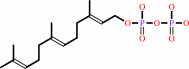 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
=
|
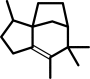 (+)-epi-isozizaene
(+)-epi-isozizaene
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
53:1155-1168
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Reprogramming the chemodiversity of terpenoid cyclization by remolding the active site contour of epi-isozizaene synthase.
|
|
R.Li,
W.K.Chou,
J.A.Himmelberger,
K.M.Litwin,
G.G.Harris,
D.E.Cane,
D.W.Christianson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The class I terpenoid cyclase epi-isozizaene synthase (EIZS) utilizes the
universal achiral isoprenoid substrate, farnesyl diphosphate, to generate
epi-isozizaene as the predominant sesquiterpene cyclization product and at least
five minor sesquiterpene products, making EIZS an ideal platform for the
exploration of fidelity and promiscuity in a terpenoid cyclization reaction. The
hydrophobic active site contour of EIZS serves as a template that enforces a
single substrate conformation, and chaperones subsequently formed carbocation
intermediates through a well-defined mechanistic sequence. Here, we have used
the crystal structure of EIZS as a guide to systematically remold the
hydrophobic active site contour in a library of 26 site-specific mutants.
Remolded cyclization templates reprogram the reaction cascade not only by
reproportioning products generated by the wild-type enzyme but also by
generating completely new products of diverse structure. Specifically, we have
tripled the overall number of characterized products generated by EIZS.
Moreover, we have converted EIZS into six different sesquiterpene synthases:
F96A EIZS is an (E)-β-farnesene synthase, F96W EIZS is a zizaene synthase, F95H
EIZS is a β-curcumene synthase, F95M EIZS is a β-acoradiene synthase, F198L
EIZS is a β-cedrene synthase, and F96V EIZS and W203F EIZS are
(Z)-γ-bisabolene synthases. Active site aromatic residues appear to be hot
spots for reprogramming the cyclization cascade by manipulating the stability
and conformation of critical carbocation intermediates. A majority of mutant
enzymes exhibit only relatively modest 2-100-fold losses of catalytic activity,
suggesting that residues responsible for triggering substrate ionization readily
tolerate mutations deeper in the active site cavity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

