 |
PDBsum entry 4jef
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.45
- thymidylate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dUMP + (6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate = 7,8-dihydrofolate + dTMP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
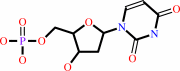 dUMP
dUMP
|
+
|
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
=
|
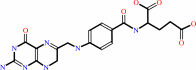 7,8-dihydrofolate
7,8-dihydrofolate
|
+
|
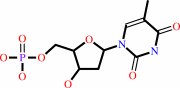 dTMP
dTMP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
58:3572-3581
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Hotspots in an obligate homodimeric anticancer target. Structural and functional effects of interfacial mutations in human thymidylate synthase.
|
|
O.M.Salo-Ahen,
A.Tochowicz,
C.Pozzi,
D.Cardinale,
S.Ferrari,
Y.Boum,
S.Mangani,
R.M.Stroud,
P.Saxena,
H.Myllykallio,
M.P.Costi,
G.Ponterini,
R.C.Wade.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Human thymidylate synthase (hTS), a target for antiproliferative drugs, is an
obligate homodimer. Single-point mutations to alanine at the monomer-monomer
interface may enable the identification of specific residues that delineate
sites for drugs aimed at perturbing the protein-protein interactions critical
for activity. We computationally identified putative hotspot residues at the
interface and designed mutants to perturb the intersubunit interaction. Dimer
dissociation constants measured by a FRET-based assay range from 60 nM for
wild-type hTS up to about 1 mM for single-point mutants and agree with
computational predictions of the effects of these mutations. Mutations that are
remote from the active site retain full or partial activity, although the
substrate KM values were generally higher and the dimer was less stable. The
lower dimer stability of the mutants can facilitate access to the dimer
interface by small molecules and thereby aid the design of inhibitors that bind
at the dimer interface.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

