 |
PDBsum entry 3hjs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3hjs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from rhodococcus opacus 1cp in complex with 4-methylcatechol
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Catechol 1,2-dioxygenase. Chain: a. Synonym: 1,2-ctd. Ec: 1.13.11.1
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Rhodococcus opacus. Nocardia opaca. Organism_taxid: 37919. Strain: 1cp. Other_details: grown on benzoate
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.205
|
R-free:
|
0.255
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
I.Matera,M.Ferraroni,F.Briganti,A.Scozzafava
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
I.Matera
et al.
(2010).
Catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from the Gram-positive Rhodococcus opacus 1CP: quantitative structure/activity relationship and the crystal structures of native enzyme and catechols adducts.
J Struct Biol,
170,
548-564.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-May-09
|
Release date:
|
12-Jan-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P95607
(CATA_RHOOP) -
Catechol 1,2-dioxygenase (Fragment) from Rhodococcus opacus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
270 a.a.
256 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.13.11.1
- catechol 1,2-dioxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Benzoate Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
catechol + O2 = cis,cis-muconate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
catechol
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 88.89% similarity
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
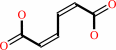 cis,cis-muconate
cis,cis-muconate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Struct Biol
170:548-564
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from the Gram-positive Rhodococcus opacus 1CP: quantitative structure/activity relationship and the crystal structures of native enzyme and catechols adducts.
|
|
I.Matera,
M.Ferraroni,
M.Kolomytseva,
L.Golovleva,
A.Scozzafava,
F.Briganti.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The first crystallographic structures of a catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from a
Gram-positive bacterium Rhodococcus opacus 1CP (Rho 1,2-CTD), a Fe(III) ion
containing enzyme specialized in the aerobic biodegradation of catechols, and
its adducts with catechol, 3-methylcatechol, 4-methylcatechol, pyrogallol
(benzene-1,2,3-triol), 3-chlorocatechol, 4-chlorocatechol, 3,5-dichlorocatechol,
4,5-dichlorocatechol and protocatechuate (3,4-dihydroxybenzoate) have been
determined and analyzed. This study represents the first extensive
characterization of catechols adducts of 1,2-CTDs. The structural analyses
reveal the diverse modes of binding to the active metal iron ion of the tested
catechols thus allowing to identify the residues selectively involved in
recognition of the diverse substrates by this class of enzymes. The comparison
is further extended to the structural and functional characteristics of the
other 1,2-CTDs isolated from Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Moreover
the high structural homology of the present enzyme with the 3-chlorocatechol
1,2-dioxygenase from the same bacterium are discussed in terms of their
different substrate specificity. The catalytic rates for Rho 1,2-CTD conversion
of the tested compounds are also compared with the calculated energies of the
highest occupied molecular orbital (E(HOMO)) of the substrates. A quantitative
relationship (R=0.966) between the ln k(cat) and the calculated electronic
parameter E(HOMO) was obtained for catechol, 3-methylcatechol, 4-methylcatechol,
pyrogallol, 3-chlorocatechol, 4-chlorocatechol. This indicates that for these
substrates the rate-limiting step of the reaction cycle is dependent on their
nucleophilic reactivity. The discrepancies observed in the quantitative
relationship for 3,5-dichlorocatechol, 4,5-dichlorocatechol and protocatechuate
are ascribed to the sterical hindrances leading to the distorted binding of such
catechols observed in the corresponding structures.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.R.Boyd,
N.D.Sharma,
P.J.Stevenson,
M.Blain,
C.McRoberts,
J.T.Hamilton,
J.M.Argudo,
H.Mundi,
L.A.Kulakov,
and
C.C.Allen
(2011).
Dioxygenase-catalysed cis-dihydroxylation of meta-substituted phenols to yield cyclohexenone cis-diol and derived enantiopure cis-triol metabolites.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
9,
1479-1490.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

