
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (dxs) from deinococcus radiodurans
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase, dxp synthase, dxps. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Deinococcus radiodurans. Organism_taxid: 1299. Gene: dxs. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.212
|
R-free:
|
0.272
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Xiang,G.Usunow,G.Lange,M.Busch,L.Tong
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Xiang
et al.
(2007).
Crystal structure of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, a crucial enzyme for isoprenoids biosynthesis.
J Biol Chem,
282,
2676-2682.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Nov-06
|
Release date:
|
26-Dec-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.2.1.7
- 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Non-Mevalonate Terpenoid biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + pyruvate + H+ = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
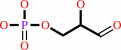 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
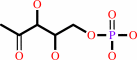 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
TPP)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
282:2676-2682
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, a crucial enzyme for isoprenoids biosynthesis.
|
|
S.Xiang,
G.Usunow,
G.Lange,
M.Busch,
L.Tong.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) is a common precursor for the synthesis of all
isoprenoids, which have important functions in living organisms. IPP is produced
by the mevalonate pathway in archaea, fungi, and animals. In contrast, IPP is
synthesized by a mevalonate-independent pathway in most bacteria, algae, and
plant plastids. 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS) catalyzes the
first and the rate-limiting step of the mevalonate-independent pathway and is an
attractive target for the development of novel antibiotics, antimalarials, and
herbicides. We report here the first structural information on DXS, from
Escherichia coli and Deinococcus radiodurans, in complex with the coenzyme
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP). The structure contains three domains (I, II, and
III), each of which bears homology to the equivalent domains in transketolase
and the E1 subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase. However, DXS has a novel
arrangement of these domains as compared with the other enzymes, such that the
active site of DXS is located at the interface of domains I and II in the same
monomer, whereas that of transketolase is located at the interface of the dimer.
The coenzyme TPP is mostly buried in the complex, but the C-2 atom of its
thiazolium ring is exposed to a pocket that is the substrate-binding site. The
structures identify residues that may have important roles in catalysis, which
have been confirmed by our mutagenesis studies.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
FIGURE 3. Crystal structures of DXS. A, schematic drawing
in stereo of the structure of the D. radiodurans DXS dimer. The
three domains of one monomer are colored cyan, green, and
yellow, respectively, and the linker between domains I and II is
colored red. The other monomer is colored gray. TPP is shown as
a stick model in magenta. The 2-fold axis of the dimer is
vertical. B, structure of E. coli DXS dimer, in the same
orientation and color scheme as A. The images were produced with
PyMol (44).
|
 |
Figure 4.
FIGURE 4. Crystal structures of transketolase and pyruvate
dehydrogenase E1 subunit. A, schematic drawing of the structure
of yeast transketolase dimer (35). B, structure of E. coli
pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit dimer (36). The structures are
viewed in the same orientation as that for DXS in Fig. 3. The
images were produced with PyMol (44).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2007,
282,
2676-2682)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Cordoba,
H.Porta,
A.Arroyo,
C.San Román,
L.Medina,
M.Rodríguez-Concepción,
and
P.León
(2011).
Functional characterization of the three genes encoding 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase in maize.
|
| |
J Exp Bot,
62,
2023-2038.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Côté,
F.Boileau,
V.Roy,
M.Ouellet,
C.Levasseur,
M.J.Morency,
J.E.Cooke,
A.Séguin,
and
J.J.MacKay
(2010).
Gene family structure, expression and functional analysis of HD-Zip III genes in angiosperm and gymnosperm forest trees.
|
| |
BMC Plant Biol,
10,
273.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Gheyi,
L.Rodgers,
R.Romero,
J.M.Sauder,
and
S.K.Burley
(2010).
Mass spectrometry guided in situ proteolysis to obtain crystals for X-ray structure determination.
|
| |
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom,
21,
1795-1801.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Matsue,
H.Mizuno,
T.Tomita,
T.Asami,
M.Nishiyama,
and
T.Kuzuyama
(2010).
The herbicide ketoclomazone inhibits 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase in the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway and shows antibacterial activity against Haemophilus influenzae.
|
| |
J Antibiot (Tokyo),
63,
583-588.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Shaanan,
and
D.M.Chipman
(2009).
Reaction mechanisms of thiamin diphosphate enzymes: new insights into the role of a conserved glutamate residue.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
2447-2453.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Jurgenson,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2009).
The structural and biochemical foundations of thiamin biosynthesis.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
78,
569-603.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.A.Brammer,
and
C.F.Meyers
(2009).
Revealing substrate promiscuity of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase.
|
| |
Org Lett,
11,
4748-4751.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Daum,
S.Herrmann,
B.Wilkinson,
and
A.Bechthold
(2009).
Genes and enzymes involved in bacterial isoprenoid biosynthesis.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
13,
180-188.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Costelloe,
J.M.Ward,
and
P.A.Dalby
(2008).
Evolutionary Analysis of the TPP-Dependent Enzyme Family.
|
| |
J Mol Evol,
66,
36-49.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Dong,
X.Xu,
A.M.Edwards,
C.Chang,
M.Chruszcz,
M.Cuff,
M.Cymborowski,
R.Di Leo,
O.Egorova,
E.Evdokimova,
E.Filippova,
J.Gu,
J.Guthrie,
A.Ignatchenko,
A.Joachimiak,
N.Klostermann,
Y.Kim,
Y.Korniyenko,
W.Minor,
Q.Que,
A.Savchenko,
T.Skarina,
K.Tan,
A.Yakunin,
A.Yee,
V.Yim,
R.Zhang,
H.Zheng,
M.Akutsu,
C.Arrowsmith,
G.V.Avvakumov,
A.Bochkarev,
L.G.Dahlgren,
S.Dhe-Paganon,
S.Dimov,
L.Dombrovski,
P.Finerty,
S.Flodin,
A.Flores,
S.Gräslund,
M.Hammerström,
M.D.Herman,
B.S.Hong,
R.Hui,
I.Johansson,
Y.Liu,
M.Nilsson,
L.Nedyalkova,
P.Nordlund,
T.Nyman,
J.Min,
H.Ouyang,
H.W.Park,
C.Qi,
W.Rabeh,
L.Shen,
Y.Shen,
D.Sukumard,
W.Tempel,
Y.Tong,
L.Tresagues,
M.Vedadi,
J.R.Walker,
J.Weigelt,
M.Welin,
H.Wu,
T.Xiao,
H.Zeng,
and
H.Zhu
(2007).
In situ proteolysis for protein crystallization and structure determination.
|
| |
Nat Methods,
4,
1019-1021.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Scott,
A.Ciulli,
and
C.Abell
(2007).
Coenzyme biosynthesis: enzyme mechanism, structure and inhibition.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
1009-1026.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

