 |
PDBsum entry 2a7n

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2a7n
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.3.15
- (S)-2-hydroxy-acid oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (2S)-2-hydroxycarboxylate + O2 = a 2-oxocarboxylate + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2S)-2-hydroxycarboxylate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
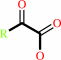 2-oxocarboxylate
2-oxocarboxylate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FMN)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.99.31
- (S)-mandelate dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-mandelate + A = phenylglyoxylate + AH2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
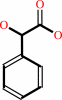 (S)-mandelate
(S)-mandelate
|
+
|
|
=
|
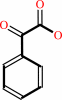 phenylglyoxylate
phenylglyoxylate
|
+
|
AH2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
65:543-552
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of the G81A mutant form of the active chimera of (S)-mandelate dehydrogenase and its complex with two of its substrates.
|
|
N.Sukumar,
A.Dewanti,
A.Merli,
G.L.Rossi,
B.Mitra,
F.S.Mathews.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
(S)-Mandelate dehydrogenase (MDH) from Pseudomonas putida, a membrane-associated
flavoenzyme, catalyzes the oxidation of (S)-mandelate to benzoylformate.
Previously, the structure of a catalytically similar chimera, MDH-GOX2, rendered
soluble by the replacement of its membrane-binding segment with the
corresponding segment of glycolate oxidase (GOX), was determined and found to be
highly similar to that of GOX except within the substituted segments. Subsequent
attempts to cocrystallize MDH-GOX2 with substrate proved unsuccessful. However,
the G81A mutants of MDH and of MDH-GOX2 displayed approximately 100-fold lower
reactivity with substrate and a modestly higher reactivity towards molecular
oxygen. In order to understand the effect of the mutation and to identify the
mode of substrate binding in MDH-GOX2, a crystallographic investigation of the
G81A mutant of the MDH-GOX2 enzyme was initiated. The structures of ligand-free
G81A mutant MDH-GOX2 and of its complexes with the substrates 2-hydroxyoctanoate
and 2-hydroxy-3-indolelactate were determined at 1.6, 2.5 and 2.2 A resolution,
respectively. In the ligand-free G81A mutant protein, a sulfate anion previously
found at the active site is displaced by the alanine side chain introduced by
the mutation. 2-Hydroxyoctanoate binds in an apparently productive mode for
subsequent reaction, while 2-hydroxy-3-indolelactate is bound to the enzyme in
an apparently unproductive mode. The results of this investigation suggest that
a lowering of the polarity of the flavin environment resulting from the
displacement of nearby water molecules caused by the glycine-to-alanine mutation
may account for the lowered catalytic activity of the mutant enzyme, which is
consistent with the 30 mV lower flavin redox potential. Furthermore, the altered
binding mode of the indolelactate substrate may account for its reduced activity
compared with octanoate, as observed in the crystalline state.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of water arrangements in the active
sites of the reduced native and G81A mutant form of MDH-GOX2.
Hydrogen-bonding distances are in Å. (a) Native reduced
enzyme. The network of three water molecules (Wat169^WT,
Wat196^WT, Wat142^WT) and one sulfate ion are shown along with
their interactions with each other, with nearby side chains and
with two other waters, Wat110^WT and Wat375^WT. (b) G81A mutant
enzyme. The three waters (Wat282^GA, Wat283^GA and Wat284^GA)
displace the native sulfate ion and three-water network and take
up new positions. Wat54^GA is in the same position as Wat97^WT
of the native enzyme. R is a ribityl phosphate group and R' is a
Leu side chain.
|
 |
Figure 8.
Figure 8 Schematic diagram of the active-site structures of the
2-hydroxyoctanoate and 3-indolelactate complexes of the G81A
mutant form of MDH-GOX2. Hydrogen-bonding interactions between
the carboxylate and hydroxyl O atoms and nearby side chains or
water molecules are shown as dashed lines and the distances are
in Å. Residues making hydrophobic contact to the ligand
are indicated as shown at the bottom right. C atoms are black, O
atoms red and N atoms cyan. Covalent bonds within the ligand are
drawn with pink lines, while those within the protein are drawn
with orange lines. (a) The 2-hydroxyoctanoate-G81A complex. The
ligand is labeled `Octanoate'. (b) The
(D,L)-2-hydroxy-3-indolelactate-G81A complex. The ligand is
labeled `ILAC'. This diagram was prepared using the program
LIGPLOT (Wallace et al., 1995[Wallace, A. C., Laskowski, R. A. &
Thornton, J. M. (1995). Protein Eng. 8, 127-134.]).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2009,
65,
543-552)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

