 |
PDBsum entry 1q9s

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.26
- riboflavin kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
riboflavin + ATP = FMN + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
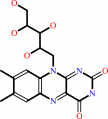 riboflavin
riboflavin
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+) or Zn(2+) or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
42:12532-12538
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Ligand binding-induced conformational changes in riboflavin kinase: structural basis for the ordered mechanism.
|
|
S.Karthikeyan,
Q.Zhou,
A.L.Osterman,
H.Zhang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Riboflavin kinase (RFK) is an essential enzyme catalyzing the phosphorylation of
riboflavin (vitamin B(2)) in the presence of ATP and Mg(2+) to form the active
cofactor FMN, which can be further converted to FAD. Previously, the crystal
structures of RFKs from human and Schizosaccharomyces pombe have been determined
in the apo form and in complex with MgADP. These structures revealed that RFK
adopts a novel kinase fold and utilizes a unique nucleotide binding site. The
structures of the flavin-bound RFK obtained by soaking pre-existing crystals
were also reported. Because of crystal packing restraints, these flavin-bound
RFK complexes adopt conformations nearly identical with that of corresponding
flavin-free structures. Here we report the structure of human RFK cocrystallized
with both MgADP and FMN. Drastic conformational changes associated with flavin
binding are observed primarily at the so-called Flap I and Flap II loop regions.
As a result, the bound FMN molecule now interacts with the enzyme extensively
and is well-ordered. Residues from Flap II interact with Flap I and shield the
FMN molecule from the solvent. The conformational changes in Flap I resulted in
a new Mg(2+) coordination pattern in which a FMN phosphate oxygen and Asn36 side
chain carbonyl are directly coordinating to the Mg(2+) ion. The proposed
catalytic base Glu86 is well-positioned for activation of the O5' hydroxyl group
of riboflavin for the phosphoryl transfer reaction. The structural data obtained
so far on human and yeast RFK complexes provide a rationale for the ordered
kinetic mechanism of RFK.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
T.Li,
H.L.Bonkovsky,
and
J.T.Guo
(2011).
Structural analysis of heme proteins: implications for design and prediction.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
11,
13.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Brylinski,
and
J.Skolnick
(2010).
Q-Dock(LHM): Low-resolution refinement for ligand comparative modeling.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
31,
1093-1105.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Frago,
A.Velázquez-Campoy,
and
M.Medina
(2009).
The Puzzle of Ligand Binding to Corynebacterium ammoniagenes FAD Synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
6610-6619.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.J.Sandoval,
Y.Zhang,
and
S.Roje
(2008).
Flavin Nucleotide Metabolism in Plants: MONOFUNCTIONAL ENZYMES SYNTHESIZE FAD IN PLASTIDS.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
30890-30900.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Brylinski,
and
J.Skolnick
(2008).
What is the relationship between the global structures of apo and holo proteins?
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
363-377.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Frago,
M.Martínez-Júlvez,
A.Serrano,
and
M.Medina
(2008).
Structural analysis of FAD synthetase from Corynebacterium ammoniagenes.
|
| |
BMC Microbiol,
8,
160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ammelburg,
M.D.Hartmann,
S.Djuranovic,
V.Alva,
K.K.Koretke,
J.Martin,
G.Sauer,
V.Truffault,
K.Zeth,
A.N.Lupas,
and
M.Coles
(2007).
A CTP-dependent archaeal riboflavin kinase forms a bridge in the evolution of cradle-loop barrels.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
1577-1590.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.J.Sandoval,
and
S.Roje
(2005).
An FMN hydrolase is fused to a riboflavin kinase homolog in plants.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
38337-38345.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Cheek,
K.Ginalski,
H.Zhang,
and
N.V.Grishin
(2005).
A comprehensive update of the sequence and structure classification of kinases.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
5,
6.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Li,
R.M.Wynn,
M.Machius,
J.L.Chuang,
S.Karthikeyan,
D.R.Tomchick,
and
D.T.Chuang
(2004).
Cross-talk between thiamin diphosphate binding and phosphorylation loop conformation in human branched-chain alpha-keto acid decarboxylase/dehydrogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
32968-32978.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

