
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crosstalk between cofactor binding and the phosphorylation loop conformation in the bckd machine
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase alpha subunit. Chain: a. Synonym: mitochondrial precursor, branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase e1, component alpha chain, bckdh e1-alpha, bckde1a. Engineered: yes. 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase beta subunit. Chain: b. Synonym: mitochondrial precursor, branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase e1, component beta chain, bckdh e1-beta.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Groes. Other_details: expression system used bl-21 cells with overexpressing groel and groes
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from PDB file)
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.158
|
R-free:
|
0.183
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Li,R.M.Wynn,M.Machius,J.L.Chuang,S.Karthikeyan,D.R.Tomchick, D.T.Chuang
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.Li
et al.
(2004).
Cross-talk between thiamin diphosphate binding and phosphorylation loop conformation in human branched-chain alpha-keto acid decarboxylase/dehydrogenase.
J Biol Chem,
279,
32968-32978.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Apr-04
|
Release date:
|
03-Jun-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.1.2.4.4
- 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase (2-methylpropanoyl-transferring).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Oxo-acid dehydrogenase complexes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-[(R)-lipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein] + 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H+ = N6-[(R)-S(8)-2-methylpropanoyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein] + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-[(R)-lipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
N(6)-[(R)-S(8)-2-methylpropanoyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
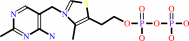 Thiamine diphosphate
Thiamine diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:32968-32978
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Cross-talk between thiamin diphosphate binding and phosphorylation loop conformation in human branched-chain alpha-keto acid decarboxylase/dehydrogenase.
|
|
J.Li,
R.M.Wynn,
M.Machius,
J.L.Chuang,
S.Karthikeyan,
D.R.Tomchick,
D.T.Chuang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The decarboxylase/dehydrogenase (E1b) component of the 4-megadalton human
branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase (BCKD) metabolic machine is a
thiamin diphosphate (ThDP)-dependent enzyme with a heterotetrameric
cofactor-binding fold. The E1b component catalyzes the decarboxylation of
alpha-keto acids and the subsequent reductive acylation of the lipoic
acid-bearing domain (LBD) from the 24-meric transacylase (E2b) core. In the
present study, we show that the binding of cofactor ThDP to the E1b active site
induces a disorder-to-order transition of the conserved phosphorylation loop
carrying the two phosphorylation sites Ser(292)-alpha and Ser(302)-alpha, as
deduced from the 1.80-1.85 A apoE1b and holoE1b structures. The induced loop
conformation is essential for the recognition of lipoylated LBD to initiate
E1b-catalyzed reductive acylation. Alterations of invariant Arg(287)-alpha,
Asp(295)-alpha, Tyr(300)-alpha, and Arg(301)-alpha that form a hydrogen-bonding
network in the phosphorylation loop result in the disordering of the loop
conformation as elucidated by limited proteolysis, accompanied by the impaired
binding and diminished reductive acylation of lipoylated LBD. In contrast,
k(cat) values for E1b-catalyzed decarboxylation of the alpha-keto acid are
higher in these E1b mutants than in wild-type E1b, with higher K(m) values for
the substrate in the mutants. ThDP binding that orders the loop prevents
phosphorylation of E1b by the BCKD kinase and averts the inactivation of
wild-type E1b, but not the above mutants, by this covalent modification. Our
results establish that the cross-talk between the bound ThDP and the
phosphorylation loop conformation serves as a feed-forward switch for multiple
reaction steps in the BCKD metabolic machine.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
FIG. 3. Substitutions of residues participating in the
hydrogen-bonding network result in markedly decreased reductive
acylation (Reaction 3) activity. Invariant residues (Arg287-
 ,
Asp295- ,
Asp295-  , Tyr300- , Tyr300-  , and
Arg301- , and
Arg301-  ) that form the
hydrogen-bonding network were changed to alanine or
phenylalanine in the case of Tyr300- ) that form the
hydrogen-bonding network were changed to alanine or
phenylalanine in the case of Tyr300-  . Reductive acylation
of lip-LBD catalyzed by wild-type or mutant E1b was measured
with [U-14C]KIV as a substrate as described under "Experimental
Procedures." Activity for reductive acylation is expressed as
percent relative to the wild type (2.3 min-1). The nonspecific
radioactivity incorporated into nonlipoylated LBD and the
wild-type or mutant E1b protein served as a blank. Results are
averages of two independent experiments. . Reductive acylation
of lip-LBD catalyzed by wild-type or mutant E1b was measured
with [U-14C]KIV as a substrate as described under "Experimental
Procedures." Activity for reductive acylation is expressed as
percent relative to the wild type (2.3 min-1). The nonspecific
radioactivity incorporated into nonlipoylated LBD and the
wild-type or mutant E1b protein served as a blank. Results are
averages of two independent experiments.
|
 |
Figure 7.
FIG. 7. ThDP inhibits the phosphorylation of wild-type but
not mutant E1b. A, the reaction mixture contained human apoE1b
protein, lipoylated E2b, and maltose-binding protein-tagged rat
BCKD kinase in the absence and presence of increasing ThDP
concentrations. The phosphorylation reaction was initiated by
adding 0.4 mM [  -32P]ATP and was
incubated at 25 °C for 1 min. The reaction mixtures were
separated by SDS-PAGE. 32P incorporation into the -32P]ATP and was
incubated at 25 °C for 1 min. The reaction mixtures were
separated by SDS-PAGE. 32P incorporation into the  subunit
of E1b proteins was quantified by PhosphorImaging. The
PhosphorImage counts in wild-type and each mutant E1b in the
absence of ThDP was set as 100% with respect to the
corresponding E1b protein. B, PhosphorImaging of 32P
incorporation into the subunit
of E1b proteins was quantified by PhosphorImaging. The
PhosphorImage counts in wild-type and each mutant E1b in the
absence of ThDP was set as 100% with respect to the
corresponding E1b protein. B, PhosphorImaging of 32P
incorporation into the  subunit of the S302A- subunit of the S302A-
 E1b
mutant and E1b double mutants containing the S302A- E1b
mutant and E1b double mutants containing the S302A-  mutation
and a second mutation in the hydrogen-bonding network. The
phosphorylation was carried out in the absence of ThDP. mutation
and a second mutation in the hydrogen-bonding network. The
phosphorylation was carried out in the absence of ThDP.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
32968-32978)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.Brunetti-Pierri,
B.Lanpher,
A.Erez,
E.A.Ananieva,
M.Islam,
J.C.Marini,
Q.Sun,
C.Yu,
M.Hegde,
J.Li,
R.M.Wynn,
D.T.Chuang,
S.Hutson,
and
B.Lee
(2011).
Phenylbutyrate therapy for maple syrup urine disease.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
20,
631-640.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Islam,
M.Nautiyal,
R.M.Wynn,
J.A.Mobley,
D.T.Chuang,
and
S.M.Hutson
(2010).
Branched-chain amino acid metabolon: interaction of glutamate dehydrogenase with the mitochondrial branched-chain aminotransferase (BCATm).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
265-276.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Y.Pei,
K.M.Erixon,
B.F.Luisi,
and
F.J.Leeper
(2010).
Structural insights into the prereaction state of pyruvate decarboxylase from Zymomonas mobilis .
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
1727-1736.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kale,
and
F.Jordan
(2009).
Conformational ensemble modulates cooperativity in the rate-determining catalytic step in the E1 component of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
33122-33129.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kato,
R.M.Wynn,
J.L.Chuang,
S.C.Tso,
M.Machius,
J.Li,
and
D.T.Chuang
(2008).
Structural basis for inactivation of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation: role of disordered phosphorylation loops.
|
| |
Structure,
16,
1849-1859.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.I.Bunik,
and
D.Degtyarev
(2008).
Structure-function relationships in the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase family: substrate-specific signatures and functional predictions for the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
874-890.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.E.Homanics,
K.Skvorak,
C.Ferguson,
S.Watkins,
and
H.S.Paul
(2006).
Production and characterization of murine models of classic and intermediate maple syrup urine disease.
|
| |
BMC Med Genet,
7,
33.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Stetefeld,
M.Jenny,
and
P.Burkhard
(2006).
Intersubunit signaling in glutamate-1-semialdehyde-aminomutase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
13688-13693.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Wynn,
M.Kato,
M.Machius,
J.L.Chuang,
J.Li,
D.R.Tomchick,
and
D.T.Chuang
(2004).
Molecular mechanism for regulation of the human mitochondrial branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
2185-2196.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

