 |
PDBsum entry 1q9d

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase complexed with a new allosteric site inhibitor (i-state)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: d-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphohydrolase, fbpase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sus scrofa. Pig. Organism_taxid: 9823. Tissue: liver. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from
)
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.35Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.191
|
R-free:
|
0.246
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.B.Honzatko,J.Y.Choe
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.Y.Choe
et al.
(2003).
Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by a new class of allosteric effectors.
J Biol Chem,
278,
51176-51183.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-Aug-03
|
Release date:
|
02-Dec-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00636
(F16P1_PIG) -
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 from Sus scrofa
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
338 a.a.
328 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.11
- fructose-bisphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (later stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
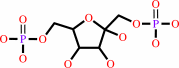 beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
278:51176-51183
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by a new class of allosteric effectors.
|
|
J.Y.Choe,
S.W.Nelson,
K.L.Arienti,
F.U.Axe,
T.L.Collins,
T.K.Jones,
R.D.Kimmich,
M.J.Newman,
K.Norvell,
W.C.Ripka,
S.J.Romano,
K.M.Short,
D.H.Slee,
H.J.Fromm,
R.B.Honzatko.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A highly constrained pseudo-tetrapeptide (OC252-324) further defines a new
allosteric binding site located near the center of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
In a crystal structure, pairs of inhibitory molecules bind to opposite faces of
the enzyme tetramer. Each ligand molecule is in contact with three of four
subunits of the tetramer, hydrogen bonding with the side chain of Asp187 and the
backbone carbonyl of residue 71, and electrostatically interacting with the
backbone carbonyl of residue 51. The ligated complex adopts a quaternary
structure between the canonical R- and T-states of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase,
and yet a dynamic loop essential for catalysis (residues 52-72) is in a
conformation identical to that of the T-state enzyme. Inhibition by the
pseudo-tetrapeptide is cooperative (Hill coefficient of 2), synergistic with
both AMP and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, noncompetitive with respect to Mg2+, and
uncompetitive with respect to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. The ligand dramatically
lowers the concentration at which substrate inhibition dominates the kinetics of
fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Elevated substrate concentrations employed in
kinetic screens may have facilitated the discovery of this uncompetitive
inhibitor. Moreover, the inhibitor could mimic an unknown natural effector of
fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, as it interacts strongly with a conserved residue
of undetermined functional significance.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
FIG. 3. Kinetic mechanism of inhibition of FBPase by OC252.
A, data are taken at 1-20 µM F16P[2] in 50 mM Hepes, pH
7.5, with 5 mM MgCl[2]. Curves are fits to the data using
Equation 3. B, data are taken at 0.1-5 mM Mg2+ (corrected for
chelation by EDTA) in 50 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, with 20 µM
F16P[2]. Curves are fits to the data using Equation 4.
|
 |
Figure 4.
FIG. 4. OC252-FBPase complex. The top panel gives
orthogonal views of the complex showing FBPase as a ribbon with
atoms of Mg2+, F6P, P[i], and OC252 as spheres. The bottom panel
shows electron density covering a pair of OC252 molecules from
an omit map contoured at a level of 1  with a cut-off radius
of 1 Å (bottom). This drawing was prepared with MOLSCRIPT
(41). with a cut-off radius
of 1 Å (bottom). This drawing was prepared with MOLSCRIPT
(41).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2003,
278,
51176-51183)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Illingworth,
P.D.Scott,
K.E.Parkes,
C.R.Snell,
M.P.Campbell,
and
C.A.Reynolds
(2010).
Connectivity and binding-site recognition: applications relevant to drug design.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
31,
2677-2688.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Mohler,
Y.He,
Z.Wu,
D.J.Hwang,
and
D.D.Miller
(2009).
Recent and emerging anti-diabetes targets.
|
| |
Med Res Rev,
29,
125-195.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Lu,
D.Dunaway-Mariano,
and
K.N.Allen
(2008).
The catalytic scaffold of the haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase enzyme superfamily acts as a mold for the trigonal bipyramidal transition state.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
5687-5692.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Combettes,
and
C.Kargar
(2007).
Newly approved and promising antidiabetic agents.
|
| |
Therapie,
62,
293-310.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Erion,
P.D.van Poelje,
Q.Dang,
S.R.Kasibhatla,
S.C.Potter,
M.R.Reddy,
K.R.Reddy,
T.Jiang,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(2005).
MB06322 (CS-917): A potent and selective inhibitor of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase for controlling gluconeogenesis in type 2 diabetes.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
7970-7975.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

