 |
PDBsum entry 1itz

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Maize transketolase in complex with tpp
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Transketolase. Chain: a, b, c. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Zea mays. Organism_taxid: 4577. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.166
|
R-free:
|
0.200
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Gerhardt,S.Echt,G.Bader,J.Freigang,M.Busch,A.Bacher,R.Huber, M.Fischer
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.Gerhardt
et al.
(2003).
Structure and properties of an engineered transketolase from maize.
Plant Physiol,
132,
1941-1949.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Feb-02
|
Release date:
|
15-Feb-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q7SIC9
(TKTC_MAIZE) -
Transketolase, chloroplastic from Zea mays
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
675 a.a.
666 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.2.1.1
- transketolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate = aldehydo-D- ribose 5-phosphate + D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
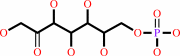 D-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate
D-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate
|
+
|
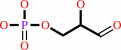 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
=
|
aldehydo-D- ribose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
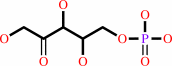 D-xylulose 5-phosphate
D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
TPP)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Plant Physiol
132:1941-1949
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and properties of an engineered transketolase from maize.
|
|
S.Gerhardt,
S.Echt,
M.Busch,
J.Freigang,
G.Auerbach,
G.Bader,
W.F.Martin,
A.Bacher,
R.Huber,
M.Fischer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The gene specifying plastid transketolase (TK) of maize (Zea mays) was cloned
from a cDNA library by southern blotting using a heterologous probe from sorghum
(Sorghum bicolor). A recombinant fusion protein comprising thioredoxin of
Escherichia coli and mature TK of maize was expressed at a high level in E. coli
and cleaved with thrombin, affording plastid TK. The protein in complex with
thiamine pyrophoshate was crystallized, and its structure was solved by
molecular replacement. The enzyme is a C2 symmetric homodimer closely similar to
the enzyme from yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Each subunit is folded into
three domains. The two topologically equivalent active sites are located in the
subunit interface region and resemble those of the yeast enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.C.Willige,
M.Kutzer,
F.Tebartz,
and
D.Bartels
(2009).
Subcellular localization and enzymatic properties of differentially expressed transketolase genes isolated from the desiccation tolerant resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum.
|
| |
Planta,
229,
659-666.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Domain,
X.R.Bina,
and
S.B.Levy
(2007).
Transketolase A, an enzyme in central metabolism, derepresses the marRAB multiple antibiotic resistance operon of Escherichia coli by interaction with MarR.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
66,
383-394.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Izawa,
M.Kishimoto,
M.Konishi,
T.Omasa,
S.Shioya,
and
H.Ohtake
(2006).
Recognition of culture state using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis with an artificial neural network.
|
| |
Proteomics,
6,
3730-3738.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.A.Esakova,
L.E.Meshalkina,
and
G.A.Kochetov
(2005).
Effects of transketolase cofactors on its conformation and stability.
|
| |
Life Sci,
78,
8.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

