 |
PDBsum entry 1gbn

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.13
- ornithine aminotransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2-oxocarboxylate + L-ornithine = L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + an L-alpha-amino acid
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
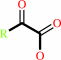 2-oxocarboxylate
2-oxocarboxylate
|
+
|
L-ornithine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 58.33% similarity
|
=
|
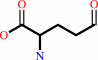 L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
|
+
|
L-alpha-amino acid
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
5:1067-1075
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Human ornithine aminotransferase complexed with L-canaline and gabaculine: structural basis for substrate recognition.
|
|
S.A.Shah,
B.W.Shen,
A.T.Brünger.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: Ornithine aminotransferase (OAT) is a 45 kDa pyridoxal-5'-phosphate
(PLP)-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of L-ornithine and
2-oxoglutarate to glutamate-delta-semialdehyde and glutamic acid, respectively.
In humans, loss of OAT function causes an accumulation of ornithine that results
in gyrate atrophy of the choroid and retina, a disease that progressively leads
to blindness. In an effort to learn more about the structural basis of this
enzyme's function, we have determined the X-ray structures of OAT in complex
with two enzyme-activated suicide substrates: L-canaline, an ornithine analog,
and gabaculine, an irreversible inhibitor of several related aminotransferases.
RESULTS: The structures of human OAT bound to the inhibitors gabaculine and
L-canaline were solved to 2.3 A at 110K by difference Fourier techniques. Both
inhibitors coordinate similarly in the active site, binding covalently to the
PLP cofactor and causing a 20 degrees rotation in the cofactor tilt relative to
the ligand-free form. Aromatic-aromatic interactions occur between the bound
gabaculine molecule and active-site residues Tyr85 and Phe177, whereas Tyr55 and
Arg180 provide specific contacts to the alpha-amino and carboxyl groups of
L-canaline. CONCLUSIONS: The OAT-L-canaline complex structure implicates Tyr55
and Arg180 as the residues involved in coordinating with the natural substrate
ornithine during normal enzyme turnover. This correlates well with two
enzyme-inactivating point mutations associated with gyrate atrophy, Tyr55-->His
and Arg180-->Thr. The OAT-gabaculine complex provides the first structural
evidence that the potency of the inhibitor is due to energetically favourable
aromatic interactions with residues in the active site. This aromatic-binding
mode may be relevant to structure-based drug design efforts against other
omega-aminotransferase targets, such as GABA aminotransferase.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Substrate and inhibitor chemical structures.
Chemical structures of (a) Image -Ornithine, (b)
a-amino-g-amino-oxybutyric acid ( Image -canaline) and (c)
5-amino-1,3,-cyclohexadienyl carboxylic acid (gabaculine).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1997,
5,
1067-1075)
copyright 1997.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Tanner
(2008).
Structural biology of proline catabolism.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
35,
719-730.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Stránská,
D.Kopecný,
M.Tylichová,
J.Snégaroff,
and
M.Sebela
(2008).
Ornithine delta-aminotransferase: An enzyme implicated in salt tolerance in higher plants.
|
| |
Plant Signal Behav,
3,
929-935.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Rajaram,
P.Ratna Prasuna,
H.S.Savithri,
and
M.R.Murthy
(2008).
Structure of biosynthetic N-acetylornithine aminotransferase from Salmonella typhimurium: studies on substrate specificity and inhibitor binding.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
429-441.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Rajaram,
K.Prasad,
P.Ratna Prasuna,
N.Ramachandra,
S.R.Bharath,
H.S.Savithri,
and
M.R.Murthy
(2006).
Cloning, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the biosynthetic N-acetylornithine aminotransferases from Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
980-983.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Tocilj,
J.D.Schrag,
Y.Li,
B.L.Schneider,
L.Reitzer,
A.Matte,
and
M.Cygler
(2005).
Crystal structure of N-succinylarginine dihydrolase AstB, bound to substrate and product, an enzyme from the arginine catabolic pathway of Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
15800-15808.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Drahl,
B.F.Cravatt,
and
E.J.Sorensen
(2005).
Protein-reactive natural products.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
44,
5788-5809.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.W.McKee,
L.D.Kanbi,
K.L.Childs,
R.W.Grosse-Kunstleve,
P.D.Adams,
J.C.Sacchettini,
and
T.R.Ioerger
(2005).
FINDMOL: automated identification of macromolecules in electron-density maps.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1514-1520.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Eliot,
and
J.F.Kirsch
(2004).
Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
73,
383-415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Terwilliger
(2003).
Improving macromolecular atomic models at moderate resolution by automated iterative model building, statistical density modification and refinement.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1174-1182.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.W.Noland,
J.M.Newman,
J.Hendle,
J.Badger,
J.A.Christopher,
J.Tresser,
M.D.Buchanan,
T.A.Wright,
M.E.Rutter,
W.E.Sanderson,
H.J.Müller-Dieckmann,
K.S.Gajiwala,
and
S.G.Buchanan
(2002).
Structural studies of Salmonella typhimurium ArnB (PmrH) aminotransferase: a 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose lipopolysaccharide-modifying enzyme.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
1569-1580.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Cheong,
J.C.Escalante-Semerena,
and
I.Rayment
(2002).
Structural studies of the L-threonine-O-3-phosphate decarboxylase (CobD) enzyme from Salmonella enterica: the apo, substrate, and product-aldimine complexes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9079-9089.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Sandmark,
S.Mann,
A.Marquet,
and
G.Schneider
(2002).
Structural basis for the inhibition of the biosynthesis of biotin by the antibiotic amiclenomycin.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
43352-43358.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Schneider,
H.Käck,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(2000).
The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
R1-R6.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Poupon,
F.Jebai,
G.Labesse,
F.Gros,
J.Thibault,
J.P.Mornon,
and
M.Krieger
(1999).
Structure modelling and site-directed mutagenesis of the rat aromatic L-amino acid pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent decarboxylase: a functional study.
|
| |
Proteins,
37,
191-203.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Storici,
G.Capitani,
D.De Biase,
M.Moser,
R.A.John,
J.N.Jansonius,
and
T.Schirmer
(1999).
Crystal structure of GABA-aminotransferase, a target for antiepileptic drug therapy.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
8628-8634.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.N.Jansonius
(1998).
Structure, evolution and action of vitamin B6-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
8,
759-769.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Jhee,
P.McPhie,
H.S.Ro,
and
E.W.Miles
(1998).
Tryptophan synthase mutations that alter cofactor chemistry lead to mechanism-based inactivation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
14591-14604.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

