 |
PDBsum entry 1ynh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of n-succinylarginine dihydrolase, astb, bound to substrate and product, an enzyme from the arginine catabolic pathway of escherichia coli
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Succinylarginine dihydrolase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: n-succinylarginine dihydrolase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from
)
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.95Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.219
|
R-free:
|
0.246
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Tocilj,J.D.Schrag,Y.Li,B.L.Schneider,L.Reitzer,A.Matte,M.Cygler
|
Key ref:

|
 |
A.Tocilj
et al.
(2005).
Crystal structure of N-succinylarginine dihydrolase AstB, bound to substrate and product, an enzyme from the arginine catabolic pathway of Escherichia coli.
J Biol Chem,
280,
15800-15808.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Jan-05
|
Release date:
|
22-Mar-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P76216
(ASTB_ECOLI) -
N-succinylarginine dihydrolase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
447 a.a.
439 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.3.23
- N-succinylarginine dihydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N2-succinyl-L-arginine + 2 H2O + 2 H+ = N2-succinyl-L-ornithine + 2 NH4+ + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
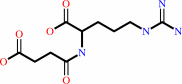 N(2)-succinyl-L-arginine
N(2)-succinyl-L-arginine
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
=
|
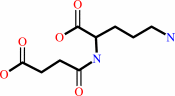 N(2)-succinyl-L-ornithine
N(2)-succinyl-L-ornithine
|
+
|
2
×
NH4(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
280:15800-15808
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of N-succinylarginine dihydrolase AstB, bound to substrate and product, an enzyme from the arginine catabolic pathway of Escherichia coli.
|
|
A.Tocilj,
J.D.Schrag,
Y.Li,
B.L.Schneider,
L.Reitzer,
A.Matte,
M.Cygler.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The ammonia-producing arginine succinyltransferase pathway is the major pathway
in Escherichia coli and related bacteria for arginine catabolism as a sole
nitrogen source. This pathway consists of five steps, each catalyzed by a
distinct enzyme. Here we report the crystal structure of N-succinylarginine
dihydrolase AstB, the second enzyme of the arginine succinyltransferase pathway,
providing the first structural insight into enzymes from this pathway. The
enzyme exhibits a pseudo 5-fold symmetric alpha/beta propeller fold of
circularly arranged betabetaalphabeta modules enclosing the active site. The
crystal structure indicates clearly that this enzyme belongs to the
amidinotransferase (AT) superfamily and that the active site contains a
Cys-His-Glu triad characteristic of the AT superfamily. Structures of the
complexes of AstB with the reaction product and a C365S mutant with bound the
N-succinylarginine substrate suggest a catalytic mechanism that consists of two
cycles of hydrolysis and ammonia release, with each cycle utilizing a mechanism
similar to that proposed for arginine deiminases. Like other members of the AT
superfamily of enzymes, AstB possesses a flexible loop that is disordered in the
absence of substrate and assumes an ordered conformation upon substrate binding,
shielding the ligand from the bulk solvent, thereby controlling substrate access
and product release.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIG. 1. The AST pathway (after EcoCyc (3)).
|
 |
Figure 4.
FIG. 4. Structural comparison of E. coli AstB with a
representative amidinotransferase. a, the active site residues
of the AstB C365S mutant with the N-succinylarginine substrate.
In this figure Ser365 was replaced by the native Cys365 taken
from the native structure. The oxygen atoms are red, nitrogen
atoms are blue, sulfur atoms are yellow, and carbon atoms are
gray. The hydrogen bonds between the ligand and protein atoms
are marked by green dashed lines. b, the active site of arginine
deaminase (Protein Data Bank codes 1LXY [PDB]
or 1S9R) with the reaction product in a similar orientation to
that shown in a.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2005,
280,
15800-15808)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
T.W.Linsky,
A.F.Monzingo,
E.M.Stone,
J.D.Robertus,
and
W.Fast
(2008).
Promiscuous partitioning of a covalent intermediate common in the pentein superfamily.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
15,
467-475.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Shirai,
Y.Mokrab,
and
K.Mizuguchi
(2006).
The guanidino-group modifying enzymes: structural basis for their diversity and commonality.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
1010-1023.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

