 |
PDBsum entry 1e9x

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1e9x
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.15.36
- sterol 14alpha-demethylase (ferredoxin).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 14alpha-methyl steroid + 6 reduced [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin] + 3 O2 + 5 H+ = a Delta14 steroid + formate + 6 oxidized [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin] + 4 H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
14alpha-methyl steroid
|
+
|
6
×
reduced [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin]
|
+
|
 3
×
O2
3
×
O2
|
+
|
5
×
H(+)
|
=
|
Delta(14) steroid
|
+
|
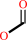 formate
formate
|
+
|
6
×
oxidized [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin]
|
+
|
4
×
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
98:3068-3073
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of cytochrome P450 14alpha -sterol demethylase (CYP51) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in complex with azole inhibitors.
|
|
L.M.Podust,
T.L.Poulos,
M.R.Waterman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cytochrome P450 14alpha-sterol demethylases (CYP51) are essential enzymes in
sterol biosynthesis in eukaryotes. CYP51 removes the 14alpha-methyl group from
sterol precursors such as lanosterol, obtusifoliol, dihydrolanosterol, and
24(28)-methylene-24,25-dihydrolanosterol. Inhibitors of CYP51 include triazole
antifungal agents fluconazole and itraconazole, drugs used in treatment of
topical and systemic mycoses. The 2.1- and 2.2-A crystal structures reported
here for 4-phenylimidazole- and fluconazole-bound CYP51 from Mycobacterium
tuberculosis (MTCYP51) are the first structures of an authentic P450 drug
target. MTCYP51 exhibits the P450 fold with the exception of two striking
differences-a bent I helix and an open conformation of BC loop-that define an
active site-access channel running along the heme plane perpendicular to the
direction observed for the substrate entry in P450BM3. Although a channel
analogous to that in P450BM3 is evident also in MTCYP51, it is not open at the
surface. The presence of two different channels, with one being open to the
surface, suggests the possibility of conformationally regulated
substrate-in/product-out openings in CYP51. Mapping mutations identified in
Candida albicans azole-resistant isolates indicates that azole resistance in
fungi develops in protein regions involved in orchestrating passage of CYP51
through different conformational stages along the catalytic cycle rather than in
residues directly contacting fluconazole. These new structures provide a basis
for rational design of new, more efficacious antifungal agents as well as
insight into the molecular mechanism of P450 catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Ribbon representation of the MTCYP51 structures
with the inhibitors bound. Front (A) and top (B) views of the of
4-PI- (yellow) and FLU- (blue) bound MTCYP51 superimposed with
an rms deviation of 0.45 Å. Superimpositions for all
figures were done by using two-step fitting as implemented in
SWISS-PDB VIEWER (33). The first step was performed by using
entire structures; for the second step, an rms-deviation cutoff
of 1.8 Å was used to select the most structurally
homologous regions for subsequent fitting. The second round
results in better fitting of the most homologous regions and
further divergence of less homologous regions. Heme, red; 4-PI,
orange; FLU, light-blue. The I helix is shown also in red. A
large cavity of 2,600 Å3, shown in blue, leads from the
active site to the molecular surface along the protein domain
interface (channel 2). Structural elements significantly
deviating among P450 structures are labeled in black, and  -sheets that
are part of the putative substrate-binding site are labeled in
red. All figures, if not otherwise indicated, are generated by
using SWISS-PDB VIEWER (33). -sheets that
are part of the putative substrate-binding site are labeled in
red. All figures, if not otherwise indicated, are generated by
using SWISS-PDB VIEWER (33).
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Superimposition and alignment of the I helix in
known P450 structures. Front (A) and top (B) views of the I
helix from superimposed P450 structures assigned in
sequence-alignment shown in C. Each structure was superimposed
pairwise with MTCYP51 so that rms deviation for the most
structurally homologous regions did not exceed 1.2 Å. (C)
Alignment of the I helix sequences performed by using BCM SEARCH
LAUNCHER (34). Residues identical or homologous in at least half
of the compared sequences are shaded in dark or light,
respectively. The position of conserved glycine is marked
according to MTCYP51 sequence (P77901).
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Kim,
Y.R.Lim,
S.O.Ohk,
B.J.Kim,
and
Y.J.Chun
(2011).
Functional expression and characterization of CYP51 from dandruff-causing Malassezia globosa.
|
| |
FEMS Yeast Res,
11,
80-87.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Leroux,
and
A.S.Walker
(2011).
Multiple mechanisms account for resistance to sterol 14α-demethylation inhibitors in field isolates of Mycosphaerella graminicola.
|
| |
Pest Manag Sci,
67,
44-59.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Guillon,
C.Logé,
F.Pagniez,
V.Ferchaud-Roucher,
M.Duflos,
C.Picot,
and
P.Le Pape
(2011).
Synthesis and in vitro antifungal evaluation of 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1-[(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)methylamino]-3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ols.
|
| |
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem,
26,
261-269.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Guillon,
F.Pagniez,
F.Giraud,
D.Crépin,
C.Picot,
M.Le Borgne,
F.Morio,
M.Duflos,
C.Logé,
and
P.Le Pape
(2011).
Design, synthesis, and in vitro antifungal activity of 1-[(4-substituted-benzyl)methylamino]-2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ols.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
6,
816-825.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Li,
J.Shen,
G.Liu,
Y.Tang,
and
T.Hoshino
(2011).
Exploring coumarin egress channels in human cytochrome P450 2A6 by random acceleration and steered molecular dynamics simulations.
|
| |
Proteins,
79,
271-281.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Warrilow,
C.M.Martel,
J.E.Parker,
N.Melo,
D.C.Lamb,
W.D.Nes,
D.E.Kelly,
and
S.L.Kelly
(2010).
Azole binding properties of Candida albicans sterol 14-alpha demethylase (CaCYP51).
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
54,
4235-4245.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Sheng,
S.Chen,
H.Ji,
G.Dong,
X.Che,
W.Wang,
Z.Miao,
J.Yao,
J.Lü,
W.Guo,
and
W.Zhang
(2010).
Evolutionary trace analysis of CYP51 family: implication for site-directed mutagenesis and novel antifungal drug design.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
16,
279-284.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.I.Lepesheva,
H.W.Park,
T.Y.Hargrove,
B.Vanhollebeke,
Z.Wawrzak,
J.M.Harp,
M.Sundaramoorthy,
W.D.Nes,
E.Pays,
M.Chaudhuri,
F.Villalta,
and
M.R.Waterman
(2010).
Crystal structures of Trypanosoma brucei sterol 14alpha-demethylase and implications for selective treatment of human infections.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
1773-1780.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Cools,
J.E.Parker,
D.E.Kelly,
J.A.Lucas,
B.A.Fraaije,
and
S.L.Kelly
(2010).
Heterologous expression of mutated eburicol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51) proteins of Mycosphaerella graminicola to assess effects on azole fungicide sensitivity and intrinsic protein function.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
76,
2866-2872.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ouellet,
J.B.Johnston,
and
P.R.Ortiz de Montellano
(2010).
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis cytochrome P450 system.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
493,
82-95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Krishnamoorthy,
P.Gajendrarao,
S.Thangapandian,
Y.Lee,
and
K.W.Lee
(2010).
Probing possible egress channels for multiple ligands in human CYP3A4: a molecular modeling study.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
16,
607-614.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Pochapsky,
S.Kazanis,
and
M.Dang
(2010).
Conformational plasticity and structure/function relationships in cytochromes P450.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
13,
1273-1296.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Powell,
J.Tomberg,
A.M.Deacon,
R.A.Nicholas,
and
C.Davies
(2009).
Crystal structures of penicillin-binding protein 2 from penicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae reveal an unexpectedly subtle mechanism for antibiotic resistance.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
1202-1212.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Planche,
M.T.Scotti,
A.G.López,
V.de Paulo Emerenciano,
E.M.Pérez,
and
E.Uriarte
(2009).
Design of novel antituberculosis compounds using graph-theoretical and substructural approaches.
|
| |
Mol Divers,
13,
445-458.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.K.Chen,
P.S.Doyle,
L.V.Yermalitskaya,
Z.B.Mackey,
K.K.Ang,
J.H.McKerrow,
and
L.M.Podust
(2009).
Trypanosoma cruzi CYP51 Inhibitor Derived from a Mycobacterium tuberculosis Screen Hit.
|
| |
PLoS Negl Trop Dis,
3,
e372.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Sheng,
Z.Miao,
H.Ji,
J.Yao,
W.Wang,
X.Che,
G.Dong,
J.Lü,
W.Guo,
and
W.Zhang
(2009).
Three-dimensional model of lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase from Cryptococcus neoformans: active-site characterization and insights into azole binding.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
53,
3487-3495.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Ghosh,
J.Griswold,
M.Erman,
and
W.Pangborn
(2009).
Structural basis for androgen specificity and oestrogen synthesis in human aromatase.
|
| |
Nature,
457,
219-223.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Lamping,
A.Ranchod,
K.Nakamura,
J.D.Tyndall,
K.Niimi,
A.R.Holmes,
M.Niimi,
and
R.D.Cannon
(2009).
Abc1p is a multidrug efflux transporter that tips the balance in favor of innate azole resistance in Candida krusei.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
53,
354-369.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.P.Cañas-Gutiérrez,
M.J.Angarita-Velásquez,
J.M.Restrepo-Flórez,
P.Rodríguez,
C.X.Moreno,
and
R.Arango
(2009).
Analysis of the CYP51 gene and encoded protein in propiconazole-resistant isolates of Mycosphaerella fijiensis.
|
| |
Pest Manag Sci,
65,
892-899.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ouellet,
J.Lang,
M.Couture,
and
P.R.Ortiz de Montellano
(2009).
Reaction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis cytochrome P450 enzymes with nitric oxide.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
863-872.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Johnston,
P.M.Kells,
L.M.Podust,
and
P.R.Ortiz de Montellano
(2009).
Biochemical and structural characterization of CYP124: A methyl-branched lipid {omega}-hydroxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
20687-20692.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.H.Xu,
S.Fushinobu,
H.Ikeda,
T.Wakagi,
and
H.Shoun
(2009).
Crystal structures of cytochrome P450 105P1 from Streptomyces avermitilis: conformational flexibility and histidine ligation state.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
1211-1219.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Suryadevara,
S.Olepu,
J.W.Lockman,
J.Ohkanda,
M.Karimi,
C.L.Verlinde,
J.M.Kraus,
J.Schoepe,
W.C.Van Voorhis,
A.D.Hamilton,
F.S.Buckner,
and
M.H.Gelb
(2009).
Structurally simple inhibitors of lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase are efficacious in a rodent model of acute Chagas disease.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
52,
3703-3715.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Bonifacio,
D.Millo,
P.H.Keizers,
R.Boegschoten,
J.N.Commandeur,
N.P.Vermeulen,
C.Gooijer,
and
G.van der Zwan
(2008).
Active-site structure, binding and redox activity of the heme-thiolate enzyme CYP2D6 immobilized on coated Ag electrodes: a surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering study.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
13,
85-96.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.N.Eddine,
J.P.von Kries,
M.V.Podust,
T.Warrier,
S.H.Kaufmann,
and
L.M.Podust
(2008).
X-ray structure of 4,4'-dihydroxybenzophenone mimicking sterol substrate in the active site of sterol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
15152-15159.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Warrilow,
C.Ugochukwu,
D.Lamb,
D.Kelly,
and
S.Kelly
(2008).
Expression and Characterization of CYP51, the Ancient Sterol 14-demethylase Activity for Cytochromes P450 (CYP), in the White-Rot Fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium.
|
| |
Lipids,
43,
1143-1153.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.C.Peng,
J.L.Cape,
T.Rushmore,
G.J.Crouch,
and
J.P.Jones
(2008).
Cytochrome P450 2C9 type II binding studies on quinoline-4-carboxamide analogues.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
51,
8000-8011.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ouellet,
L.M.Podust,
and
P.R.de Montellano
(2008).
Mycobacterium tuberculosis CYP130: crystal structure, biophysical characterization, and interactions with antifungal azole drugs.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
5069-5080.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.McLean,
P.Carroll,
D.G.Lewis,
A.J.Dunford,
H.E.Seward,
R.Neeli,
M.R.Cheesman,
L.Marsollier,
P.Douglas,
W.E.Smith,
I.Rosenkrands,
S.T.Cole,
D.Leys,
T.Parish,
and
A.W.Munro
(2008).
Characterization of active site structure in CYP121. A cytochrome P450 essential for viability of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
33406-33416.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.G.Dover,
A.Bhatt,
V.Bhowruth,
B.E.Willcox,
and
G.S.Besra
(2008).
New drugs and vaccines for drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections.
|
| |
Expert Rev Vaccines,
7,
481-497.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Li,
Z.Chang,
Z.Pan,
Z.Q.Fu,
and
X.Wang
(2008).
Modes of heme binding and substrate access for cytochrome P450 CYP74A revealed by crystal structures of allene oxide synthase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
13883-13888.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Korosec,
J.Acimovic,
M.Seliskar,
D.Kocjan,
K.F.Tacer,
D.Rozman,
and
U.Urleb
(2008).
Novel cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors targeting human lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51).
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
16,
209-221.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.W.Munro,
H.M.Girvan,
and
K.J.McLean
(2007).
Variations on a (t)heme--novel mechanisms, redox partners and catalytic functions in the cytochrome P450 superfamily.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
585-609.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.I.Lepesheva,
and
M.R.Waterman
(2007).
Sterol 14alpha-demethylase cytochrome P450 (CYP51), a P450 in all biological kingdoms.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1770,
467-477.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.I.Lepesheva,
M.Seliskar,
C.G.Knutson,
N.V.Stourman,
D.Rozman,
and
M.R.Waterman
(2007).
Conformational dynamics in the F/G segment of CYP51 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis monitored by FRET.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
464,
221-227.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Podust,
J.P.von Kries,
A.N.Eddine,
Y.Kim,
L.V.Yermalitskaya,
R.Kuehne,
H.Ouellet,
T.Warrier,
M.Alteköster,
J.S.Lee,
J.Rademann,
H.Oschkinat,
S.H.Kaufmann,
and
M.R.Waterman
(2007).
Small-molecule scaffolds for CYP51 inhibitors identified by high-throughput screening and defined by X-ray crystallography.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
51,
3915-3923.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Zhao,
D.Liu,
Q.Zhang,
S.Zhang,
J.Wan,
and
W.Xiao
(2007).
Expression and homology modeling of sterol 14alpha-demethylase from Penicillium digitatum.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Lett,
277,
37-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Haining,
and
M.Nichols-Haining
(2007).
Cytochrome P450-catalyzed pathways in human brain: metabolism meets pharmacology or old drugs with new mechanism of action?
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
113,
537-545.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.G.Rupasinghe,
H.Duan,
H.L.Frericks Schmidt,
D.A.Berthold,
C.M.Rienstra,
and
M.A.Schuler
(2007).
High-yield expression and purification of isotopically labeled cytochrome P450 monooxygenases for solid-state NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1768,
3061-3070.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.H.Chen,
C.Q.Sheng,
X.H.Xu,
Y.Y.Jiang,
W.N.Zhang,
and
C.He
(2007).
Identification of Y118 amino acid residue in Candida albicans sterol 14alpha-demethylase associated with the enzyme activity and selective antifungal activity of azole analogues.
|
| |
Biol Pharm Bull,
30,
1246-1253.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.V.Shumyantseva,
T.V.Bulko,
G.P.Kuznetsova,
A.V.Lisitsa,
E.A.Ponomarenko,
I.I.Karuzina,
and
A.I.Archakov
(2007).
Electrochemical reduction of sterol-14alpha-demethylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (CYP51b1).
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
72,
658-663.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Chérasse,
A.C.Maurin,
C.Chaveroux,
C.Jousse,
V.Carraro,
L.Parry,
C.Deval,
C.Chambon,
P.Fafournoux,
and
A.Bruhat
(2007).
The p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF) is a cofactor of ATF4 for amino acid-regulated transcription of CHOP.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
35,
5954-5965.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Imbert,
S.Imbert-Bouyer,
C.Kauffmann-Lacroix,
G.Daniault,
and
M.H.Rodier
(2006).
Effect of azoles on the secretion of a Candida albicans metallopeptidase.
|
| |
Mycopathologia,
161,
147-152.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.W.Chiang,
H.C.Yeh,
L.H.Wang,
and
N.L.Chan
(2006).
Crystal structure of the human prostacyclin synthase.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
364,
266-274.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Prosser,
Y.Guo,
Z.Jia,
and
G.Jones
(2006).
Structural motif-based homology modeling of CYP27A1 and site-directed mutational analyses affecting vitamin D hydroxylation.
|
| |
Biophys J,
90,
3389-3409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.A.Pikuleva
(2006).
Cytochrome P450s and cholesterol homeostasis.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
112,
761-773.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Accoceberry,
and
T.Noël
(2006).
[Antifungals cellular targets and mechanisms of resistance]
|
| |
Therapie,
61,
195-199.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.T.Pearson,
J.J.Hill,
J.Swank,
N.Isoherranen,
K.L.Kunze,
and
W.M.Atkins
(2006).
Surface plasmon resonance analysis of antifungal azoles binding to CYP3A4 with kinetic resolution of multiple binding orientations.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
6341-6353.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.McLean,
D.Clift,
D.G.Lewis,
M.Sabri,
P.R.Balding,
M.J.Sutcliffe,
D.Leys,
and
A.W.Munro
(2006).
The preponderance of P450s in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome.
|
| |
Trends Microbiol,
14,
220-228.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.de Groot
(2006).
Designing better drugs: predicting cytochrome P450 metabolism.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
11,
601-606.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.Pietila,
P.K.Vohra,
B.Sanyal,
N.L.Wengenack,
S.Raghavakaimal,
and
C.F.Thomas
(2006).
Cloning and characterization of CYP51 from Mycobacterium avium.
|
| |
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol,
35,
236-242.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.V.Strushkevich,
I.N.Harnastai,
G.I.Lepesheva,
and
S.A.Usanov
(2006).
Role of C-terminal sequence of cytochrome P450scc in folding and functional activity.
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
71,
1027-1034.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.E.Summons,
A.S.Bradley,
L.L.Jahnke,
and
J.R.Waldbauer
(2006).
Steroids, triterpenoids and molecular oxygen.
|
| |
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci,
361,
951-968.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Qi,
S.Bakht,
B.Qin,
M.Leggett,
A.Hemmings,
F.Mellon,
J.Eagles,
D.Werck-Reichhart,
H.Schaller,
A.Lesot,
R.Melton,
and
A.Osbourn
(2006).
A different function for a member of an ancient and highly conserved cytochrome P450 family: from essential sterols to plant defense.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
18848-18853.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Rupp,
S.Raub,
C.Marian,
and
H.D.Höltje
(2005).
Molecular design of two sterol 14alpha-demethylase homology models and their interactions with the azole antifungals ketoconazole and bifonazole.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
19,
149-163.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Bouvier,
A.Rahier,
and
B.Camara
(2005).
Biogenesis, molecular regulation and function of plant isoprenoids.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
44,
357-429.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yasui,
S.Hayashi,
and
H.Sakurai
(2005).
Possible involvement of singlet oxygen species as multiple oxidants in p450 catalytic reactions.
|
| |
Drug Metab Pharmacokinet,
20,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.van Burik
(2005).
Role of new antifungal agents in prophylaxis of mycoses in high risk patients.
|
| |
Curr Opin Infect Dis,
18,
479-483.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Mestres
(2005).
Structure conservation in cytochromes P450.
|
| |
Proteins,
58,
596-609.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Helmick,
A.E.Fletcher,
A.M.Gardner,
C.R.Gessner,
A.N.Hvitved,
M.C.Gustin,
and
P.R.Gardner
(2005).
Imidazole antibiotics inhibit the nitric oxide dioxygenase function of microbial flavohemoglobin.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
49,
1837-1843.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Kirton,
C.W.Murray,
M.L.Verdonk,
and
R.D.Taylor
(2005).
Prediction of binding modes for ligands in the cytochromes P450 and other heme-containing proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
58,
836-844.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Park,
and
D.S.Perlin
(2005).
Establishing surrogate markers for fluconazole resistance in Candida albicans.
|
| |
Microb Drug Resist,
11,
232-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Mellado,
G.Garcia-Effron,
L.Alcazar-Fuoli,
M.Cuenca-Estrella,
and
J.L.Rodriguez-Tudela
(2004).
Substitutions at methionine 220 in the 14alpha-sterol demethylase (Cyp51A) of Aspergillus fumigatus are responsible for resistance in vitro to azole antifungal drugs.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
48,
2747-2750.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Xiao,
V.Madison,
A.S.Chau,
D.Loebenberg,
R.E.Palermo,
and
P.M.McNicholas
(2004).
Three-dimensional models of wild-type and mutated forms of cytochrome P450 14alpha-sterol demethylases from Aspergillus fumigatus and Candida albicans provide insights into posaconazole binding.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
48,
568-574.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Benveniste
(2004).
Biosynthesis and accumulation of sterols.
|
| |
Annu Rev Plant Biol,
55,
429-457.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Nascimento,
G.H.Goldman,
S.Park,
S.A.Marras,
G.Delmas,
U.Oza,
K.Lolans,
M.N.Dudley,
P.A.Mann,
and
D.S.Perlin
(2003).
Multiple resistance mechanisms among Aspergillus fumigatus mutants with high-level resistance to itraconazole.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
47,
1719-1726.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.V.Smith,
and
J.C.Sacchettini
(2003).
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a model system for structural genomics.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
13,
658-664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.F.Lewis
(2003).
P450 structures and oxidative metabolism of xenobiotics.
|
| |
Pharmacogenomics,
4,
387-395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.E.Scott,
Y.A.He,
M.R.Wester,
M.A.White,
C.C.Chin,
J.R.Halpert,
E.F.Johnson,
and
C.D.Stout
(2003).
An open conformation of mammalian cytochrome P450 2B4 at 1.6-A resolution.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
13196-13201.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Buckner,
K.Yokoyama,
J.Lockman,
K.Aikenhead,
J.Ohkanda,
M.Sadilek,
S.Sebti,
W.Van Voorhis,
A.Hamilton,
and
M.H.Gelb
(2003).
A class of sterol 14-demethylase inhibitors as anti-Trypanosoma cruzi agents.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
15149-15153.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.C.Odds,
A.J.Brown,
and
N.A.Gow
(2003).
Antifungal agents: mechanisms of action.
|
| |
Trends Microbiol,
11,
272-279.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Zarn,
B.J.Brüschweiler,
and
J.R.Schlatter
(2003).
Azole fungicides affect mammalian steroidogenesis by inhibiting sterol 14 alpha-demethylase and aromatase.
|
| |
Environ Health Perspect,
111,
255-261.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Schuler,
and
D.Werck-Reichhart
(2003).
Functional genomics of P450s.
|
| |
Annu Rev Plant Biol,
54,
629-667.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Bellinzoni,
and
G.Riccardi
(2003).
Techniques and applications: The heterologous expression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes is an uphill road.
|
| |
Trends Microbiol,
11,
351-358.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.A.Williams,
J.Cosme,
A.Ward,
H.C.Angove,
D.Matak Vinković,
and
H.Jhoti
(2003).
Crystal structure of human cytochrome P450 2C9 with bound warfarin.
|
| |
Nature,
424,
464-468.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Izumi,
H.Kaneko,
T.Yamazaki,
T.Hirata,
and
S.Kominami
(2003).
Membrane topology of guinea pig cytochrome P450 17 alpha revealed by a combination of chemical modifications and mass spectrometry.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
14663-14669.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Teague
(2003).
Implications of protein flexibility for drug discovery.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
2,
527-541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Fukuoka,
D.A.Johnston,
C.A.Winslow,
M.J.de Groot,
C.Burt,
C.A.Hitchcock,
and
S.G.Filler
(2003).
Genetic basis for differential activities of fluconazole and voriconazole against Candida krusei.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
47,
1213-1219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Poulos
(2003).
Cytochrome P450 flexibility.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
13121-13122.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Mowat,
D.Leys,
K.J.McLean,
S.L.Rivers,
A.Richmond,
A.W.Munro,
M.Ortiz Lombardia,
P.M.Alzari,
G.A.Reid,
S.K.Chapman,
and
M.D.Walkinshaw
(2002).
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of a novel cytochrome P450 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
704-705.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Sanglard,
and
F.C.Odds
(2002).
Resistance of Candida species to antifungal agents: molecular mechanisms and clinical consequences.
|
| |
Lancet Infect Dis,
2,
73-85.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Sanglard
(2002).
Resistance of human fungal pathogens to antifungal drugs.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
5,
379-385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.F.Gibbons
(2002).
The role of cytochrome P450 in the regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis.
|
| |
Lipids,
37,
1163-1170.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.de Groot,
and
S.Ekins
(2002).
Pharmacophore modeling of cytochromes P450.
|
| |
Adv Drug Deliv Rev,
54,
367-383.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.J.Winn,
S.K.Lüdemann,
R.Gauges,
V.Lounnas,
and
R.C.Wade
(2002).
Comparison of the dynamics of substrate access channels in three cytochrome P450s reveals different opening mechanisms and a novel functional role for a buried arginine.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
5361-5366.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Urlacher,
and
R.D.Schmid
(2002).
Biotransformations using prokaryotic P450 monooxygenases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
13,
557-564.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Sawada,
K.Kinoshita,
T.Akashi,
T.Aoki,
and
S.Ayabe
(2002).
Key amino acid residues required for aryl migration catalysed by the cytochrome P450 2-hydroxyisoflavanone synthase.
|
| |
Plant J,
31,
555-564.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Dunn,
I.J.Dmochowski,
A.M.Bilwes,
H.B.Gray,
and
B.R.Crane
(2001).
Probing the open state of cytochrome P450cam with ruthenium-linker substrates.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
12420-12425.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

