 |
PDBsum entry 7ce4

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
7ce4
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Tankyrase2 catalytic domain in complex with k-476
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Poly [adp-ribose] polymerase tankyrase-2. Chain: a. Fragment: catalytic domain. Synonym: adp-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 6,artd6,poly [adp-ribose] polymerase 5b,protein poly-adp-ribosyltransferase tankyrase-2,tnks-2,trf1-interacting ankyrin-related adp-ribose polymerase 2,tankyrase ii,tankyrase-2,tank2,tankyrase-like protein, tankyrase-related protein. Engineered: yes.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: tnks2, parp5b, tank2, tnkl. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.174
|
R-free:
|
0.203
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Takahashi,M.Suzuki,J.Saito
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.Kinosada
et al.
(2021).
The dual pocket binding novel tankyrase inhibitor K-476 enhances the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor by attracting CD8+ T cells to tumors.
Am J Cancer Res,
11,
264-276.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Jun-20
|
Release date:
|
12-May-21
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.4.2.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.4.2.30
- NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + (ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor = nicotinamide + (ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
(ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor
|
=
|
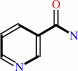 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
(ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Am J Cancer Res
11:264-276
(2021)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The dual pocket binding novel tankyrase inhibitor K-476 enhances the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor by attracting CD8+ T cells to tumors.
|
|
H.Kinosada,
R.Okada-Iwasaki,
K.Kunieda,
M.Suzuki-Imaizumi,
Y.Takahashi,
H.Miyagi,
M.Suzuki,
K.Motosawa,
M.Watanabe,
M.Mie,
T.Ishii,
H.Ishida,
J.I.Saito,
R.Nakai.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is associated with disease progression, is
activated in many cancers. Tankyrase (TNKS) has received attention as a target
molecule for Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibition. We identified K-476, a novel
TNKS inhibitor, a dual pocket binder that binds to both the nicotinamide and
ADP-ribose pockets. In a human colon cancer cell line, K-476 specifically and
potently inhibited TNKS and led to stabilization of the Axin protein, resulting
in Wnt/β-catenin pathway suppression. Aberrant Wnt/β-catenin pathway
activation was recently reported as a possible mechanism of ineffectiveness in
immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment. Because the Wnt/β-catenin pathway
activation causes dendritic cell inactivation and suppresses chemokine
production, resulting in a paucity of CD8+ T cells in tumor tissue,
which is an important effector of ICIs. Thus, TNKS inhibitors may enhance the
efficacy of ICIs. To examine whether K-476 enhances the antitumor effect of
anti-PD-L1 antibodies, K-476 was administered orally with an anti-PD-L1 antibody
to melanoma-bearing C57BL/6J mice. Although K-476 was ineffective as a
monotherapy, it significantly enhanced the antitumor effect in combination with
anti-PD-L1 antibody. In mice, intra-tumor infiltration of CD8+ T
cells was increased by combination treatment. K-476 upregulated the chemokine
expression (e.g., Ccl3 and Ccl4), which attracted CD8+
T cells. This was considered to contribute to the increased CD8+ T
cells in the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, while the potential
gastrointestinal toxicity of TNKS inhibitors has been reported, it was not
observed at effective doses. Thus, K-476 could be an attractive therapeutic
option to enhance the efficacy of ICIs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

