 |
PDBsum entry 6tqh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6tqh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, F, C, B:
E.C.1.1.1.1
- alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a primary alcohol + NAD+ = an aldehyde + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a secondary alcohol + NAD+ = a ketone + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
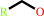 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
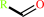 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
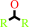 secondary alcohol
secondary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
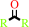 ketone
ketone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+) or Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, F, C, B:
E.C.1.2.1.10
- acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (acetylating).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
acetaldehyde + NAD+ + CoA = acetyl-CoA + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
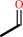 acetaldehyde
acetaldehyde
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
=
|
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
11:1426
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Filamentation of the bacterial bi-functional alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenase AdhE is essential for substrate channeling and enzymatic regulation.
|
|
P.Pony,
C.Rapisarda,
L.Terradot,
E.Marza,
R.Fronzes.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Acetaldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase (AdhE) enzymes are a key metabolic enzyme in
bacterial physiology and pathogenicity. They convert acetyl-CoA to ethanol via
an acetaldehyde intermediate during ethanol fermentation in an anaerobic
environment. This two-step reaction is associated to NAD+
regeneration, essential for glycolysis. The bifunctional AdhE enzyme is
conserved in all bacterial kingdoms but also in more phylogenetically distant
microorganisms such as green microalgae. It is found as an oligomeric form
called spirosomes, for which the function remains elusive. Here, we use
cryo-electron microscopy to obtain structures of Escherichia coli spirosomes in
different conformational states. We show that spirosomes contain active AdhE
monomers, and that AdhE filamentation is essential for its activity in vitro and
function in vivo. The detailed analysis of these structures provides insight
showing that AdhE filamentation is essential for substrate channeling within the
filament and for the regulation of enzyme activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

