 |
PDBsum entry 6s1v
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of dimeric m-pmv protease d26n mutant in complex with inhibitor
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Gag-pro-pol polyprotein. Chain: a, b. Synonym: pr180. Ec: 3.6.1.23,3.4.23.-,2.7.7.49,2.7.7.7,3.1.26.4,2.7.7.-,3.1.-.-. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Other_details: gaps in the sequence indicate residues that were not modeled because of poor electron density. Pro-0a1-val-psa-ala-met-thr.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mason-pfizer monkey virus. Mpmv. Organism_taxid: 11855. Gene: gag-pro-pol. Expressed in: escherichia coli 'bl21-gold(de3)plyss ag'. Expression_system_taxid: 866768. Synthetic: yes. Synthetic construct. Organism_taxid: 32630
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.64Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.180
|
R-free:
|
0.220
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Wosicki,M.Gilski,M.Jaskolski,H.Zabranska,I.Pichova
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.Wosicki
et al.
(2019).
Comparison of a retroviral protease in monomeric and dimeric states.
Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol,
75,
904-917.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Jun-19
|
Release date:
|
16-Oct-19
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.7.7.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.7.7.49
- RNA-directed Dna polymerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
DNA(n) + a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate = DNA(n+1) + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 DNA(n)
DNA(n)
|
+
|
2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate
|
=
|
DNA(n+1)
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.7.7.7
- DNA-directed Dna polymerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
DNA(n) + a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate = DNA(n+1) + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 DNA(n)
DNA(n)
|
+
|
2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate
|
=
|
DNA(n+1)
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.1.-.-
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.1.26.4
- ribonuclease H.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Endonucleolytic cleavage to 5'-phosphomonoester.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 6:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.4.23.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 7:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.6.1.23
- dUTP diphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dUTP + H2O = dUMP + diphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
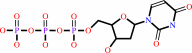 dUTP
dUTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
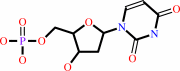 dUMP
dUMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol
75:904-917
(2019)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Comparison of a retroviral protease in monomeric and dimeric states.
|
|
S.Wosicki,
M.Gilski,
H.Zabranska,
I.Pichova,
M.Jaskolski.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Retroviral proteases (RPs) are of high interest owing to their crucial role in
the maturation process of retroviral particles. RPs are obligatory homodimers,
with a pepsin-like active site built around two aspartates (in DTG triads) that
activate a water molecule, as the nucleophile, under two flap loops.
Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (M-PMV) is unique among retroviruses as its protease
is also stable in the monomeric form, as confirmed by an existing crystal
structure of a 13 kDa variant of the protein (M-PMV PR) and its previous
biochemical characterization. In the present work, two mutants of M-PMV PR, D26N
and C7A/D26N/C106A, were crystallized in complex with a peptidomimetic inhibitor
and one mutant (D26N) was crystallized without the inhibitor. The crystal
structures were solved at resolutions of 1.6, 1.9 and 2.0 Å, respectively. At
variance with the previous study, all of the new structures have the canonical
dimeric form of retroviral proteases. The protomers within a dimer differ mainly
in the flap-loop region, with the most extreme case observed in the apo
structure, in which one flap loop is well defined while the other flap loop is
not defined by electron density. The presence of the inhibitor molecules in the
complex structures was assessed using polder maps, but some details of their
conformations remain ambiguous. In all of the presented structures the active
site contains a water molecule buried deeply between the Asn26-Thr27-Gly28
triads of the protomers. Such a water molecule is completely unique not only in
retropepsins but also in aspartic proteases in general. The C7A and C106A
mutations do not influence the conformation of the protein. The Cys106 residue
is properly placed at the homodimer interface area for a disulfide cross-link,
but the reducing conditions of the crystallization experiment prevented S-S bond
formation. An animated Interactive 3D Complement (I3DC) is available in
Proteopedia at http://proteopedia.org/w/Journal:Acta_Cryst_D:S2059798319011355.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

