 |
PDBsum entry 6aym

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase, transferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6aym
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.2.30
- aminodeoxyfutalosine nucleosidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine + H2O = dehypoxanthine futalosine + adenine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
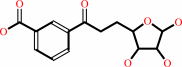 dehypoxanthine futalosine
dehypoxanthine futalosine
|
+
|
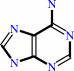 adenine
adenine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.2.9
- adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + H2O = S-(5-deoxy-D-ribos-5-yl)-L- homocysteine + adenine
|
|
2.
|
5'-deoxyadenosine + H2O = 5-deoxy-D-ribose + adenine
|
|
3.
|
S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine + H2O = 5-(methylsulfanyl)-D-ribose + adenine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
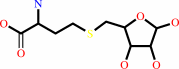 S-(5-deoxy-D-ribos-5-yl)-L- homocysteine
S-(5-deoxy-D-ribos-5-yl)-L- homocysteine
|
+
|
 adenine
adenine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
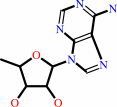 5'-deoxyadenosine
5'-deoxyadenosine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
5-deoxy-D-ribose
|
+
|
 adenine
adenine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
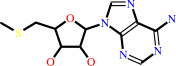 S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine
S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
5-(methylsulfanyl)-D-ribose
|
+
|
 adenine
adenine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
ACS Chem Biol
13:3173-3183
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Transition-State Analogues of Campylobacter jejuni 5'-Methylthioadenosine Nucleosidase.
|
|
R.G.Ducati,
R.K.Harijan,
S.A.Cameron,
P.C.Tyler,
G.B.Evans,
V.L.Schramm.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Campylobacter jejuni is a Gram-negative bacterium responsible for food-borne
gastroenteritis and associated with Guillain-Barré, Reiter, and irritable bowel
syndromes. Antibiotic resistance in C. jejuni is common, creating a need for
antibiotics with novel mechanisms of action. Menaquinone biosynthesis in C.
jejuni uses the rare futalosine pathway, where 5'-methylthioadenosine
nucleosidase ( CjMTAN) is proposed to catalyze the essential hydrolysis of
adenine from 6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine to form dehypoxanthinylfutalosine, a
menaquinone precursor. The substrate specificity of CjMTAN is demonstrated to
include 6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine, 5'-methylthioadenosine,
S-adenosylhomocysteine, adenosine, and 5'-deoxyadenosine. These activities span
the catalytic specificities for the role of bacterial MTANs in menaquinone
synthesis, quorum sensing, and S-adenosylmethionine recycling. We determined
inhibition constants for potential transition-state analogues of CjMTAN. The
best of these compounds have picomolar dissociation constants and were
slow-onset tight-binding inhibitors. The most potent CjMTAN transition-state
analogue inhibitors inhibited C. jejuni growth in culture at low micromolar
concentrations, similar to gentamicin. The crystal structure of apoenzyme C.
jejuni MTAN was solved at 1.25 Å, and five CjMTAN complexes with
transition-state analogues were solved at 1.42 to 1.95 Å resolution. Inhibitor
binding induces a loop movement to create a closed catalytic site with Asp196
and Ile152 providing purine leaving group activation and Arg192 and Glu12
activating the water nucleophile. With inhibitors bound, the interactions of the
4'-alkylthio or 4'-alkyl groups of this inhibitor family differ from the
Escherichia coli MTAN structure by altered protein interactions near the
hydrophobic pocket that stabilizes 4'-substituents of transition-state
analogues. These CjMTAN inhibitors have potential as specific antibiotic
candidates against C. jejuni.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

