 |
PDBsum entry 5vrk
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of ssopox asa6 mutant (f46l-c258a-w263m-i280t) - open form
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aryldialkylphosphatase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: paraoxonase,ssopox,phosphotriesterase-like lactonase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sulfolobus solfataricus. Organism_taxid: 2287. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.141
|
R-free:
|
0.175
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Hiblot,G.Gotthard,P.Jacquet,D.Daude,C.Bergonzi,E.Chabriere,M.Elias
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
P.Jacquet
et al.
(2017).
Rational engineering of a native hyperthermostable lactonase into a broad spectrum phosphotriesterase.
Sci Rep,
7,
16745.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-May-17
|
Release date:
|
10-Jan-18
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q97VT7
(PHP_SULSO) -
Aryldialkylphosphatase from Saccharolobus solfataricus (strain ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
314 a.a.
314 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 5 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.8.1
- aryldialkylphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
An aryl dialkyl phosphate + H2O = dialkyl phosphate + an aryl alcohol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
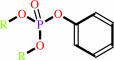 aryl dialkyl phosphate
aryl dialkyl phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
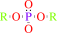 dialkyl phosphate
dialkyl phosphate
|
+
|
aryl alcohol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Divalent cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Sci Rep
7:16745
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Rational engineering of a native hyperthermostable lactonase into a broad spectrum phosphotriesterase.
|
|
P.Jacquet,
J.Hiblot,
D.Daudé,
C.Bergonzi,
G.Gotthard,
N.Armstrong,
E.Chabrière,
M.Elias.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The redesign of enzyme active sites to alter their function or specificity is a
difficult yet appealing challenge. Here we used a structure-based design
approach to engineer the lactonase SsoPox from Sulfolobus solfataricus into a
phosphotriesterase. The five best variants were characterized and their
structure was solved. The most active variant, αsD6 (V27A-Y97W-L228M-W263M)
demonstrates a large increase in catalytic efficiencies over the wild-type
enzyme, with increases of 2,210-fold, 163-fold, 58-fold, 16-fold against
methyl-parathion, malathion, ethyl-paraoxon, and methyl-paraoxon, respectively.
Interestingly, the best mutants are also capable of degrading fensulfothion,
which is reported to be an inhibitor for the wild-type enzyme, as well as others
that are not substrates of the starting template or previously reported W263
mutants. The broad specificity of these engineered variants makes them promising
candidates for the bioremediation of organophosphorus compounds. Analysis of
their structures reveals that the increase in activity mainly occurs through the
destabilization of the active site loop involved in substrate binding, and it
has been observed that the level of disorder correlates with the width of the
enzyme specificity spectrum. This finding supports the idea that active site
conformational flexibility is essential to the acquisition of broader substrate
specificity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

