 |
PDBsum entry 5glg

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5glg
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.3.1.6
- fumarate reductase (NADH).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
succinate + NAD+ = fumarate + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
succinate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 76.36% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
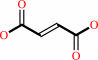 fumarate
fumarate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
9:4867
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Molecular basis of maintaining an oxidizing environment under anaerobiosis by soluble fumarate reductase.
|
|
S.Kim,
C.M.Kim,
Y.J.Son,
J.Y.Choi,
R.K.Siegenthaler,
Y.Lee,
T.H.Jang,
J.Song,
H.Kang,
C.A.Kaiser,
H.H.Park.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Osm1 and Frd1 are soluble fumarate reductases from yeast that are critical for
allowing survival under anaerobic conditions. Although they maintain redox
balance during anaerobiosis, the underlying mechanism is not understood. Here,
we report the crystal structure of a eukaryotic soluble fumarate reductase,
which is unique among soluble fumarate reductases as it lacks a heme domain.
Structural and enzymatic analyses indicate that Osm1 has a specific binding
pocket for flavin molecules, including FAD, FMN, and riboflavin, catalyzing
their oxidation while reducing fumarate to succinate. Moreover, ER-resident Osm1
can transfer electrons from the Ero1 FAD cofactor to fumarate either by free FAD
or by a direct interaction, allowing de novo disulfide bond formation in the
absence of oxygen. We conclude that soluble eukaryotic fumarate reductases can
maintain an oxidizing environment under anaerobic conditions, either by
oxidizing cellular flavin cofactors or by a direct interaction with flavoenzymes
such as Ero1.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

